Process automation is nothing new. Business leaders have sought
out opportunities to achieve greater operating efficiencies since
the beginning of the industrial revolution. Robots are hardly new
either. For years we've seen them transform the manufacturing
floor through the automation of manual and repetitive tasks.
Now, however, we're on the verge of robots driving
transformation beyond the manufacturing floor to change the
workplace as dramatically as the machines of the industrial
revolution. But this sea of change is not reserved solely for large
companies. Entities of all shapes and sizes will need to understand
the automation capabilities available, and on the horizon, to
enhance efficiencies and remain competitive.
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) essentially takes the robot out
of the human. Most back-office processes involve varying degrees of
routine, manual and repetitive tasks that are low value and
generally uninteresting to the employee. RPA is a software solution
that mimics the activity of a human being but in a much more
efficient, effective and accurate manner.
RPA isn't necessarily a new technology. Innovative
organizations have been deploying RPA over the past several years,
yet, the scale, speed and cost at which RPA is being deployed today
is indeed transformative.
Recent research from PWC estimates that 45% of work activities can
be automated, saving roughly $2 trillion in costs throughout the
global workforce. Additionally, a recent Deloitte study explains
that one robot is said to be able to do the work of two to three
resources and costs anywhere from $5,000 to $15,000. This could
result in ROI as high as 200 percent in the first year alone.
However, besides simply reducing costs, business leaders are
achieving a number of other tangible benefits:
- Transformative Change: Re-engineer core processes while driving functional automation
- Flexibility & Scalability: 24/7 operations with the ability to quickly be deployed to handle increased demand
- New Competencies: Relieving employees of the most onerous tasks, allowing them to refocus on higher-value activities
- Compliance & Controls: Ensuring accuracy and enhancing controls through standardized rules
Also adding to the attractiveness, RPA solutions can be deployed
on a smaller scale in a matter of weeks. Doing so will have a
minimal impact on legacy systems and require little involvement and
continued support from the IT department. Employees in operations
can quickly learn how to configure, deploy and manage robots in
their department.
Given the potential ROI and relative ease of implementation,
companies of all shapes and sizes are gravitating toward RPA. The
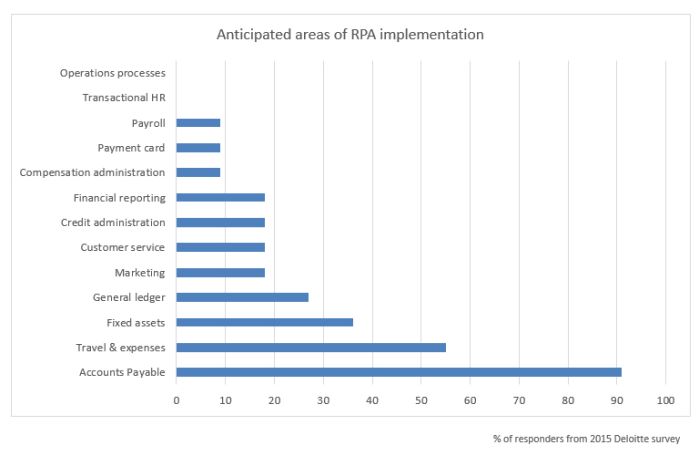
finance and accounting department is a typical starting point,
having a number of repetitive, rules-based transactional processes.
Deploying RPA in this area can help drive down costs and enhance
quality of the finance function. More mature organizations,
however, have applied RPA across other major business processes
with transactional activity, including marketing, customer service
and payroll administration.
Intelligent Automation
While RPA is being deployed today on larger and larger scales,
the next generation of technology is already here. Intelligent
Automation (IA), enabled by cognitive technology, has even more
massive transformational potential as we look toward the next
several years.
IA applications combine advanced cognitive technology, robotic
automation and powerful analytics to deliver more human-like
capabilities — such as the ability to learn, apply judgement,
and recognize images and language. These advanced solutions can
process unstructured commands and sift through massive amounts of
information to discern patterns and relationships, continuously
learning throughout its life. Whereas RPA can replace the arms and
legs of workers, IA has the capability to replace the entire
worker.
It's imperative for businesses to manage growth systematically,
giving adequate attention to scalability of processes and
technologies to guard against creating "silo"
applications. RPA and IA applications offer businesses a solution
to join disjointed organizations, bring order to chaos and drive
efficiency to all-time highs.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

