1. BACKGROUND
In addition to the trade conflict between the U.S. and China, recent events including the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russian invasion of Ukraine have further heightened interest in economic security globally. Under such circumstances, the Cabinet of Japan approved the Economic Security Promotion Bill on February 25, 2022 and submitted the bill to the ordinary session of the Diet. The bill is expected to be passed during this session of the Diet.
Economic security is considered to be an economic measure to ensure the security of a country and its people1. The Economic Security Promotion Bill consists of the following four pillars and such four pillars were positioned as economic measures for recent international situations regarding security at the expert advisory panel on economic security legislation (the "Expert Advisory Panel") organized in late November, 2021.2
- Strengthening of the supply chains of important items and raw
materials
- To mitigate the increasingly serious impact that a potential supply disruption of semiconductors and pharmaceuticals may cause due to the digitalization of industrial infrastructures and advancement of medical care
- To counter the relative decline in Japan's ability to secure supplies in times of supply disruption of important items due to the growth of emerging countries and the deepening of global value chains
- Securing safety and reliability of key infrastructures
- To mitigate the risks of and threats from cyberattacks due to digitalized and more complex infrastructure
- Implementing systems to develop and support key technologies by
both public and private sectors
- To boost research and development around the world as the means of military attacks become more sophisticated and diversified
- Prevention of data leakage of sensitive information relating to
inventions by not disclosing the patent information of such
inventions
- To reinforce measures for the prevention of leakage of sensitive information relating to national security around the world
Below is the summary of the Economic Security Promotion Bill with respect to the four pillars above. Please note that this newsletter is based on the Economic Security Promotion Bill as of February 25, 2022 and relevant government materials and there may be additions or changes to the content thereof3,4.
2. STRENGTHENING SUPPLY CHAINS
2.1 Overview
In order to ensure the stable supply of items and materials that are essential to the lives of people and the economy in Japan, the following measures will be implemented in accordance with the basic policy to be formulated by the national government: (1) designation of subject items and materials, (2) public support for private sector companies that contribute to the stable supply of subject items and materials and (3) government measures to secure the stable supply of such items and materials.
- Businesses/business operators that will be particularly affected by such measures
-
- Business operators that engage in the supply of important items and materials (see 2.2 below)
- Business operators that receive supplies of important items and materials from business operators of i. above
- Financial institutions
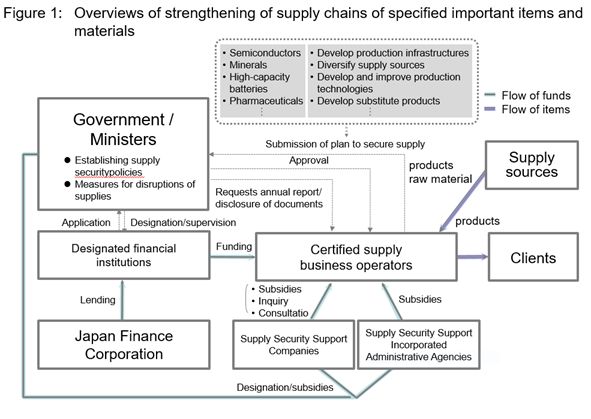
2.2 Specified important items and materials (items subject to the measures)
Items and raw materials for which a stable supply is necessary under economic security needs (see 2.1 above) will be designated as Specified Important Items and Materials by a cabinet order after the enactment of the Economic Security Promotion Bill. Computer programs can also be designated as Specified Important Items and Materials. According to the report of the second meeting of the Expert Advisory Panel, the following items are expected to be nominated as Specified Important Items and Materials.
- Semiconductors
- Important minerals that contain rare earths
- High-capacity batteries
- Pharmaceutical items
2.3 Public support for private sector businesses
The main framework of public support for certified supply business operators (see 2.4.1 below) is as follows.
