Rapidly changing business conditions have driven the need to speed up digital transformation initiatives and business process optimisation. Unfortunately, organisations are also facing an overwhelming backlog of application enhancement projects due to overworked and, generally, understaffed IT Development departments. As a result, a growing number of organisations are enabling "citizen developers".
A citizen developer is an employee who works in a non-IT related role but takes the initiative to create software tools and applications for the consumption by themselves or others, constantly looking for ways to innovate. Such trailblazers are becoming an important component of any team because they challenge the status quo and can improve the quality of everyone's work.
Now more than ever, employees are empowered to generate positive impacts on their organisations. The digital age has ushered a paradigm where, with minimal investment, computers can be used to automate processes, access and manipulate large amounts of information instantly, and be taught to make complex decisions better than that of a human user. The excitement garnered and use cases identified for Artificial Intelligence technologies such as DALL-E and ChatGPT is a prime example of this.
As Gen-Z continues to enter the workforce, the number of IT literate people with coding knowledge has increased. Digital upskilling and re-skilling programs also continue unlocking pockets of digital champions across the organisation. Hence the upsurge of citizen developers looking to drive efficiencies and eliminate barriers. Already in 2017, nearly 60% of all custom applications were built outside the IT department. Of those 30% were built by employees with either limited or no technical experience1.
This shockwave is intensifying in our organisations, with activities traditionally assigned to IT and technical roles becoming more prevalent in the day-to-day of business functions. Managers must prepare by setting up their organisations to take advantage of the benefits while balancing their oversight and governance.
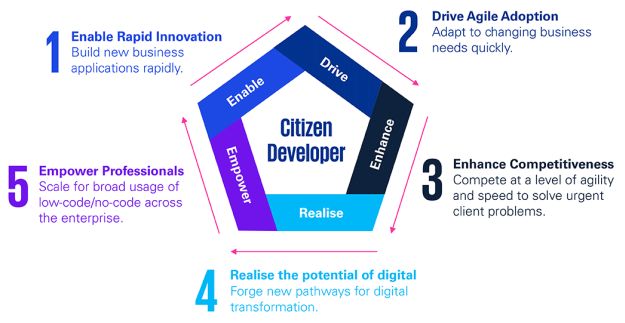
KPMG Digital Solutions focuses its approach to the citizen developer around five pillars as follows:
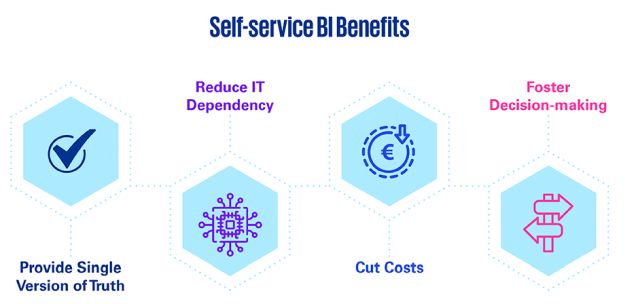
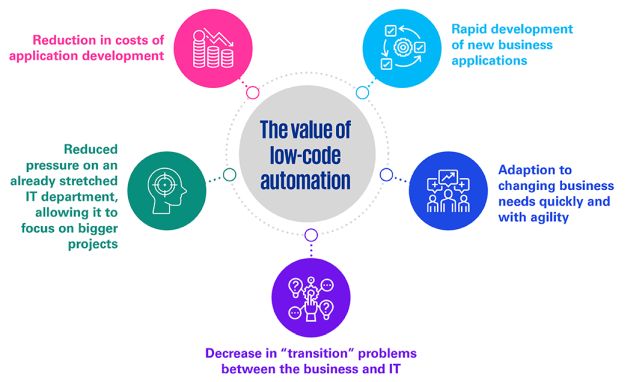
View the above slideshow to learn more about the Citizen Developer, Self-service BI benefits, the value of Low-code Automation and more about Governance, Risk and Controls.
Self-Service Analytics
Data-driven decision making is embedding itself in all organisations, across all levels. Much of the data preparation in support of analysis remains mostly manual, repetitive, and in Excel spread across the organisation. The most important insights resulting from such analysis is usually needed weekly, monthly, quarterly, or yearly and this means that some of our organisations' best people are caught up re-sourcing and cleaning data.
Creating a centre of excellence tasked with automating the cleaning and data quality management of key datasets to make them available for self-service consumption by the necessary business functions is where most organisations start. Embedding the use of dashboarding and reporting tools such as Power BI or Tableau into the organisation with the adequate technical support will accelerate the ability to extract value from data. Moreover, this shall also enable the organisation's IT functions to utilise such datasets for advanced analytical capabilities such as text mining, predictive analytics, network analysis, graph analysis, and sentiment analysis.
Low-Code/No Code
It is no longer necessary to learn a coding language to be able to create software solutions or applications. Tools like BluePrism, Power Automate and Power Apps now exist, allowing business users to build their own customised applications through drag and drop options, using workflow functionality and by filling in standard customised fields, similar to how objects can be dragged into a presentation slide and altered in terms of colours or line weightings.
Empowering your educated workforce with such toolsets and supporting them with the necessary expertise will shorten implementation times of initiatives and will result in a number of additional benefits in terms of cost savings, increased employee satisfaction, enhanced process efficiency and an improved customer experience. This may either take the form of targeted implementation support, especially for the more complex technical use-cases, or through the provision of training programmes and support.
Prioritisation and Agile delivery
Once the toolsets have been implemented and your workforce understands their purpose, expect a flood of ideas and initiatives. Focus here should be placed on identifying projects that will have a large impact on outcomes with lower complexity, requiring least effort. The use of value analysis tools and frameworks such as as the Digital Process Re-Engineering Framework (DPREF)2 can help in idenfying the quick wins and big bets from the money pits.
Once initiatives are identified, a strong project management office, well-versed in agile delivery techniques and frameworks (e.g., Scrum), will help in delivering these projects at pace, within budget and in a fashion where the organisation will start reaping benefits in the shortest period of time.
DevOps
Allowing citizen developers to contribute towards the IT solutions within an organisation brings challenges in overseeing their quality, change management, and maintenance. DevOps is a term coined to capture the policies and procedures of software development teams, that dictate how applications are managed, updated and released to users as new versions or revisions.
Especially for mid to large sized companies, bolstering governance in this area will support the citizen developer by offering a clear framework on how to go about creating their solutions.
The use of tools such as Jira and Azure DevOps can be used to support such activities.
Cybersecurity
The risk of external or internal intrusion, failure, or catastrophic events affecting the digital systems of our organisations remains top of mind. While the cost benefit of allowing your workforce to contribute solutions that drive value in the business is undeniable, without appropriate security, low-code platforms can expose sensitive, private, and confidential data, leading to possible regulatory fines and reputational damages.
Having the right oversight from IT over applications being developed and implementing adequate data management and access control mechanisms are some of the crucial steps to mitigate risks. Governance frameworks need to be updated, including policies and controls that consider the need for more widespread access to certain toolsets as well as business continuity plans to assess the criticality of citizen developed applications. Your organisation may fast be transforming covertly, equip your organisation with the proper tools and frameworks to empower your citizen developers!
Footnotes
1. 451 Research and FileMaker, Custom Apps - The Engine of Digital Transformation, August 2017
2. Process Value Stream Analysis
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.