- within Food, Drugs, Healthcare and Life Sciences topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
- within Food, Drugs, Healthcare, Life Sciences, Accounting and Audit, Government and Public Sector topic(s)
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit and Media & Information industries
China's medical device market has been rapidly developing in recent years. The average annual growth rate has been estimated at approximately 15%, much higher than the international growth rate of 5%.
Currently, China accounts for around 20% of the global medical device market. As an emerging market, it is expected to maintain its upward trajectory over the next five to 10 years, driven by key drivers such as:
- An ageing population resulting in a growing prevalence of diseases
- Disposable income growth leading to more healthcare spending per capita
- Technology advancements, including AI, IoT, big data and analytics, advanced imaging technologies and 3D printing
Overview and trends of the Chinese medical device market
Medical device industry development overview
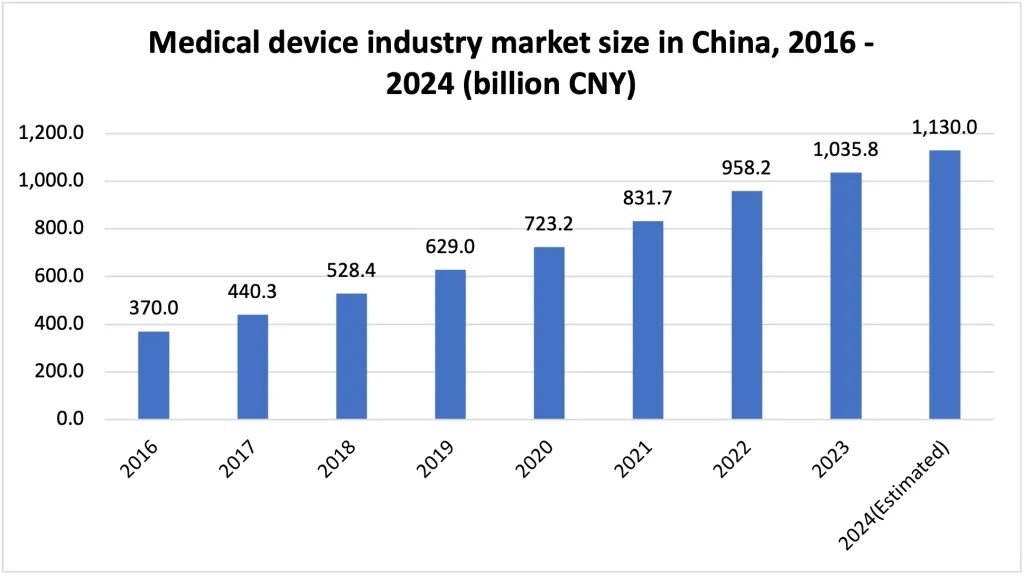
China is the world's second-largest healthcare market after the United States. The country's medical device industry has experienced remarkable growth, with a total revenue estimated at CNY 1,036 billion in 2024–nearly double the CNY 629 reported in 2019.
The industry saw a significant surge in demand for various medical devices, such as medical masks, nucleic acid test kits and ECMO (Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation) machines during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. This demand pushed revenue to over EUR 111 billion that year, accounting for around 20% of the global medical device market.
With an annual growth rate of 18.2% since 2015, the industry has consistently outpaced GDP growth in recent years. However, according to the latest China's Foreign Trade Situation Report issued by the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China (MOFCOM), medical devices with an estimated value of USD 49.4 billion were imported to China in 2023, which witnessed a decrease rate of 1.55% compared with 2022.
