- within Technology topic(s)
- in United States
- within Technology topic(s)
- in United States
- within Technology, Food, Drugs, Healthcare and Life Sciences topic(s)
Since the publication of a Bitcoin Paper by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, Blockchain has gathered a growing interest in various fields of technology.
In 2021, we wrote an article capturing a patent trend in this sector showing that from 2008 to 2018, the number of Blockchain patent families followed an exponential growth. We're now providing an update to that in 2025 showing the recent trends in Blockchain patent landscape.
Gradual decrease in first filings
The following Figure 1 shows an evolution of the number of Blockchain related priority patent applications filed worldwide from 2011 to 2023.
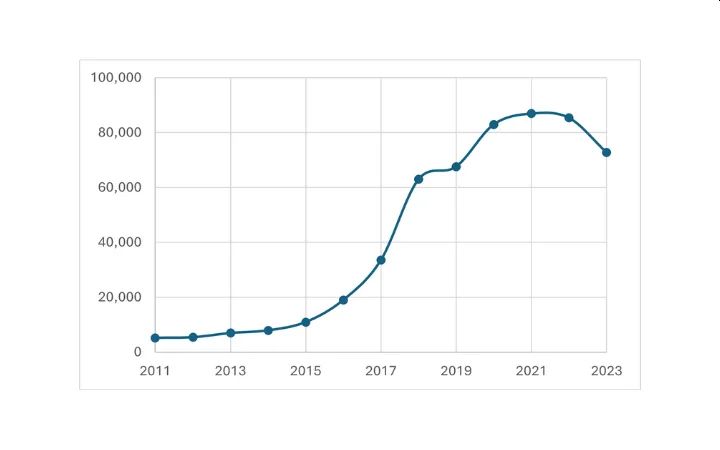
Figure 1: Number of Priority filings "Blockchain"
This graph confirms the earlier exponential trend until 2018. However, the number of first filings worldwide appear to have increased year-on-year from 2019 at a much slower rate to culminate in 2021. Finally, the number of first filings has been gradually decreasing since then. To ensure that the graph captures all first filings, its timeline stops in 2023 since all first filings in each year would have published by the date of this article (mid-August 2025).
Specific patent classification (CPSs) trends generally show a mature research phase
The graph of Figure 2 shows the number of priority patent applications filed worldwide in specific fields of technologies identified by their respective patent classifications or CPCs. The first CPC G06Q20/00 includes inventions in the fields of payment architectures, schemes or protocols. The CPC H04L9/00 regroups patent applications in the fields of arrangements for secret or secure communications and network security protocols. Finally, the CPC H04L2209/00 concerns applications relating to cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communication.
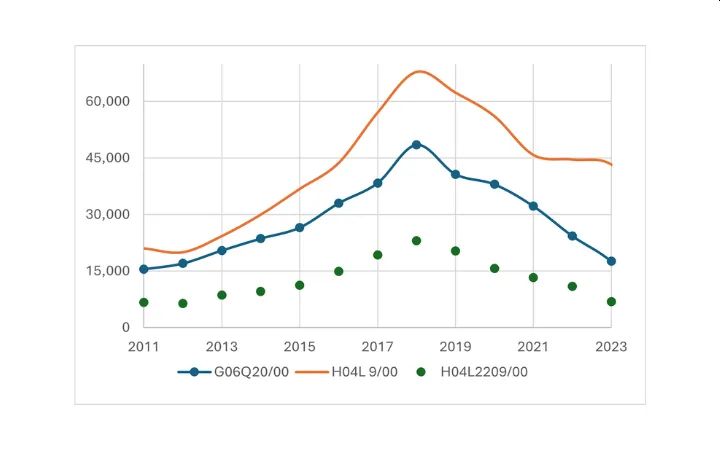
Figure 2: Number of priority filings
Blockchain related applications are usually classified as belonging to one or more of these identified technological groups and their subgroups. Figure 2 shows that for each of these classifications, the number of priority application filings reached a peak in 2018, and from then on started to decline. This is a sign that the research phase of Blockchain has matured and that the technology is gradually transitioning towards development of applications for the benefit of end users. Use cases includes application in the fields of finance, supply chain management, healthcare, carbon emissions etc.
Blockchain and Quantum – the winning combo that shows a continued growth trend
If the number of Blockchain related patent applications is in a downward trend generally, the fields combining Blockchain and Quantum displays a continued growth. Figure 3 reveals a recent uptrend in filing applications relating to both fields of technology. These inventions include those relating to applying quantum technology to Blockchain.
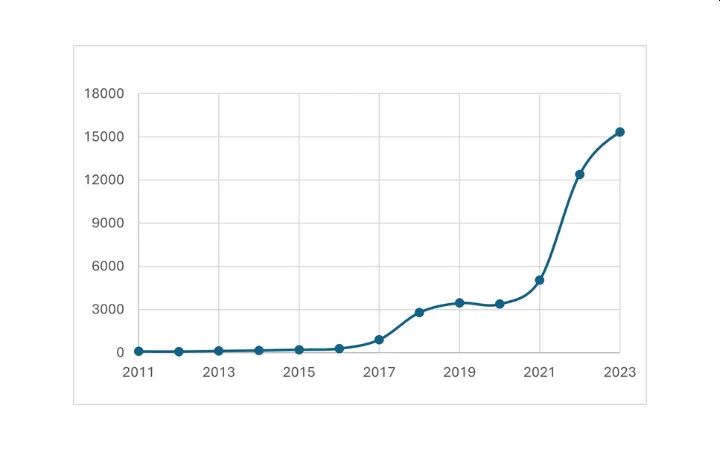
Figure 3: Number of priority filings "Blockchain and
Quantum"
Recent progress indicates that quantum computers will soon be able to break security codes used in today's secure communications, which is a serious threat to data confidentiality. For instance, a sufficiently powerful quantum computer could derive a private key, which is supposed to remain secret, from its corresponding public key, and falsify any digital signature. The security of the Blockchain would then be at risk of being compromised. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies may become vulnerable to thefts by an adversary operating a quantum computer. To mitigate the risk to the security of Blockchain, new types of cryptography called "post-quantum cryptography" are being developed to be inherently resistant to quantum attacks.
Recently, D-wave" published a research paper entitled "Blockchain with proof of Quantum". It introduced a prototype blockchain architecture in which the mining computational task is only performed by quantum computers and infeasible by classical computers. This experimental network has been developed using a quantum annealing technology. Its purported aim is to reduce energy consumption expanded by classical computers when mining while providing a blockchain which is resistant to attacks by quantum computers.
Closing thoughts
On-going and future research in post-quantum or quantum resistant cryptography will develop blockchain applications which are secure against attacks from powerful quantum computers. This area of technology will certainly produce a host of innovations deserving patent protection.
The rapid convergence of blockchain and quantum technologies presents both challenges and opportunities. While the decline in blockchain-only filings suggests a maturing field, the rise of blockchain-quantum applications demonstrates that innovation in this space is far from slowing down. As companies and researchers race to develop secure, energy-efficient, and future-proof solutions, intellectual property protection becomes a vital tool in safeguarding these breakthroughs and maintaining a competitive edge.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