- Provision of support by subsidies and interest subsidies, an inquiry system for the provision of necessary information and consultation services by corporations funded by government subsidies5
- Business loans from designated financial institutions that have received loans from Japan Finance Corporation, a public corporation wholly owned by the Japanese government that provides financial services in Japan and internationally (see 2.4.2 below)
2.4 Subject private business operators
2.4.1 Certified supply business operators
A certified supply business operator is a business operator who has submitted to the competent minister a plan concerning measures for ensuring a stable supply of Specified Important Items and Materials and has obtained approval. At least based on the words of the Economic Security Promotion Bill, it appears that there will be no restrictions concerning foreign investment or other restrictions on the qualifications for business operators who can submit such plans.
According to the opinions prepared by the Expert Advisory Panel upon the preparation of the Economic Security Promotion Bill (the "Opinions"), business activities such as the following are expected to be the target of support.
- Development of domestic production infrastructures
- Diversification of supply sources
- Stockpiling
- Development and improvement of production technologies
- Development of substitute products
- Promotion of recycling
The approval of plans will be given pursuant to the supply security policy to be set by the competent minister after the designation of Specified Important Items and Materials.
When a certified supply business operator is unable to conduct its plan, its status as a certified supply business operator may be revoked. However, it appears that no specific measures are being considered for enforcing the implementation of such plan, such as by penalties or orders. A certified supply business operator is obligated to report the status of the implementation of its plan every business year and to submit reports and necessary documents on the status of the implementation of its plan at the request of the competent minister6.
2.4.2 Designated financial institutions
A designated financial institution is a financial institution that has received a loan from Japan Finance Corporation and has been designated as a financial institution that is capable of appropriately and reliably providing support to certified supply business operators. The competent minister shall have the authority to give orders to designated financial institutions with respect to the provision of such support.
2.5 Government measures for securing stable supply
When it is difficult to secure the supply of Specified Important Items and Materials through the scheme of support for certified supply business operators, the competent minister may take necessary measures including stockpiling of Specified Important Items and Materials7. In connection with such measures, no enforceable measures are expressly provided for certified supply business operators.
2.6 Miscellaneous
The competent minister may request relevant business operators to submit reports and documents to the extent necessary for the implementation of a series of measures for strengthening supply chains and such business operators are obligated to make efforts to comply with such request. This applies to business operators other than certified supply business operators and designated financial institutions, and therefore a wide range of business operators may be subject to such obligation.
This measure will be implemented within nine months of the date of promulgation.
3. SECURING THE SAFETY AND RELIABILITY OF KEY INFRASTRUCTURES
3.1 Overview
In order to prevent the hacking of critical facilities of key infrastructures from outside, a prior assessment system will apply to the introduction of critical facilities for key infrastructures and the commission of maintenance and management of critical facilities.
- Businesses/Business Operators that will be particularly affected
-
- Companies that operate a key infrastructure (see 3.3 below)
- Companies that supply specified critical facilities (see 3.4 below) or parts to i. above
- Companies that are commissioned to manage and maintain specified critical facilities of i. above
3.2 Framework of the prior assessment system
 |
 |
3.2.1 Submission and assessment of plans
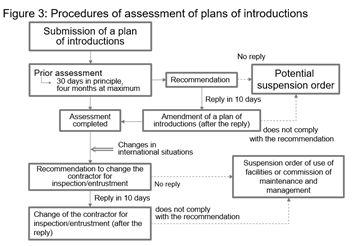
When a specified infrastructure operator (see 3.3 below) (i) introduces a specified critical facility (see 3.4 below) or (ii) outsources the maintenance and management of such facility to others, such operator needs to submit a plan of such introduction/outsourcing to the competent minister for prior assessment.
The assessment period is 30 days in principle and it may be extended to four months at maximum, and the design of the assessment system is similar to the prior assessment system in respect of inward direct investment under the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Control Act. A business operator is prohibited from proceeding with the introduction/outsourcing until the assessment is completed and the plan is approved.
When it is deemed necessary to amend the plan as a result of the assessment, the competent minister may issue a recommendation to such specified infrastructure operator to remedy the plan and such operator is required to respond within ten days as to whether or not it accepts the recommendation. If the operator does not have justifiable grounds for not responding to the recommendation, the competent minister may order the suspension of such plan, and may impose penalties for non-compliance with such order.
