Welcome to the September issue of Blakes Competitive Edge, a monthly publication of the Blakes Competition, Antitrust & Foreign Investment group. Blakes Competitive Edge provides an overview of recent developments in Canadian competition law and foreign investment, including updates on enforcement activity by the Canadian Competition Bureau (Bureau), recent initiatives and key trends.
Key Highlights
- While overall merger review activity in 2023 still lags behind the previous two years, review activity picks up significantly in August with the Bureau completing 24 reviews over the course of the month (the most in a single month since June of last year).
- The Government of Canada introduces significant amendments to the Competition Act (Act).
- The Competition Tribunal (Tribunal) imposes a significant cost award against the Commissioner of Competition (Commissioner) in connection with the challenge of the Rogers-Shaw merger.
- The Bureau concludes that the proposed acquisition of HSBC Canada by Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) is not likely to result in a substantial lessening or prevention of competition.
- The Government of Canada releases its report regarding its consultation on the future of the Act.
Merger Monitor
August 2023 Highlights
- 24 merger reviews completed
- Primary industries: mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction (25%); retail trade (21%); manufacturing (17%); finance and insurance (8%); transportation and warehousing (8%); professional, scientific and technical services (8%)
- 13 transactions received an Advance Ruling Certificate (54%); 10 transactions received a No Action Letter (42%); one transaction was resolved through other means (4%)
January – August 2023 Highlights
- 124 merger reviews completed
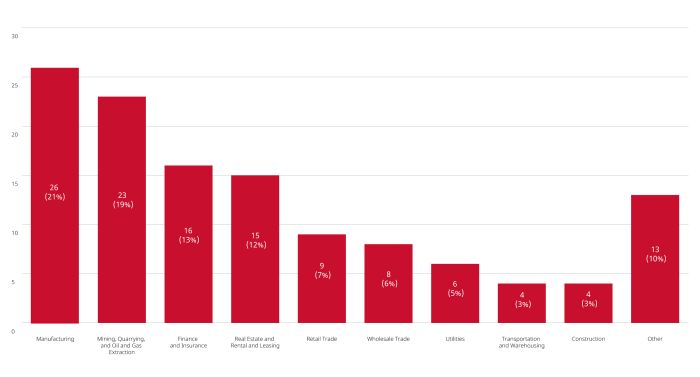
- Primary industries: manufacturing (21%); mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction (19%); finance and insurance (13%); real estate and rental and leasing (12%); retail trade (7%); wholesale trade (6%)
- Two consent agreements (remedies) registered
- One judicial decision filed
- 56 transactions received an Advance Ruling Certificate (45%); 64 transactions received a No Action Letter (52%); one transaction was resolved through other means (1%)
Merger Reviews Completed Year to Date in 2023 by Primary Industry
Legislative Reform
Government announces significant changes to the Competition Act
- On September 21, 2023, the federal government proposed key amendments to the Act. This followed on the heels of the Prime Minister's recent announcement that the government would "address the escalating price of groceries" by amending the Act to enhance competition and help reduce the cost of groceries. The proposed changes to the Actwill (i) give the Bureau the power to compel third parties to produce information to the Bureau in connection with market studies, (ii) "empower the Bureau to take action against collaborations that stifle competition and consumer choice, in particular situations where large grocers prevent smaller competitors from establishing operations nearby," and (iii) remove the efficiencies defence, which currently allows mergers with economic efficiency gains to proceed if those efficiency gains outweigh the anti-competitive effects from the merger. The New Democratic Party leader had earlier introduced a private member's bill that proposed even more significant amendments to the Act. For more information about the amendments, see our September 2023 Blakes Bulletin: Canadian Government Introduces Important Amendments to the Competition Act. For more information on the government's consultation on the future of the Act, see below, as well as our November 2022 Blakes Bulletin: Canadian Government Announces Review of the Competition Act and our April 2023 Blakes Business Class Seminar: Sweeping Changes to Canada's Competition and Foreign Investment Rules.
Merger Enforcement Activity
Significant costs awarded against the Commissioner in connection with the Rogers-Shaw decision
- On August 28, 2023, in Canada (Commissioner of Competition) v. Rogers Communications Inc and Shaw Communications Inc, the Commissioner was ordered to pay a total of C$9.7-million to Rogers and C$3.2-million to Shaw, the highest award ever made by the Tribunal for counsel fees and disbursements (e.g., experts). Despite the quantum, the amounts awarded to the respondents represent a small fraction of the legal fees and expenses actually incurred. A key factor contributing to the Tribunal's costs decision was its finding that the Commissioner's conduct "was much more unreasonable" than the conduct of the respondents. In reaching this conclusion, the Tribunal pointed in part to the Commissioner's insistence on challenging the transaction as initially proposed rather than accounting for the proposed sale of Freedom Mobile to Videotron, despite the Tribunal's repeated suggestions to include the proposed sale. The Tribunal also found that the Commissioner had adopted an unnecessarily contentious approach at numerous points in the litigation.
Competition Bureau finds the proposed acquisition of HSBC Canada by RBC unlikely to result in substantial lessening or prevention of competition
- On September 1, 2023, the Bureau announced the conclusion of its review of the proposed acquisition of HSBC Canada by RBC. As detailed in its report to the Minister of Finance, the Bureau concluded that the transaction is not likely to lessen or prevent competition substantially. The transaction remains subject to approval by the Minister of Finance.
