- within Finance and Banking topic(s)
- in European Union
- with readers working within the Retail & Leisure industries
- within Finance and Banking topic(s)
- within Employment and HR, Insurance and Real Estate and Construction topic(s)
- in European Union
In October 2024, the Indonesian Government, through the Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan or "OJK"), enacted a new regulation on bullion business activities, namely OJK Regulation No. 17 of 2024 on the Implementation of Bullion Business Activities ("OJK Reg. 17/2024").
The enactment of OJK Reg. 17/2024 is initially mandated under Law No. 4 of 2023 on Development and Strengthening of Financial Sector ("PPSK Law"). A bullion business activity is generally defined as an activity related to Gold business that can be in the form of saving, financing, trading, custody, and/or other activities conducted by financial services providers.
Following the issuance of PPSK Law and OJK Reg. 17/2024, the banking industry saw a rapid rise in bullion business activities. This was marked by the establishment of bullion businesses by two state-owned financial institutions, (i) PT Pegadaian (Persero) ("Pegadaian"), which is collectively owned by PT Bank Republik Indonesia (Persero) Tbk and the Indonesian Government, and (ii) PT Bank Indonesia Syariah Tbk ("BSI").
Pegadaian obtained its bullion business license based on OJK Letter No. S-325/PL.02/2024, which was issued on 23 December 2024. This made Pegadaian the first financial institution to receive a bullion business license from OJK. Then, BSI followed suit. OJK issued a bullion business license to BSI in mid-February 2025.
With regard to the above, we provide this article covering (i) Definition of Bullion Business Activities, (ii) Eligibility and Requirement of Bullion Business Activities, (iii) Classification of Bullion Business Activities, (iv) Phases in Bullion Business Activities, (v) Electronic Bullion Business Activities; and (vi) Sanctions.
Definition of Bullion Business Activities: According to OJK Reg. 17/2024, bullion business activities are activities related to gold business, carried out by financial services institutions such as banks, capital markets, insurance, pension funds, venture capital, micro-financial institutions, financing institutions, and other financial services institutions. In this case, gold is referred to precious metal in bullion/slab form and does not constitute as currency with the Aurum content of 99.9%.
Eligibility and Requirements of Bullion Business Activities: As mentioned above, bullion business activities must be conducted by financial services institutions. However, not all types of financial services institutions are eligible to engage in such activities. OJK Reg. 17/2024 only permits the institutions that are primarily engaged in lending or financing activities, excluding community economic banks (bank perekonomian rakyat), sharia economic community banks (bank perekonomian rakyat syariah), and microfinance institutions.
Moreover, OJK Reg. 17/2024 also requires:
- the financial services institution to meet the minimum capital requirement of IDR 14 trillion. This requirement applies to conventional banks, sharia units of conventional banks, and non-conventional banks having bullion business activities;
- the institution to meet the minimum solvability level of composite 2 or "Healthy" based on the recent assessment of OJK; and
- the institution to establish a specialized working unit dedicated to providing bullion business activities and services as supervised by a director who is specifically responsible for the bullion business.
Additionally, an eligible financial services institution must obtain a business license issued by OJK by submitting the required documents, including (i) data of the head of the bullion business unit, (ii) business plan, (iii) evidence of operational readiness to exercise bullion business activities, (iv) evidence of risk management readiness, and (v) evidence on access to global market networks.
Classification of Bullion Business Activities: OJK Reg. 17/2024 provides specific provisions on the scope of activities that can be conducted under the bullion business framework. These activities may be carried out under both Sharia (Islamic) principles and conventional (non-Sharia) principles.