3.2.2 Subsequent recommendations and orders
Even in the case where specified critical facilities have been introduced or where the maintenance and management of such facilities have been outsourced to others after the prior assessment of the plans for the same were completed, if it is subsequently recognized that there is a high risk of these facilities being used as a means of interference due to a change in the international situation or other circumstances, the competent minister may issue a recommendation or an order in the same manner as set out in 3.2.1above8.
Specifically, penalties are provided for cases where (i) a recommendation is given for inspection or examination of such critical facilities or for change of a contractor to which the maintenance and management is outsourced, and (ii) if an operator does not have justifiable grounds for not responding to the recommendation, the competent minister may order the suspension of the use of such critical facility and the outsourcing of the maintenance and management of such facility, and penalties may be imposed in cases where an operator does not comply with such order. The operator is required to respond within ten days as to whether or not it accepts the recommendation, which is similar to 3.2.1 above.
3.3 Specified infrastructure operators (subject key infrastructure operators)
Specific social infrastructure operators are designated by the competent minister as those that meet both of the following conditions.
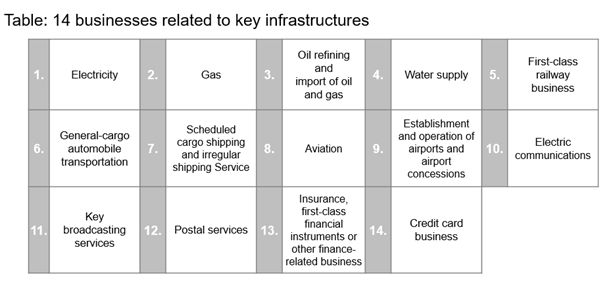
- Infrastructure operators that fall under any of the following 14 types of businesses
- Infrastructure operators that meet the criteria set by the competent minister for determining whether they are operators (i) who employ critical facilities, the suspension or malfunction of which will (ii) cause disruptions to the stable supply of services and (iii) have a high risk of impairing the security of Japan and its people.
3.4 Specified critical facilities (subject facilities)
"Specified critical facilities" mean the facilities that fall under the criteria set by the competent minister in consideration of the importance of the stable supply of services of the business operator and of the risk of such critical facilities being used as a means of interference by outside parties. The definition of facilities includes computer programs in addition to machines and equipment.
3.5 Miscellaneous
3.5.1 Authority for investigation
The competent minister may request business operators that engage in the businesses listed in the above table to submit reports or documents to the extent necessary for designation as specified infrastructure operators.
To the extent necessary for the implementation of the assessment of or recommendations for specified infrastructure operators, the competent minister may also request specified infrastructure operators to submit reports and documents or conduct on-site inspections.
3.5.2 Transitional measures
Business operators are exempted from the obligation to submit implementation plans to the relevant authorities in respect of the following acts.
- Acts conducted by a specified infrastructure operator within six months after being designated as a specified infrastructure operator
- Acts concerning a specified critical facility within six months after such facility came to fall under the category of specified critical facilities by the revision of the relevant ministerial ordinance
- Acts concerning the outsourcing of maintenance and management within six months after newly falling under the category of outsourcing of maintenance and management by the revision of the relevant ministerial ordinance
3.5.3 Effective period
The effective period of this measure is stated as being within one year and six months from the date of promulgation of the designation of specified infrastructure operators and within one year and nine months from the date of the promulgation of the assessment system (including recommendations and orders).
4. PROMOTION OF KEY TECHNOLOGIES BY PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SECTORS
4.1 Overview
For advanced technologies critical for the stability of people's daily lives and economic activities, a framework of government support and cooperation between the public and private sectors will be implemented. According to the Opinions, specified key technologies (see 4.3 below) appear to include the areas of space engineering, marine engineering, quantum technology, artificial intelligence and biotechnology.