Other Enforcement Activity
Criminal charges laid against two executives in a bid-rigging case in Montérégie
- On September 19, 2023, criminal charges were laid against two individuals in the Court of Quebec in connection with alleged bid-rigging for paving contracts awarded by the ministère des Transports du Québec (MTQ) for the Montérégie region. The accused individuals allegedly participated in an illegal agreement with their competitors to submit cover bids for tenders launched by the MTQ in 2008. See the Bureau's news release regarding the charges for more information.
Shipping companies fined for participation in an international conspiracy to reduce competition
- On August 17, 2023, the Ontario Superior Court fined shipping companies Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha (NYK) and Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd. ("K" Line) C$1.5-million and C$460,000, respectively, for breaches of the Act. NYK and "K" Line both pleaded guilty to one count of conspiracy under the Act, admitting to entering into agreements with other suppliers to increase the base freight rates they proposed to certain vehicle manufacturers in Japan for the supply of "roll-on/roll-off" services for shipments to Canada in connection with contract negotiations in 2008. "K" Line also pleaded guilty to one count of bid-rigging under the Act for entering into an agreement in response to a General Motors Company tender for "roll-on/roll-off" shipping services. See the Bureau's news release regarding the fines for more information.
Non-Enforcement Activity
Government of Canada released What We Heard Report on the Future of Canada's Competition Policy Consultation
- On September 20, 2023, the Government of Canada released its What We Heard Report on the Future of Canada's Competition Policy Consultation. The consultation received submissions from over 130 identified stakeholders, and more than 400 responses from members of the general public, commenting on a broad range of issues under the Act. Recognizing that "a framework law must apply broad, yet understandable principles. It cannot be the vehicle to resolve every shortcoming in the free market, to address every consumer grievance or perceived unfairness that may occur between businesses. Crucially, it cannot dictate specific outcomes, particularly in the unique legal environment of Canada's federal system and its separation of powers between the federal and sub-federal levels." The report concluded that "the task at hand is to consider how best to rebalance the regime to better limit concentration and deter anticompetitive practices, while avoiding overcorrection and preserving certainty in compliance."
Section 36 Remedies Under the Competition Act
Federal Court declines to certify class action against Amazon.com Inc.
- On August 28, 2023, the Federal Court in Difederico et al. v. Amazon.com Inc. et al. declined to certify a class action alleging that certain contracts between Amazon and third parties who sold their goods on Amazon's platform (Third Party Sellers) violated the criminal conspiracy provision of the Act (sections 45 and 46). The court agreed that Amazon may have competed with at least some of the Third Party Sellers through its sales on its own platform, and that the contracts may have had the effect of increasing or controlling the prices at which Third Party Sellers sold their products on other e-commerce websites through the operation of the "most favoured nation" provisions in these agreements. However, the court found that the plaintiffs' pleadings failed to disclose a reasonable cause of action under section 45 because, among other reasons, the plaintiffs failed to plead an objective intent to enter into an agreement of the kind described under paragraphs 45(1)(a), (b) or (c) of the Act, or material facts to support an allegation with respect to the sub-elements of these paragraphs. The court's conclusion was based in part on its holding that section 45 only criminalizes agreements that are unambiguously harmful to competition and consumers. Additionally, given that the plaintiffs' pleadings failed to disclose a reasonable cause of action under section 45, the court concluded that it was plain and obvious that the plaintiffs' pleadings did not disclose a reasonable cause of action under section 46 of the Act. Section 46 criminalizes the implementation of agreements entered into outside of Canada that would have violated section 45 of the Act if entered into in Canada.
Investment Canada Act
Non-Cultural Investments
April 2023 Highlights
- Zero reviewable investment approvals and 78 notifications filed (51 for acquisitions and 27 for the establishment of a new Canadian business)
- Country of ultimate control: U.S. (49%); U.K. (10%); France (9%); Germany (4%)
May 2023 Highlights
- Zero reviewable investment approvals and 103 notifications filed (78 for acquisitions and 25 for the establishment of a new Canadian business)
- Country of ultimate control: U.S. (55%); U.K. (7%); France (7%); Australia (3%)
June 2023 Highlights
- One reviewable investment approval and 125 notifications filed (95 for acquisitions and 30 for the establishment of a new Canadian business)
- Country of ultimate control: U.S. (51%); France (7%); U.K. (6%); China (3%); India (3%)
January – June 2023 Highlights
- Four reviewable investment approvals and 568 notifications filed (427 for acquisitions and 141 for the establishment of a new Canadian business)
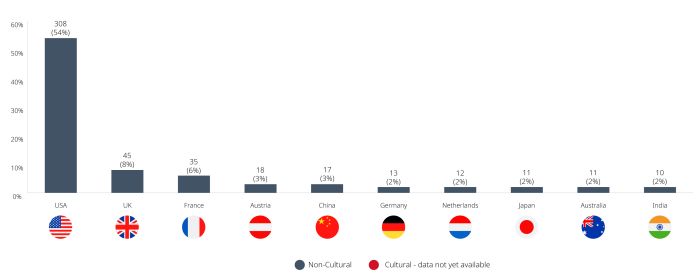
- Country of ultimate control: U.S. (54%); U.K. (8%); France (6%); Austria (3%); China (3%)
Blakes Notes
- Browse our thought-leadership insights from the Competition, Antitrust & Foreign Investment group to learn more.
For permission to reprint articles, please contact the bulletin@blakes.com Marketing Department.
© 2025 Blake, Cassels & Graydon LLP.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


