- with readers working within the Property industries
- within International Law, Law Department Performance and Consumer Protection topic(s)
Agriculture has long been at the heart of human development, evolving from early farming practices to today's high-tech, precision-driven agriculture. However, as the global population increases and climate change threatens food security, agricultural innovation has become more critical than ever. One way to measure and drive progress in this space is through patents, so as to protect new technologies while also serving as a valuable tool for identifying and understanding advancements in agricultural science and engineering.
Agriculture has long been at the heart of human development, evolving from early farming practices to today's high-tech, precision-driven agriculture. However, as the global population increases and climate change threatens food security, agricultural innovation has become more critical than ever. One way to measure and drive progress in this space is through patents, so as to protect new technologies while also serving as a valuable tool for identifying and understanding advancements in agricultural science and engineering.
The past decade has seen a significant increase in patent filings within the agricultural sector. This trend highlights the sector's ongoing transformation, spurred by advances in biotechnology, artificial intelligence, irrigation systems, pest management, and climate-resilient crops. The uptrend in patent filings from 2014 to the present illustrates the industry's commitment to innovation and the commercialisation of cutting-edge solutions.
Why patents matter in agriculture
Patents are far more than a legal mechanism to safeguard inventions - they are also a rich repository of technical knowledge. A patent application requires the inventor to disclose, in detail, how the invention works. This disclosure provides a roadmap for others in the industry to understand emerging technologies, potentially improving their own processes or inspiring new solutions.
For agriculture, this is particularly important. With patents covering everything from genetic modifications in crops to automated machinery, irrigation technologies, and sustainable farming solutions, they encapsulate a wealth of information that can transform farming practices. For example, patents for drought-resistant crop varieties not only protect the breeders' investments but also share essential insights about the genetic traits that make the crops resilient. Full patent documents are typically easily available online. One valuable online resource to locate these documents is Google Patents, which can be accessed at this link.
Moreover, patents play a critical role in fostering collaboration between research institutions, private companies, and governments. In an increasingly interconnected world, these partnerships are vital to solving complex agricultural challenges.
The South African Context: A Strategic Opportunity
South Africa, with its diverse climate and rich agricultural heritage, is uniquely positioned to benefit from agricultural innovation. However, as with any jurisdiction, its intellectual property landscape presents both opportunities and risks.
If a patent is not filed in South Africa, the protected technology cannot be enforced in the country. This creates an opportunity for local businesses and innovators to freely use such technologies, either directly or as part of their own advancements. For example, if a revolutionary pest management system is patented in the United States but not in South Africa, local agricultural businesses can adopt the system without facing infringement claims. They may also improve on the technology and file their own patents locally or internationally.
This highlights a key advantage of monitoring patent filings globally: the ability to identify and leverage innovations that have not been extended to South Africa. By closely studying such patents, local innovators can gain a competitive edge and even leapfrog into more advanced farming techniques.
A Snapshot of Growth in Agricultural Patents
Patent filing trends provide a powerful lens through which to observe the growth and direction of agricultural innovation. From 2014 to the present, the number of patent filings in agriculture has steadily increased. This upward trajectory reflects the convergence of traditional farming practices with modern technologies like machine learning, precision irrigation, and genome editing.
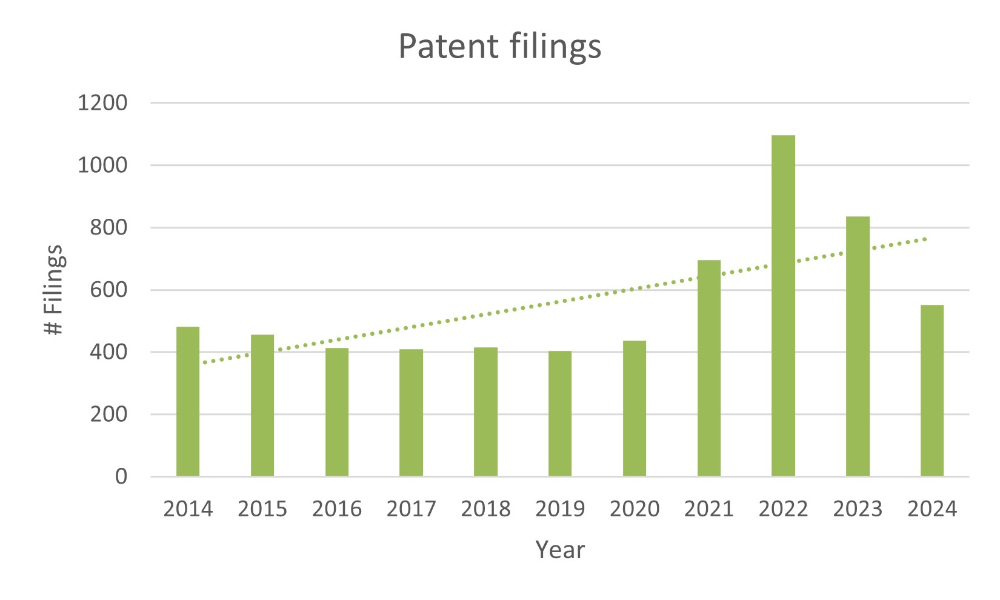
Figure 1: Number of patent filings since 2014 relating to innovations in the agricultural sector
The growth in patent filings is not limited to one region or type of innovation. Globally, patents have been filed for:
- Biotechnology advancements: Innovations such as CRISPR gene-editing techniques for creating pest-resistant or higher-yield crops.
- Smart farming solutions: Technologies integrating IoT devices to monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health in real time.
- Automation and robotics: Machines that automate planting, harvesting, and pest control, reducing reliance on manual labour.
- Sustainability-focused technologies: Developments in composting, biofertilisers, and water-efficient irrigation systems.
- Leveraging Patents for Agricultural Growth
To remain competitive in the global agricultural landscape, it is crucial for businesses, researchers, and policymakers to prioritise patents both as a source of innovation and as a tool for strategy. Businesses should actively monitor global patent filings to identify untapped technologies that could be utilised locally. Meanwhile, researchers should focus on developing solutions that address specific regional challenges, such as drought resistance in South Africa's arid regions or pest control methods suited to local ecosystems.
For governments, creating an environment that encourages agricultural innovation is key. Offering incentives for patent filings, funding research programs, and supporting public-private partnerships can accelerate the pace of agricultural transformation.
Conclusion
Patents are more than just a tool for protecting intellectual property—they are a window into the future of agriculture. By disclosing how technology works, patents provide a foundation for further innovation and collaboration. Where a country like South Africa is sometimes overlooked in global company's patent filing strategy, South African companies stand to benefit by utilising and building upon these innovations to drive local growth.
As the upward trend in agricultural patent filings continues, it highlights the importance of innovation in addressing global challenges like food security and climate change. By leveraging patents strategically, the agricultural sector can ensure it remains resilient, sustainable, and equipped to feed the growing global population.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