In general, bullion business activities are categorized into five classifications with its own specific requirements, which are summarized as follows:
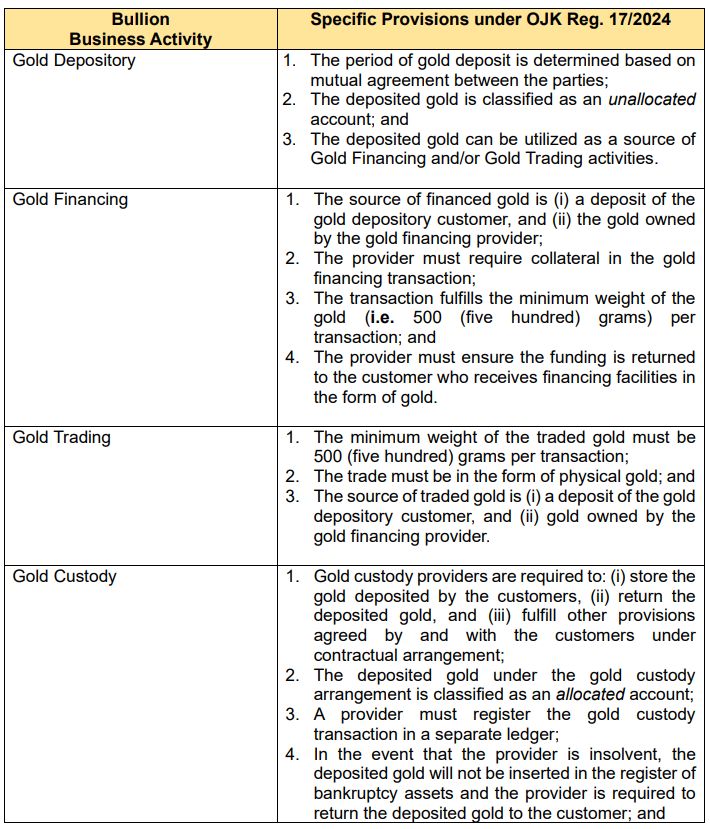
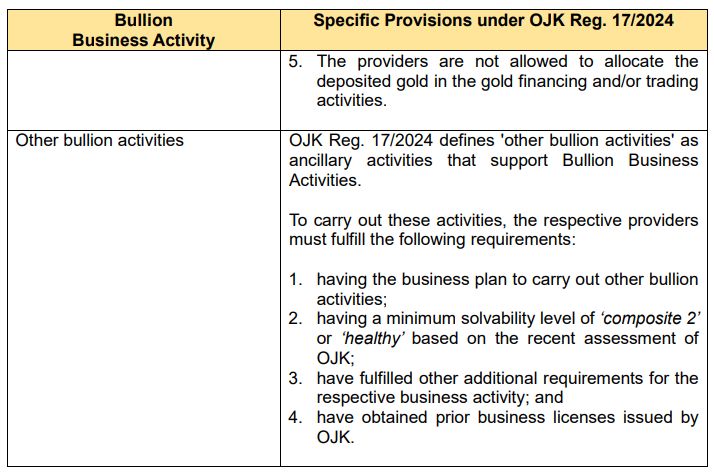
Phases in Bullion Business Activities: Considering these activities are new, OJK Regulation 17/2024 require the Bullion Business Activities to be conducted in three consecutive phases: the first, the second, and the third phases. Each phase outlines both permitted and restricted business activities, as follows:
- First Phase: During the first phase, the
bullion business providers are only allowed to conduct (i) the
management of gold deposit, (ii) the distribution of gold
financing, (iii) the gold trading, and/or (v) the gold custody with
the provision that the respective gold must be from the unallocated
account and can be utilized up to the maximum 70% (Article 28
(1) of OJK Reg. 17/2024).
Please note that in particular, the conventional banks are prohibited from carrying out gold trading activity during the first phase.
- Second Phase: After the first phase, the
bullion business providers are only permitted to the same
activities as those in the first phase, with the maximum
utilization of gold of up to 80%.
- Third Phase: In the final, third phase of bullion business activities, the providers are permitted to conduct the four activities mentioned earlier, along with additional "other activities." The maximum utilization of gold increases up to 90%.
Electronic Bullion Business Activities:
Based on OJK Reg.17/2024, bullion business activities may be carried out electronically with certain requirements, among others: the reliability and security of the electronic system including the cyber security, ensuring the availability of physical trading of the gold, and establishing the management risk of information technology.
Moreover, electronic bullion business activities must be registered and licensed as the Electronic System Operators at the Minister of Communications and Digital Affairs, based on Regulation of the Minister of Communication and Informatics No. 5 of 2020 concerning Implementation of Electronic System Operator for Private Scope as amended by Regulation No.10 of 2022.
Sanction: OJK Reg. 17/2024 also stipulates various administrative sanctions for violations in bullion business activities. The sanctions vary from written warnings to administrative fines and/or the revocation of bullion business licenses. The administrative fines under OJK Reg. 17/2024 are set at IDR 100 million.
For instance, these administrative sanctions may be imposed for violations such as: (a) failure to fulfill the obligations of a bullion business provider, (b) conducting bullion business activities without adhering to financial accounting standards, (c) non-fulfillment of the minimum required transacted gold weight, and others.
Concluding Remarks: The introduction of the bullion business activities under PPSK Law and OJK Reg. 17/2024 represents a significant milestone in the development of Indonesia's financial industry especially the banking system. OJK Reg. 17/2024 establishes a regulatory framework for bullion banking activities, outlining key requirements and operational guidelines for the financial service companies including banks.
Given the substantial potential of the bullion business in Indonesia, this regulatory framework provides new opportunities for business actors to engage in bullion-related financial services electronically and/or otherwise. To ensure compliance and sustainability, prospective bullion business providers must conduct thorough legal analysis. This includes assessing whether the proposed business institution and activities meets all regulatory requirements including the licensing, financial reporting standards, transaction thresholds, and risk management obligations under OJK Reg. 17/2024.
By adhering to these regulatory provisions, business actors can mitigate legal risks, enhance market credibility, and contribute to the growth of Indonesia's bullion industry within a wellregulated financial ecosystem.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.