- Businesses/Business Operators that will be particularly affected
-
- Companies and research institutions that engage in research and development of specified key technologies
- Investigation organizations with knowledge of specified key technologies
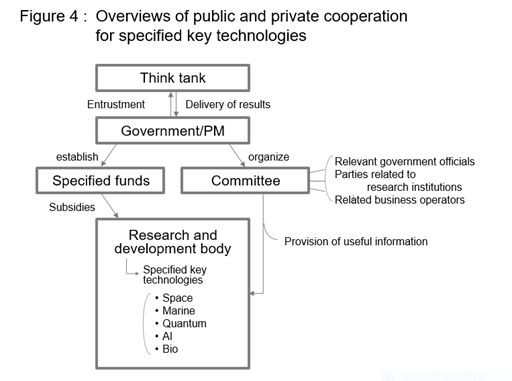
4.2 Specified key technologies
"Specified key technologies" mean technologies that fall under both of the following:
- Advanced technologies that can be essential for the maintenance of people's lives and economic activities in the future
- Technologies that could harm the safety of Japan and its people in the case of unauthorized use of the results of research concerning such technology by outside parties or the instability of the supply of items, materials or services that use such technology
4.3 Establishment of funds
The Prime Minister may designate a fund established under the Act on the Promotion of Science, Technology and Innovation aimed at the promotion of research and development of specified key technologies and the appropriate use of their results as a specified fund and grant subsidies to such fund.
4.4 Organization of a committee
The government may organize a committee of researchers and competent ministers for state-funded research and development for the purpose of the promotion and appropriate use of specified key technologies.
Such committee will mainly discuss the following.
- Collection and analysis of information useful for research and development of specified key technologies9
- Preparing policies for effective promotion of research and development of specified key technologies
- Handling of results of research and development of specified key technologies
- Conducting appropriate management of information on specified key technologies
4.5 Outsourcing to a think tank
In order to promote the research and development of specified key technologies and appropriate use of the research results, the Prime Minister may kick-start the necessary investigation and research.
The Prime Minister may outsource all or part of such investigation and research to a competent institution and the head of a competent administrative authority may provide the necessary information and documents for the investigation and research at the request of such institution.
4.6 Miscellaneous
The effective period of this measure is stated as being within nine months from the date of promulgation.
5. NON-DISCLOSURE OF PATENT APPLICATIONS
5.1 Overview
In order to prevent the leakage of information through patent application procedures regarding inventions of which disclosure may be likely to harm the security of Japanese citizens, (i) a system of withholding the publication of such patent applications and (ii) measures to protect the information relating to such patent applications will be implemented.
- Businesses/Business Operators that will be particularly affected
-
- Companies that engage in research of nuclear technology or technologies related to development of military weapons
- Companies that receive information from i. above or are licensed by i. above
5.2 Procedures
A two-stage examination will be introduced implemented to determine whether or not to designate an invention as a subject for protection (see 5.3 below) in order to prevent the leakage of information of such invention.
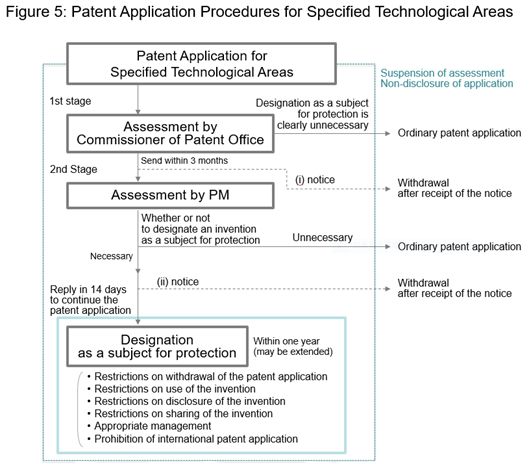
- Examination process
-
- First stage of examination
An examination will be conducted to determine whether an invention falls under the category of a technological area that is highly likely to include inventions of which disclosure may harm the security of Japan and its people10 (the "Specified Technological Areas"), by taking into account the criteria listed in the relevant cabinet order. Inventions which fall under such category will be, in principle, advanced to the second stage of the examination. Such determination as to whether or not to advance the examination to the second stage will take place within three months from the date on which the first stage of the examination began. - Second stage of examination
With the cooperation of national agencies and external experts, the need for designation as a subject for protection will be determined by taking into account threats to Japan and its people if the invention is disclosed and the potential impact on industrial advancement in the case of non-disclosure of such invention11.
