- within Transport topic(s)
- in Australia
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
- within Transport topic(s)
- in Australia
- within International Law, Government, Public Sector and Intellectual Property topic(s)
- with readers working within the Technology and Law Firm industries
Introduction
India's EV Imperative
India's commitment to reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels has positioned EVs as a cornerstone of its sustainable mobility strategy. The government's vision includes achieving 30% EV penetration by 2030, aligning with global environmental goals.
Objectives and Scope
- Analyze the current state of India's EV market.
- Examine the regulatory environment and recent policy developments.
- Identify challenges and opportunities in the EV ecosystem.
- Explore avenues for strategic international collaborations.
- Provide policy recommendations to accelerate EV adoption and infrastructure development.
Indian EV Market Snapshot
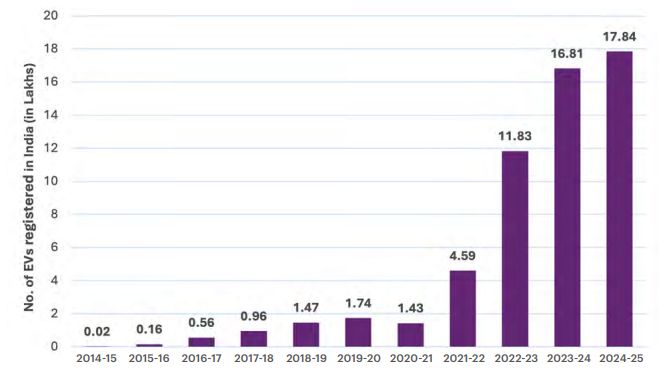
EV Registration Trend
Projected Growth
Globally, the EV industry continues to grow at a rapid pace. In the year 2023, the global EV market was valued at US$255.54 billion, and it is projected to soar to around US$2,108.80 billion by the year 2033, growing at a 23.42% Compound Annual Growth Rate ("CAGR") from the year 2024 to 2033. India's own EV story is part of this broader trend but carries unique characteristics and extraordinary growth potential. According to Fortune Business Insights, India's EV market stood at US$3.21 billion in the year 2022 and is forecasted to surge to US$113.99 billion by the year 2029, reflecting a remarkable 66.52% CAGR.
This bullish outlook aligns with the Indian government's ambitious targets, by the year 2030, India aims for EVs to make up 30% of private car sales, 70% of commercial vehicles, 40% of buses, and 80% of 2Ws and Three Wheelers ("3Ws"). In total, this amounts to a projected 80 million EVs on the road by the year 2030, according to Confederation of Indian Industry's estimates. Recent sales data underscores the growing traction. In May 2024, EV sales in India surged by 20.88% to reach 1.39 million units. Notably, this strong growth occurred despite a broader global slowdown in EV demand in the year 2024. India's EV sales still managed to expand by around 20%, outpacing the roughly 4% growth seen in the overall Indian passenger vehicle market that year.
Segment-wise Breakdown: 2W, 4W, and Commercial Vehicles
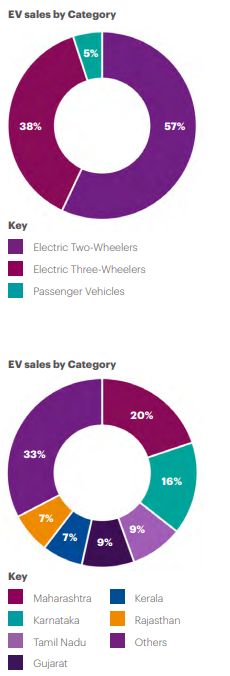
India's electric mobility story is led overwhelmingly by light vehicles. In FY 2023-24 the country registered about 9,44,000 battery scooters and 6,35,000 e-3Ws, while sales of electric cars stood near 84,000 and electric buses numbered only a few hundred. 2Ws and 3Ws therefore account for more than 95% of all EVs sold, a profile very different from that of Europe, China, or the United States.
Several forces explain this skew. Scooters and motorcycles remain the backbone of personal transport, so an electric version that delivers annual fuel savings of roughly INR 27,000 can reach total cost parity within 18 months. On the commercial side, e-rickshaws give last mile passengers and small cargo operators a cheaper, quieter alternative to petrol or diesel 3Ws. Growing competition among domestic startups and legacy manufacturers is further pushing sticker prices down toward those of conventional models.
The dominance of light electric mobility is seeding a broader ecosystem. India already has more than 1 million e-rickshaws, many still informal serving urban and peri-urban corridors, and the charger networks, financing products, and consumer familiarity built around these vehicles will lower barriers for larger EV segments. The pattern mirrors China's early trajectory, where mass adoption of e-2Ws and bikes created the industrial and market foundations for today's rapid scaleup of cars, buses, and trucks.
Sale of EVs in the financial year 2023 – 2024
Usability Comparison: Passenger vs Commercial Vehicle Segments
Passenger EV uptake depends on point-ofuse convenience including reliable home or workplace charging, acceptable realworld range, manageable upfront pricing, confidence in residual value, and the inherently fragmented purchasing decisions of millions of households. Commercial and fleet use cases operate on different economics. Vehicles log high, predictable daily kilometres, cycle through depots where scheduled charging or battery exchange can be standardised, and concentrate fuel and maintenance savings across large operating bases so rupee-per-kilometre cost parity is often reached earlier than in retail ownership. Because each fleet vehicle typically replaces a high-mileage diesel counterpart and removes concentrated urban emissions, rebalancing fiscal incentives away from private passenger cars toward buses, last-mile delivery, ridehail and municipal service fleets can yield materially higher environmental and publichealth returns on limited public funds.
Regulatory Environment
Overview of EV-specific Regulations
The Indian government has introduced several policies to promote EV adoption, including:
FAME-II Scheme: Launched in 2019 with a budget of INR 10,000 crore to support the adoption of EVs through subsidies and infrastructure development.
Production-Linked Incentive Scheme: Aims to enhance manufacturing capabilities for advanced automotive technology products with a budgetary outlay of INR 25,938 crore.
Scheme to promote manufacturing of electric passenger cars in India. This initiative is part of India's broader strategy to become a global hub for EV production, while also supporting the country's commitment to achieving net zero emissions by 2070.
Aims to attract fresh investments from international automakers and encourage sustainable economic growth through green mobility.
Recent Amendments Impacting EV Manufacturing and Infrastructure
The Ministry of Power issued the "Guidelines for Installation and Operation of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure-2024" ("2024 Guidelines") on September 17, 2024, emphasizing the role of public-private partnerships and simplifying the process for setting up EV charging stations.
Incentives and Compliance Requirements
Various incentives are provided to manufacturers and consumers, including tax benefits, subsidies, and support for research and development.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


