According to the regulations of the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO), after patent authorization, patent owners must comply with relevant laws and regulations and pay the prescribed annual fees on time to maintain the validity of the patent.
Compared with the Chinese patent annual fee system, the South Korean patent annual fee system has significant differences. Therefore, for those who wish to maintain their patents in South Korea, understanding the rules of South Korean patent annual fees and ensuring timely payment is an important step in protecting patent rights. This helps to effectively manage and safeguard the patent rights of patent owners in South Korea, preventing the loss of patent rights due to delayed payment.
This article will introduce the South Korean patent annual fees from the aspects of patent types, protection periods, payment deadlines, and fees.
1. Patent Types and Protection Periods
The South Korean patent system, similar to China's, is divided into three types: invention patents, utility model patents, and design patents.
The protection period for invention patents is 20 years from the date of application; for pesticides or pharmaceuticals, the protection can be extended under certain conditions, up to a maximum of 5 years;
The protection period for utility model patents is 10 years from the date of application; some patents can be extended under certain conditions, up to a maximum of 5 years;
The protection period for design patents is 20 years from the date of application.
2. Payment Deadlines
The payment of South Korean patent annual fees is calculated from the date of authorization. When authorized, a one-time payment of annual fees for the 1st to 3rd year is required. From the 4th year, annual fees must be paid annually. For example, the information for a South Korean invention patent is as follows:
Application date: September 4, 2018
Authorization date: August 2, 2022
Legal effective term: September 4, 2038 (20 years from the date
of application)
4th year annual fee deadline: August 2, 2025
The patent owner should pay the 4th year annual fee before August 2, 2025 to keep the patent alive. Subsequently, annual fees must be paid before August 2 each year to maintain the validity of the patent.
3. Payment Methods and Required Documents
There are three ways to pay patent annual fees in South Korea:
Online payment: Using the electronic application system for online payment or through internet giro transfer. Since South Korea uses a unique online certificate system, this method usually needs to be completed locally in South Korea.
On-site payment: Submitting forms at the office in South Korea, where staff will issue a receipt. Once the receipt is received, the fee can be paid at any bank in South Korea, and the next day will be credited as the payment date.
Mail payment: Filling out a payment form and paying through a South Korean postal money order.
Regardless of the method, all documents must be in Korean, not English. For applicants without a residential or business address in South Korea, a representative with a residential or business address in South Korea must be designated for payment, and a power of attorney must be submitted.
4. Official Fees
The biggest difference between South Korean and Chinese patent annual fees is that South Korean patents are calculated based on the number of claims, which means that the more claims a patent application has, the higher the official fees paid during the maintenance phase of the subsequent annual fees. The specific fee details are as follows:
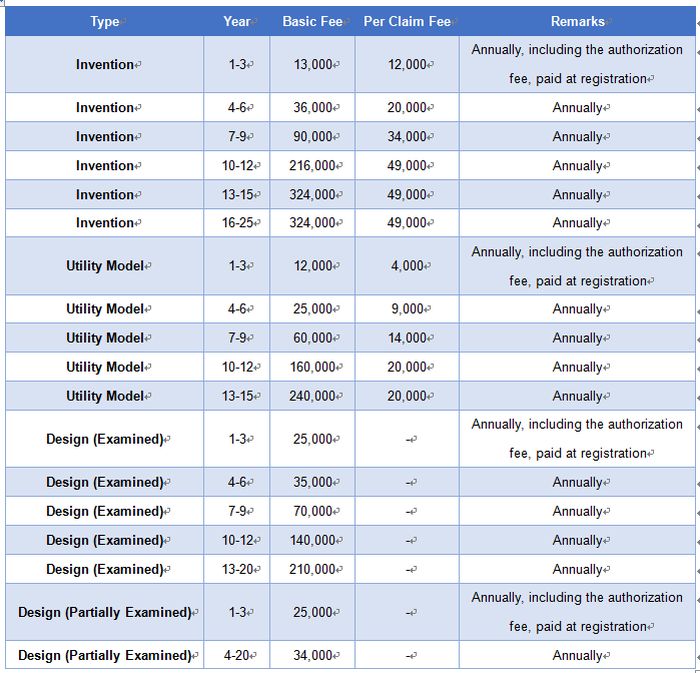
5. Grace Period and Restoration Period
If the annual fee is not paid on time, the patent owner can make up the payment within a 6-month grace period, but a late fee must be paid at the same time. The late fee increases from the first month after the payment deadline, with a maximum of 18% of the annual fee.
