- within Privacy topic(s)
- with Finance and Tax Executives
- in United States
- with readers working within the Healthcare industries
- with Senior Company Executives and HR
- with readers working within the Business & Consumer Services, Retail & Leisure and Telecomms industries
On August 14, 2025, the long-awaited California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) Final Regulations were approved by the State. These rules are here to protect consumer data like never before. The effective date for these regulations is anticipated to be either Oct. 1, 2025, or Jan. 1, 2026, pending review by the Office of Administrative Law.
As businesses prepare to comply with these regulations, understanding the key updates and their implications is crucial. This article delves into the significant aspects of the CCPA Final Regulations, offering insights and guidance for businesses navigating this complex landscape.
Overview
The CCPA Final Regulations encompass several critical areas designed to enhance privacy protection and data security. In addition to some refinements to the existing rules, especially relating to transparency requirements, there are three main areas where the regulation has expanded on:
- Cybersecurity Audits: Ensuring robust security measures and compliance.
- Privacy Risk Assessments: Evaluating potential risks associated with data processing activities.
- Automated Decision-Making Technology (ADMT): Governing the use of technologies that impact consumer decision-making.
Details on each of the above are outlined in this article. Businesses must start preparing to ensure compliance with these transformative changes.
Key Regulatory Updates
1. Mandatory Annual Cybersecurity Audits
With the growing importance of cybersecurity, the CCPA mandates annual, independent audits for businesses that meet specific risk-based thresholds. These audits are crucial for ensuring the security and integrity of personal and sensitive information and, for many companies, are required to be submitted by April 1, 2028.
Who's Affected?
- Businesses deriving 50% or more of their revenue from data sales/sharing; and/or
- Those with annual revenue over $25 million (adjusted for inflation) that process significant amounts of personal/sensitive information.
What is Required?
Companies that meet these thresholds will need to:
- Implement annual, independent cybersecurity audits;
- Prepare a written certification by a member of the executive management team responsible for cybersecurity compliance, attesting to the audit's completion and specifics; and
- Submit audit results annually to the California Consumer Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA).
What are the Audit Components?
Companies should ensure that the audit covers all required elements, including:
- Overview of Systems and Data Environments: Comprehensive understanding of the business's data handling and storage.
- Evaluation Aligned with Industry Standards: Ensuring "reasonable security" through recognized benchmarks (NIST, ISO, etc.)
- Gap Analysis and Remediation Actions: Identifying vulnerabilities and addressing them promptly.
- Breach and Incident Review: Learning from past incidents to prevent future occurrences.
- Auditing of 18 Specific Controls:
- Authentication: Multi-factor authentication and strong passwords.
- Encryption: Protecting data both at rest and in transit.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Securing internal connections.
- Account Management and Access Controls: Restricting access based on necessity.
- Inventory and Management: Documenting all personal information that is collected, processed, stored, and shared, as well as key details about that information.
- Secure Configuration: Implementing software updates and secure environments.
- Vulnerability Scans and Testing: Regular checks and penetration testing.
- Audit-Log Management: Effective log storage and monitoring.
- Network Monitoring and Defenses: Preventive measures against intrusions.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Protections: Robust malware defenses.
- Segmentation of Information Systems: Proper configuration of network elements.
- Limitation and Control of Ports, Services, and Protocols: Restricting unnecessary access points.
- Cybersecurity Awareness and Education: Continuous training and threat awareness.
- Secure Development Practices: Ensuring secure coding and application testing.
- Oversight of Third Parties: Monitoring compliance of external partners.
- Retention and Disposal of Personal Information: Secure data destruction methods.
- Incident Response Management: Preparedness for security incidents.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plans: Ensuring data recovery and backups.
