- within Tax topic(s)
- within Tax topic(s)
- with Senior Company Executives, HR and Finance and Tax Executives
- with readers working within the Metals & Mining industries
I. Individuals
1.1 Personal Income Tax
An individual is subject to income tax on his/her total net income in Greece and abroad. Net income sourced in Greece is taxed irrespective of the residence of the individual. Income arising abroad is taxed if the relevant individual is a tax resident of Greece. The tax year is the calendar year. For income tax purposes, the income derived by individuals is divided into certain categories. Taxable income is calculated based on the rules of each category and the total taxable income of the individual is the aggregate of the categories.
Note: An individual being in Greece for a period exceeding one hundred eighty-three (183) days, cumulatively, during any twelve-month period, shall be considered a Greek tax resident from the first day of his/her presence in Greece.
1.1.1 Income from Employment, Pension Income Freelance Activities
Employment & Pension Income
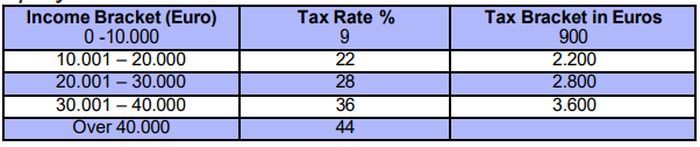
Under conditions there are some tax reductions such as number of children, amount of total income.
Freelancers
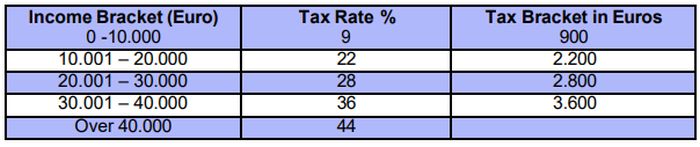
Tax reductions for employees and pensioners do not apply, whereas as for the income of freelancers for the year 2023 and onwards a deemed minimum income is taken into account for income tax purposes (tax on notional income) according to recently introduced tax provisions.
1.1.2 Solidarity Contribution
As of January 1, 2023, the solidarity tax has been abolished for all private and public sector employees, as well as for pensioners.
1.1.3 Income from Immovable Property
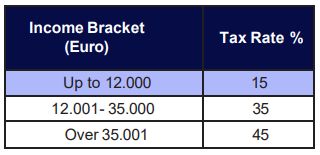
Under certain conditions, property owners are not taxed for rent that was not collected.
1.1.4 Social Insurance Contributions ("SIC")
All salaries are subject to social insurance deductions. There are numerous social insurance foundations, each one competent for a different professional specialty. The most common Social Insurance Foundation is IKA. Most of the foundations have now been unified under the "umbrella" foundation of EFKA.
SIC Rates
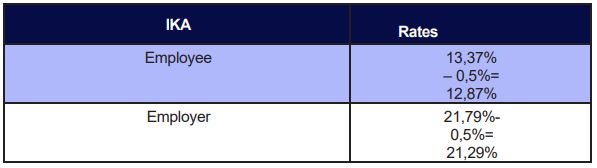
The above percentages apply when both pension and health deductions are covered by IKA. In cases when extra social insurance deductions are required (e.g., such as TEAYEK -social insurance foundation regarding employees working in stores) the above percentages differ as follows:
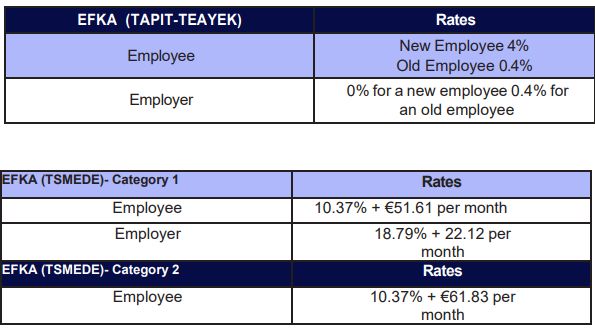
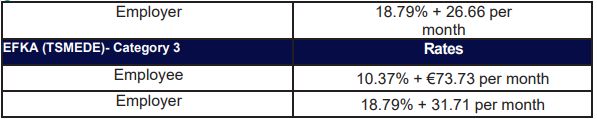
All percentages are calculated on the gross salary with a pre-set limit of deductions. All percentages are indeed calculated on the gross salary as long as the salary doesn't exceed the amount of € 7373,53 per month.