If the payment is still not made within the grace period, the patent right will be considered abandoned. Within 3 months from the date when the late fee period expires, restoration can be applied for by paying double the official fee. If the patentee can prove that the failure to pay within the prescribed time limit was due to force majeure, they may apply for restoration within one year after the grace period has expired.
6. Check the legal Status
The legal status and payment information of South Korean patents can be checked on the Korean Intellectual Property Information Service website: https://www.kipo.go.kr

Enter the patent number or application number, and then click on the search button, as shown in the following image:
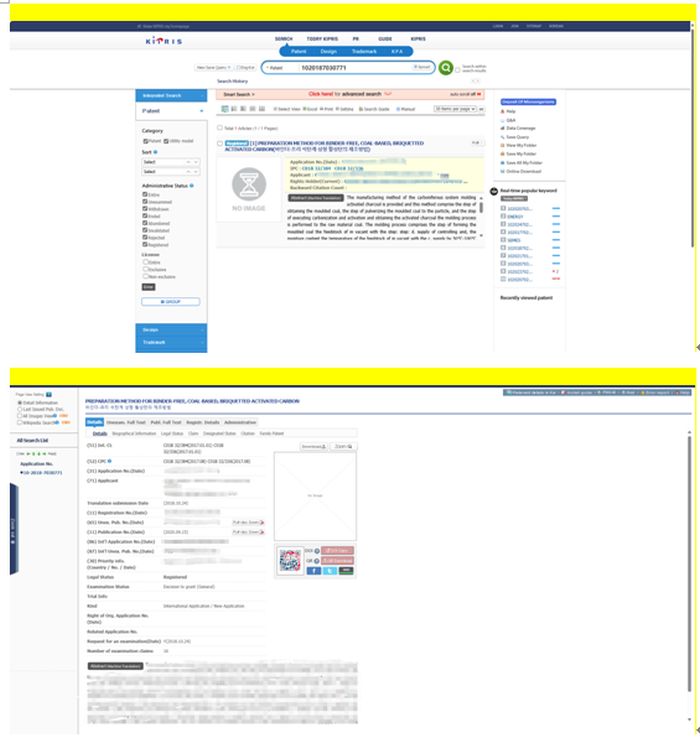
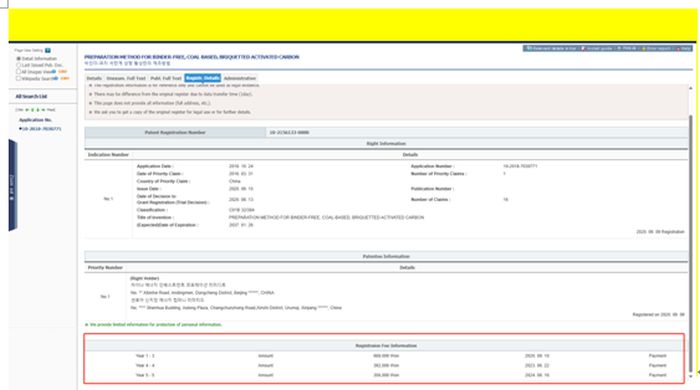
In the search results, click on the patent name to view the legal status, and click on "Registr. Details" to view the payment information, as shown in the following image:
Kangxin provides comprehensive overseas patent annual fee monitoring and payment services. Should you require our assistance, please feel free to reach out to us at annuity@kangxin.com. Our dedicated team is committed to delivering efficient, professional, and hassle-free services, guaranteeing a seamless experience for all your patent annuity needs.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