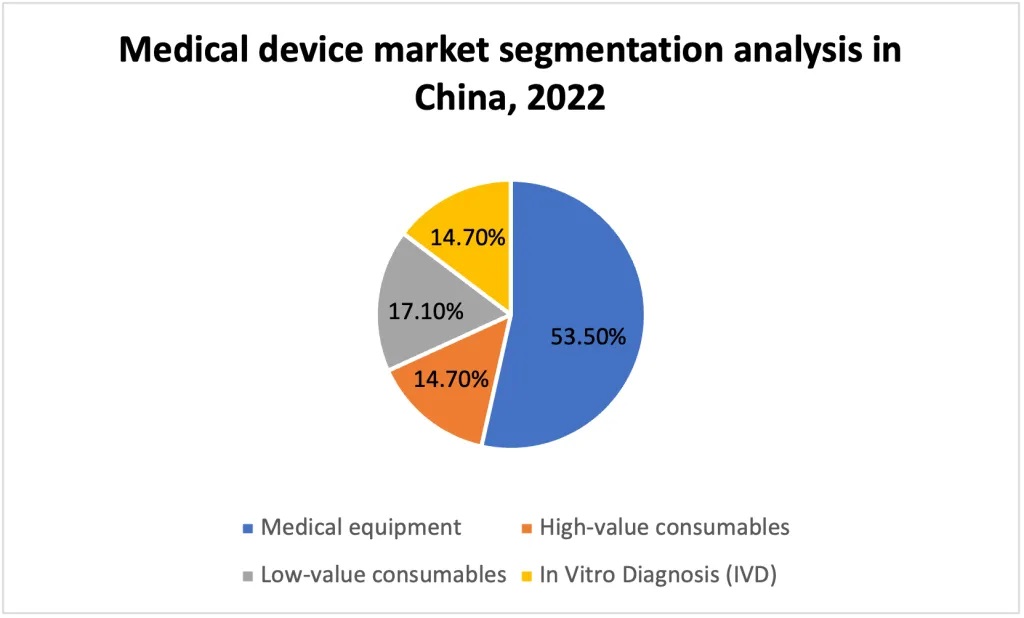
According to the definition from China's Medical Device Research Institute, the medical device market can be divided into four segments:
- Medical equipment
- High-value consumables
- Low-value consumables
- In Vitro Diagnosis (IVD)
In 2022, medical equipment dominated China's medical device market, making up 53.5% of its total size. The remaining market was distributed more evenly, with in-vitro diagnostics (IVD) accounting for 14.7%, high-value consumables for 17.1% and low-value consumables also at 14.7%.
From 2017 to 2023, the number of medical device enterprises and products in China has steadily grown each year. By the end of 2023, China had 36,675 medical device manufacturing enterprises, marking an 8.54% increase compared to 2022.
Medical equipment in China is classified into three categories based on risk: Class I (least risky), Class II and Class III (most risky). The number of enterprises producing these devices is as follows:
- Class I: 25,817 enterprises, reflecting a 9.68% year-on-year increase
- Class II: 17,187 enterprises, with an 8.50% growth
- Class III: 2,670 enterprises, showing a 15.48% increase
Producing medical equipment requires a production license and product registration, and operating it requires operational qualification. Class I registration is relatively simple, while Class II and III devices undergo a more complex and time-consuming process, often involving local testing and clinical trials before registration.
Factors driving the medical device industry
Policy factors
Centralised procurement
Centralised procurement, also known as Volume-based Procurement (VBP), aims to lower prices through large-volume procurement. This is done to realise the so-called volume-for-price strategy, aiming to enhance the accessibility and affordability of universal healthcare in China.
In July 2019, the General Office of the State Council issued the "Governance of High-value Medical Supplies Reform Program" (State Office issued [2019] No. 37), which explores the classification of high-value medical supplies centralised procurement by the principles of quantity procurement and quantity-price linkage. It demonstrates the government's ambition to improve the accessibility and affordability of universal healthcare coverage in China. This will not only lead to changes in profit structure and lower profit margins of the medical device industry but also bring opportunities for localisation and concentration.
Several regional VBP programmes have been launched, primarily focusing on vascular interventions, orthopaedic implants and ophthalmic materials. Since 2019, provinces such as Yunnan, Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shandong have implemented centralised procurement. In Anhui, the average price reduction for joint reconstruction procurement reached 81%, with spine implant products seeing reductions of more than 50% and some items reduced by up to 95%. In Jiangsu, the average price reduction for artificial hip prostheses was 47%. Among the winning bidders, each province's centralised procurement typically included one to three imported enterprises, while over 10 selected enterprises were local.
In November 2020, the Chinese government introduced its first centralised purchasing programme for high-value medical commodities. Coronary stents, as the first batch of national centralised procurement products, saw an average price reduction of 93%. In 2021, the centralised procurement of orthopaedic joints, including artificial hip and knee joints, resulted in an average price reduction of 82%. In 2022, the national procurement of orthopaedic spine products led to an average price reduction of 84%.
Unique Identification of Medical Devices (UDI)
The Unique Identification of Medical Devices (UDI for short), the ID card of medical devices, is the unique code identifying the licence holder, the model and the packaging information of the medical device. The UDI system plays an active role in achieving transparency in the whole life cycle of medical devices and improving their traceability.
