- within Finance and Banking topic(s)
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
- within Litigation, Mediation & Arbitration, Food, Drugs, Healthcare and Life Sciences topic(s)
As the digital transformation in the financial sector continues to spread rapidly on a global scale, the regulations of Türkiye, the European Union ("EU"), and the United States ("US") play a significant role in shaping this next-generation banking model.
The legal framework for the establishment of digital banks in Türkiye is based on Banking Law No. 5411 ("Law"), while the specific regulations in this area have been established by the Regulation on the Operational Principles of Digital Banks and Service Model Banking ("Regulation"), published in the Official Gazette on December 29, 2021.
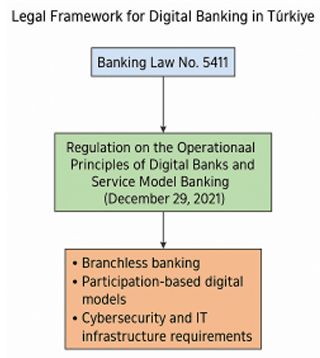
This regulation makes it possible to establish banks operating only through digital channels without opening physical branches, and it also opens the way for the participatory banking model, which adopts the principles of interest free banking, to have a digital structure.
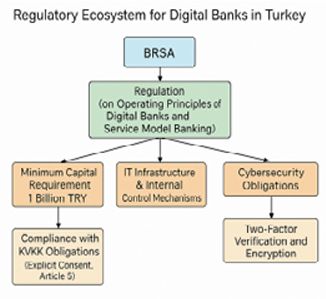
The regulation sets forth comprehensive obligations in various areas such as information system infrastructure, internal control mechanisms, and cybersecurity, including a minimum capital requirement of 1 billion TRY for the establishment of digital banks, and inspections are conducted in this context.
The Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency ("BRSA") ensures the proper monitoring of digital banks' compliance with regulations, thereby guaranteeing that digitalization in the financial sector advances on solid foundations.
The BRSA monitors the compliance of digital banks with the legal framework, carefully examining the adequacy of their technological infrastructure, data security policies, and resilience against cyberattacks. In this regard, regulations such as the Personal Data Protection Law ("PDPL") and the BRSA's Data Security and Cybersecurity Regulation set forth the obligations of digital banks to protect customer data
For example, digital banks must obtain explicit consent from their customers to process and store personal data, in accordance with Article 5 of the PDPL, which outlines the principle of "lawfulness of personal data processing." Additionally, under the Cybersecurity and Advanced Technologies Regulation, digital banks are required to implement security measures such as encryption methods and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure transaction security.
On a global scale, the EU has established operational transparency and data security requirements for digital banking through regulations such as the PSD2 Directive and GDPR. Similarly, in the US, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency ("OCC") introduced the innovative Special Purpose National Bank Charter ("SPNB") model for licensing digital banks, allowing them to operate independently without integrating into the traditional banking system. In both regions, regulators provide a flexible yet effective regulatory environment that balances financial stability and consumer rights, promoting the growth of the sector. In Türkiye, the legal regulations for digital banking are being shaped in line with global developments, providing a solid foundation for digital banks to operate securely and sustainably.
The reason for the preference of the digital method in participatory banking is that the interest-free financial system can be effectively presented to a wider audience through digital platforms. The branchless operation and low cost structure of digital banking enable the rapid and efficient delivery of participatory banking's interest-free products. As a result, digital banks can provide services in line with participatory banking principles more quickly, securely, and accessibly. For example, some digital participatory banks offer participatory accounts based on products with physical backing, such as gold and silver, through their mobile applications or enable real-time digital fund pool management, allowing users to directly direct their savings to interest-free investment instruments. These innovative digital solutions not only enhance the user experience of participatory banking services but also strengthen the alignment of interest free financial principles with the digital age. Therefore, digital banking is preferred as a model that is compatible with participatory banking. One of the key aspects of this model is that the structure of participatory banking activities, which differentiates from traditional banking, facilitates secondary and virtual connection directly with the customer.
In conclusion, while digital banking creates a significant transformation in the global financial system, the regulatory frameworks in regions such as Türkiye, the European Union, and the United States play a crucial role in ensuring that digital banks operate in a secure, transparent, and sustainable manner. In Türkiye, regulations related to digital banking pave the way for the digital participatory banking model, allowing the provision of services to a wide audience through digital platforms in line with the principles of interest-free banking. In the European Union, regulations such as the PSD2 Directive and GDPR set the data security and transparency requirements for digital banks, while in the US, the innovative licensing model introduced by the OCC enables digital banks to operate independently. Both regions strive to maintain a balance between customer security, financial stability, and innovation while regulating digital banking. Türkiye, by closely following these global developments, is taking significant steps to grow digital banking both securely and efficiently. In conclusion, digital banking is transforming the banking sector through the opportunities offered by technology, while safeguarding both consumer rights and financial stability through effective supervision and regulations.
For additional legal details regarding the digital banking sector, please feel free to contact our Banking and Finance team.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.