II. Corporate Taxation
2.1 Corporate Income Tax
Legal entities, which are duly registered in accordance with the Greek Corporate Law, are subject to corporate income tax on their worldwide income while non-resident companies, such as branches of foreign entities, are taxed only on income derived from Greece.
Companies and freelancers may be subject to paying tax in advance. The in advance paid tax is each time offset with next year's fiscal obligations.
2.1.1 Tax Rates
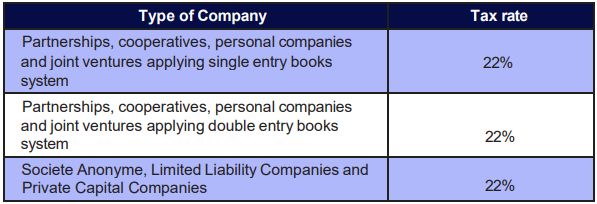
Notes:
1. The taxable period is the financial year. This may end on 31 December or 30June.
2. The corporate income tax return must be filed by the final day of the sixth month following the end of the financial year. The income tax can be payable in 8 monthly installments commencing upon the filing of the tax return.
2.1.2 Deductible Expenses


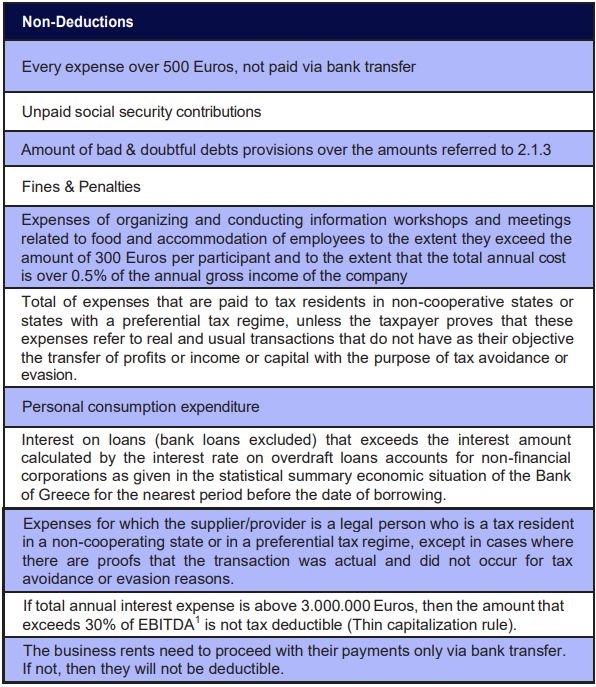
2.1.3 Non-Deductible Expenses
2.1.4 Depreciation
Depreciation on fixed assets is computed annually at fixed rates, the most important of which are:
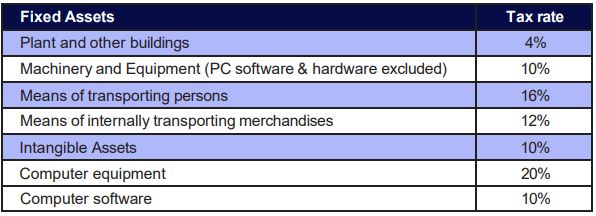
2.1.5 Tax Incentives
Tax incentives are given if a company makes productive investments. There are two kinds of incentives:
- State grants
- Tax reliefs
The total amount of support depends on the size of the enterprise and the geographical area.
Both incentives require a decision from the related authorities. The amount allocated every year for both grants and tax reliefs are limited.
2.2 Capital Gains Tax
Companies: Capital gains are not taxed separately but are added to the company's taxable income.
Individuals: Transfer of non-listed shares is subject to capital gain tax at the rate of 15%. Transfer of listed shares is again taxed at 15% and additionally 20 is imposed on the gross sale proceeds of listed shares.
To view the full article click here
Footnote
1. tax exempt income is not included in this EBITDA
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