- First stage of examination
- Non-disclosure of procedures and notification to applicants
Publication of patent applications and approval procedures will be suspended during the period from the start of the first stage of the examination until the termination of such examination or of designation as a subject invention.
The patent applicant will be notified (i) when a patent application is advanced to the second stage of the examination and (ii) before the invention is designated as an invention subject for protection as a result of the second stage of the examination.
When the applicant receives a notice of (ii), the applicant will decide whether or not to continue such application procedure within 14 days (if the invention is designated as a subject invention, the withdrawal of the patent application will be restricted) and if the applicant continues with the patent application procedures, the disclosure of such invention will be prohibited until the expiration of the effective period of protection or until the applicant receives a notice of non-designation.
- Designation as subject for protection
After the procedures above are completed, if the Prime Minister acknowledges that it is appropriate to designate an invention as a subject invention for protection in consideration of (i) the necessity of such designation and (ii) the adverse impact on the advancement of the industry in the case of such designation, such invention will be designated as a subject invention for protection.
5.3 Effect of designation
When an invention is designated as a subject invention for protection, the following restrictions will apply to the applicant. Penalties may be imposed in the event of the violation of some of the following.
- Restriction on withdrawal of the patent application
- Restriction on the use of such invention by an unauthorized person
- Prohibition of the disclosure of such invention
- Implementation of approval systems for sharing the invention with other business operators
- Obligation of appropriate management of such invention
- Prohibition of making an international patent application for such invention
The effective period of protection is no more than one year, but the period may be extended for a period of not more than one year when the necessity of such extension after the expiry of the original period is discussed and it is deemed as necessary.
5.4 Prohibition of international patent applications
Inventions that fall within specified technological areas and that are created in Japan are prohibited from being the subject of patent applications in other countries in principle, and penalties may be imposed for the violation thereof.
When a person wishes to submit a patent application in other countries of an invention that may fall under specified technological areas, such person may inquire [with the competent authority] as to whether the prohibition of international applications applies to such invention or not.
5.5 Miscellaneous
5.5.1 Compensation
Those who suffered losses as a result of the designation of an invention as a subject for protection may receive compensation for such reasonable losses from the government.
5.5.2 Transitional measures
This measure will not apply to patent applications that are pending as at the time of the enactment of the Economic Security Promotion Bill. This measure will also not apply to pending patent applications that come to newly fall under specified technological areas by the revision of the relevant cabinet order.
5.5.3 Effective period
The effective period of this measure is stated as being within two years from the date of promulgation thereof.
6. CONCLUSION
This newsletter analyzed the Economic Security Promotion Bill, which has attracted attention in Japan as well as overseas. Before the Economic Security Promotion Bill, regulations related to economic security mainly comprised measures such as export control and restrictions on inward direct investment. These regulations were directed at relatively limited fields including technologies of a sensitive nature and industrial areas important in terms of national security. On the other hand, the Economic Security Promotion Bill covers a wide range of industrial and technological areas and the enactment of the bill will have a significant impact on business activities.
It is necessary for companies to first of all determine whether their business activities would be subject to the Economic Security Promotion Bill and if so, whether they should take appropriate procedures as stipulated under the bill. Regarding the first pillar of the bill, suppliers of specified items and materials may receive government support by preparing a plan to stabilize the supply of such specified items and materials and acquiring approval thereof. For the second pillar, operators of key infrastructures are required to undergo an assessment prior to the implementation of facilities and the outsourcing of the maintenance and management of such facilities. The third pillar allows operators that engage in the research and development of specified key technologies to receive subsidies from specified funds. For the fourth pillar, business operators that engage in specified technologies concerning national security (nuclear technologies and technologies for military weapons) will be required not to disclose their patent applications.