In 2019, the National Health Commission issued the "Medical Device Unique Identification System Pilot Work Program", which marked the official start of China's UDI initiative. As part of the country's ongoing medical and health reform, 69 varieties in nine categories, including osteosynthesis implants, spinal implants and joint replacement implants, were selected as the first batch of medical device unique identification pilot products. Additionally, 108 hospitals and 23 orthopaedic companies, including Wego, AK-Medical and Double, were selected as the first trial companies.
Since the launch of the pilot programme, both the framework of the unique identification system and the unique identification data platform have been established. The next step of the government's plan is to explore the application and integration of UDI in the fields of medical, health insurance and supervision.
Society factors
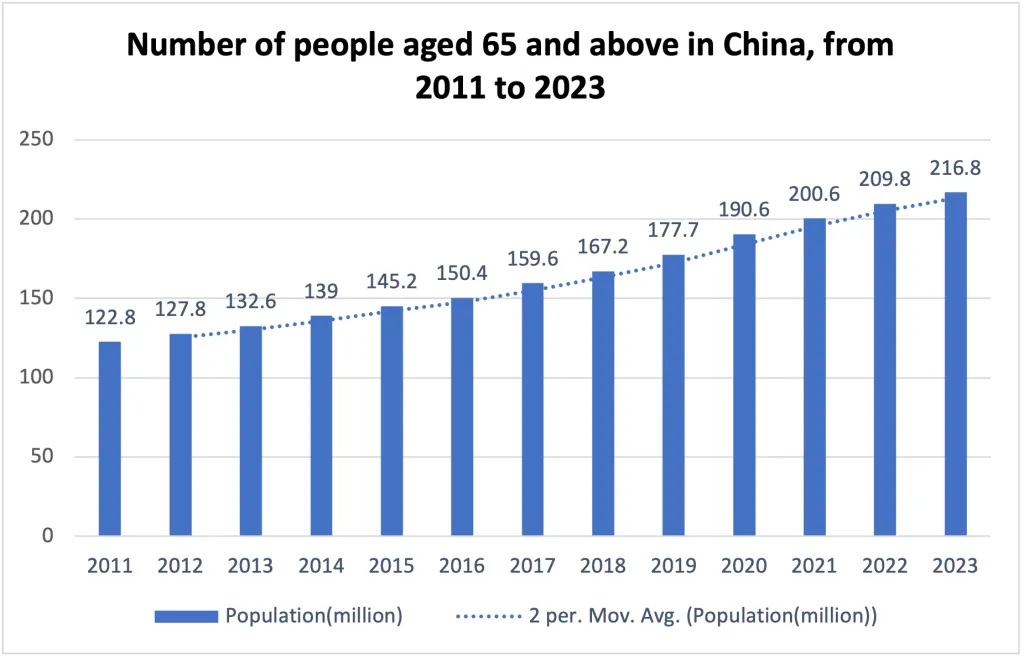
According to the National Bureau of Statistics, the number of people over 65 has continuously increased from 2011 to 2023, reaching 216.8 million. This accounts for 15.4% of China's total population in 2023. This demographic is predicted to reach 20% in 2030 and 30% by 2050.