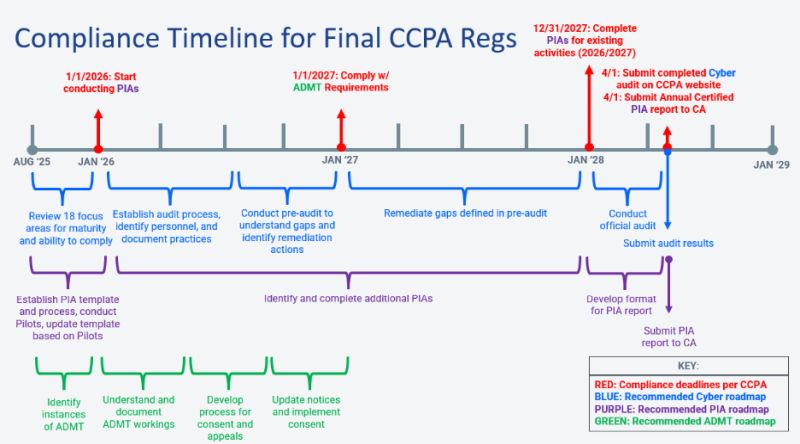
What are the Compliance Timelines?
The certification and cyber audit must be submitted via the CPPA's website no later than April 1 following the year the audit was conducted, starting with the following compliance activation dates (adjusted for the size of the company):
- April 1, 2028: Revenue over $100 million
- April 1, 2029: Revenue $50–$100 million
- April 1, 2030: Revenue under $50 million
What are the Ongoing Requirements?
Companies must submit audit results annually to the CPPA by April 1 following the audit year and retain all audit-related documents for at least five years.
2. Data Protection Risk Assessments (PIA) for High-Risk Processing
Privacy impact assessments (PIAs) are crucial for identifying and mitigating privacy risks in projects and systems, ensuring compliance with legal regulations. They protect individual privacy, enhance transparency, improve data management practices, and facilitate communication among stakeholders. Conducting PIAs helps maintain public trust and demonstrates an organization's commitment to safeguarding personal data. Under these updated regulations, businesses engaging in high-risk data processing must conduct a PIA to evaluate the implications of their activities.
Who's Affected?
Businesses engaging in high-risk data processing must conduct PIAs to evaluate the implications of their activities. High-risk data processing activities are defined as:
- Selling/sharing personal information
- Processing sensitive personal information
- Using ADMT for significant decisions
- Automated processing for systematic observation
- Presence in sensitive locations
- Training ADMT systems with consumer data
What are the Assessment Components?
Companies should ensure that the assessment covers all required elements, including:
- Detailed processing description
- Risk/benefit analysis
- Mitigation measures
- Consideration of less intrusive alternatives
What are the Compliance Timelines?
- Jan. 1, 2026: Start conducting PIAs.
- Dec. 31, 2027: Complete assessments for ongoing activities.
- April 1, 2028: Submit annual certified reports to CPPA.
What are the Ongoing Requirements?
Companies must maintain documentation for each assessment. The CPPA or the California Attorney General may request copies with 30 days' notice.
3. New Governance Obligations for ADMT
ADMT encompasses technologies that have a significant impact on consumer decisions. The new regulations go into effect on Jan. 1, 2027, and impose expanded governance obligations for these technologies. ADMT refers to technologies that execute or facilitate decision-making processes, including machine learning, statistics, and artificial intelligence (AI).
What is Required?
- Pre-Use Notices: Inform consumers before data collection.
- Right to Know and Appeal: Explain ADMT workings (logic, inputs/outputs, data sources, and assumptions) and allow consumer appeals.
- Opt-Out Mechanism: Provide a distinct opt-out link on websites.
- Opt-In Consent: Capture opt-in consent for collecting/processing sensitive and minors' data.
- Human Review Exception: Exemptions for systems with human oversight.
What Should Companies Do Now and How Can They Prepare?
Conclusion
The CCPA Final Regulations mark a significant step forward in privacy protection and data governance. Businesses must proactively address these changes to ensure compliance and protect consumer privacy. Preparing for these regulations involves thorough audits, risk assessments, and transparency in data practices. By following the outlined steps and timelines, businesses can navigate this complex landscape effectively, safeguarding both their operations and consumer trust.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