The second and fourth pillars will call for protection in terms of legal compliance. On the other hand, the first and third pillars will require assertive measures to utilize new support to be provided by the bill. In both cases, high-level management decisions will be essential. The bill is expected to come into effect within two years of its enactment. In the meantime, it is necessary for companies to analyze the details of the various systems and measures and prepare appropriate policies.
Footnotes
1. The ground for the Economic Security Bill is stated as below.
"Due to the growing complexity of international situations and changes in socioeconomic structures, so as to ensure economic security, it has become increasingly important to take preemptive measures to prevent the occurrence of actions related to the economy that may harm the security of the country and its people. In light of such situation, in order to promote economic measures for ensuring economic security comprehensively and effectively, it is necessary to formulate a basic policy for ensuring security by implementing integral economic measures. Furthermore, as economic measures for ensuring economic security, it is important to establish a system for securing the stable supply of critical items and materials and the stable provision of essential social infrastructure services, and a system for supporting the development of important technologies and for non-disclosure of patent applications. Above is the ground for the submission of this bill."
2. The international situation regarding economic security is discussed in detail in the materials of the Expert Advisory Panel based on case studies.
https://www.cas.go.jp/jp/seisaku/keizai_anzen_hosyohousei/index.html
https://www.cas.go.jp/jp/seisaku/keizai_anzen_hosyohousei/dai1/siryou3.pdf
3. Specifically, it is necessary to pay close attention to the revision of the Economic Security Promotion Bill after discussions, the regulation of the details of the system by government ordinances and guidelines, and the disclosure of public authorities' views through public comments.
4. On March 11, 2022, the Democratic Party for the People submitted a comprehensive economic security promotion bill to the House of Councillors (the "DPFP Bill"). In comparison with the Economic Security Promotion Bill, the DPFP Bill is different in that it contains provisions for ensuring the stable supply of food, implementation of a security clearance system, and building an economic environment that guarantees human rights. Regarding security clearance and building an economic environment that guarantees human rights, such ideas are also mentioned in the opinion by the Japan Business Federation as of February 9, 2022 in response to the opinion by the Expert Advisory Panel (the "JBF's Opinion"). Although the commentary for the DPFP Bill is not included in this newsletter, it is advisable to pay attention to future developments in respect of the bill to see the direction of future discussions.
The DPFP Bill: https://new-kokumin.jp/news/policy/2022_0311_3
JBF's Opinion: https://www.keidanren.or.jp/policy/2022/015.html
5. Supply Security Support Companies and Supply Security Support Incorporated Administrative Agencies (with respect to the inquiry and consultation services, only by Supply Security Support Companies)
6. There is a fine for non-compliance with such obligation.
7. According to the Opinions, such potential measures other than stockpiling include procurement from foreign countries, call for reduction of use and commission of production.
8. At the moment, the text of the Economic Security Promotion Bill appears to provide that such subsequent recommendations and orders only apply to critical facilities subject to assessment applications. However, if the Economic Security Promotion Bill is applied to critical facilities that were introduced or the maintenance and management of which was outsourced prior to the enforcement of the Economic Security Promotion Bill (before the end of the transitional measure period), it will have a significant impact on such facilities, and it would be necessary to pay close attention to whether such interpretation and application will be made.
9. According to the Opinions, it is expected that such information will include specific prospects of the implementation of such technologies in society, results of research conducted by the government, sample data, cyber-security information on cyberattacks and vulnerabilities, and confidential contract information and information on the government conditions related to national safety and security.
10. According to the Opinions, such areas will be chosen from technologies concerning nuclear technology and development of military weapons.
11. It is stated in the Opinions that single-use technologies used for the development of nuclear weapons or other weapons should be the main targets of such designation as a subject for projection and the designation for dual-use technologies that could be used for purposes other than weapons should be limited.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.





