- within International Law topic(s)
- in Asia
- with readers working within the Law Firm and Construction & Engineering industries
- in Asia
- in Asia
- in Asia
- within Government, Public Sector, Employment and HR and Energy and Natural Resources topic(s)
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
Introduction
India is poised to become one of the world's next economic powers. In pursuit of this vision, the country has adopted a dual strategy of strengthening domestic capabilities while actively deepening international trade relationships. One of the key tools employed by India and by many nations navigating the complexity of global commerce is the use of Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs), which reduce or eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers. For India, RTAs have become instrumental in establishing stable and predictable trade partnerships amid global volatility. Notably, India ranks 10th globally in terms of RTA usage, following leaders such as the European Union and the United Kingdom, which have long leveraged such agreements to secure their positions in the international trading system.
India's increasing integration into the global economy is reflected in its active participation in a broad array of RTAs. These agreements are not merely symbolic; they yield tangible economic benefits, such as reduced or zero customs duties on qualifying imports, which help Indian industries access raw materials at lower costs, strengthen supply chains, and improve global competitiveness.
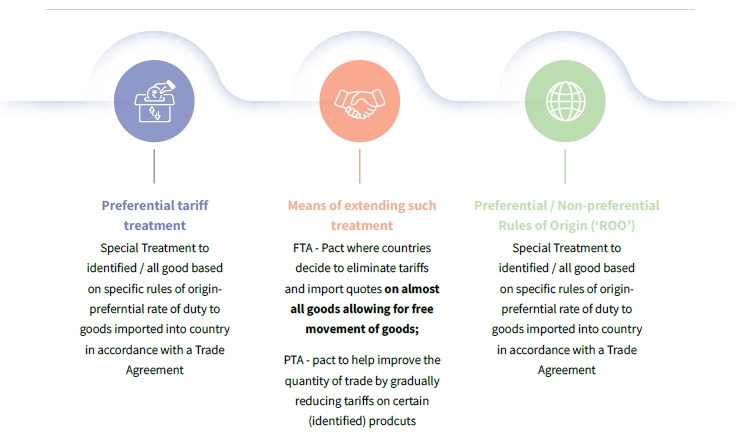
What are RTAs
RTAs are either bilateral (between two countries) or plurilateral/multilateral (involving more than two countries) reciprocal trade arrangements entered into by countries across various regions. These agreements aim to reduce trade barriers and facilitate smoother movement of goods and services, thereby promoting deeper economic cooperation. RTAs play a crucial role in bridging the gap between developed and developing economies. For developing countries, they offer opportunities to lower trade costs, enhance exports, and accelerate economic growth. By granting preferential treatment to signatory countries, RTAs promote mutual benefit through reduced tariffs, improved market access, and investment-friendly frameworks.
General Framework of FTAs
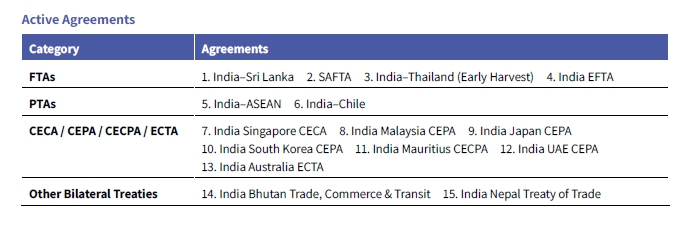
India till now has implemented 15 FTAs and 6 PTAs, and is negotiating more than 20 new pacts, most notably with the United Kingdom and the European Union. The latest milestone is the India‑EFTA Trade & Economic Partnership Agreement (March 2024) with Switzerland, Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein, underscoring India's shift toward high‑standard, plurilateral deals that lower trade barriers and stimulate investment.
Core Provisions Shared by Most Indian FTAs
Most Indian FTAs share a core set of provisions aimed at facilitating trade and investment among partner countries. These typically include commitments on tariff elimination or reduction, allowing for preferential access to goods originating from the FTA partner. Rules of Origin (RoO) play a critical role in determining eligibility for such preferences, ensuring that only goods with substantial economic connection to the partner country qualify. Further, FTAs usually provide for national treatment and most-favoured nation treatment [MFN], customs cooperation, and trade facilitation measures to reduce procedural delays at borders. Many agreements also include dispute settlement mechanisms, investment protection clauses, and provisions for sanitary and phytosanitary [SPS] standards and technical barriers to trade [TBT]. Increasingly, India's newer FTAs incorporate chapters on services trade, intellectual property, e-commerce, and sustainable development, reflecting the evolving priorities of modern trade policy. Recently, The India-UK CETA has been signed on 24 July 2025 and negotiations were finalised on 6 May 2025 after over three years and fifteen rounds of talk.
To view the full article please click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