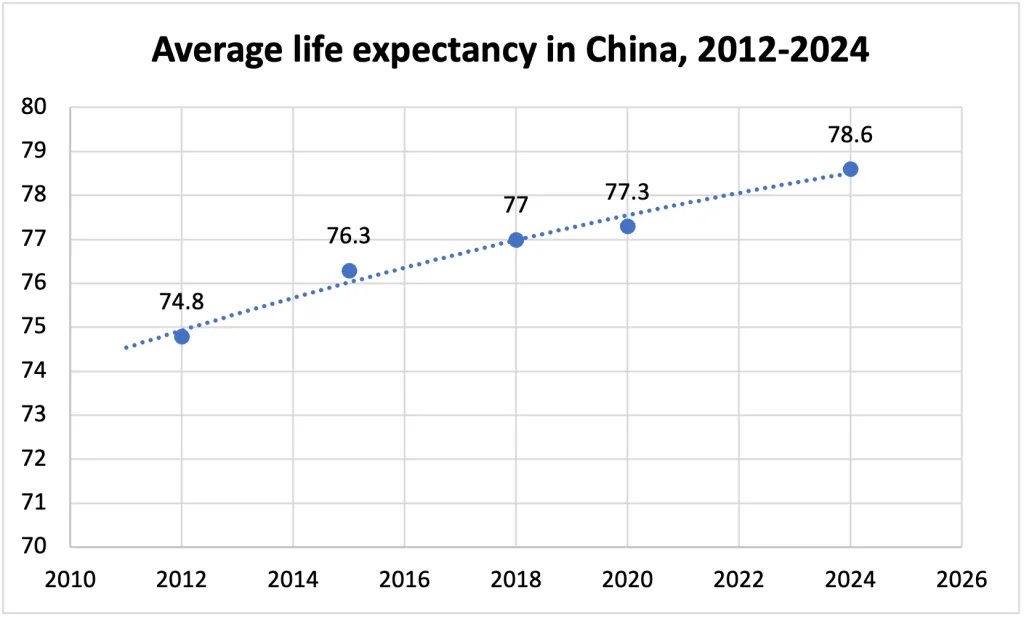
According to the statistics from the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, the average life expectancy of Chinese residents has increased from 74.8 years in 2012 to 78.6 years in 2024. As life expectancy increases, so does the demand for advanced medical devices to manage chronic diseases and age-related health issues. This drives growth and innovation in the medical device industry to meet these evolving needs.
As China's population ages, the demand for medical devices designed for elderly care has surged. This includes devices for monitoring chronic conditions, mobility aids, orthopaedic equipment and telemedicine tools. Elderly individuals are particularly vulnerable to conditions like osteoporosis, which leads to low bone density and increases the risk of fractures. Nearly 50% of patients with bone-related orthopaedic diseases, such as osteoarthritis, vertebral compression fractures and osteoporosis, are elderly. As the elderly population continues to grow, the number of orthopaedic patients in China is expected to rise. Given the strong correlation between age and the incidence of orthopaedic diseases, there is a significant demand for orthopaedic implant devices for the elderly.
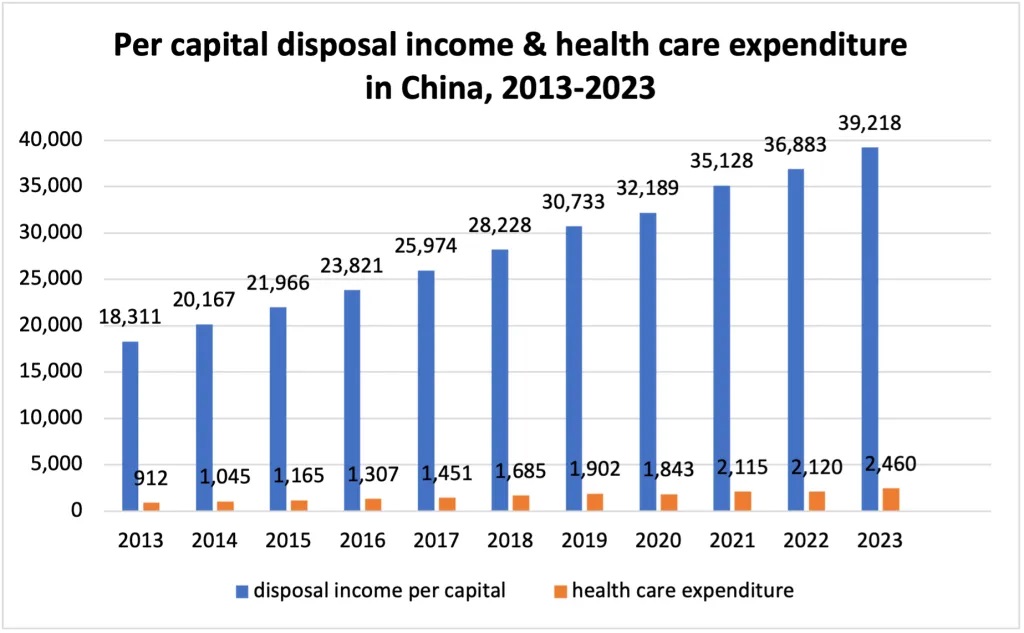
As China's economy grows, both per capita income and health care consumption expenditure continue to increase. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, China's per capita disposable income nearly doubled over the past decade, rising from CNY 18,311 in 2013 to CNY 39,218 in 2023.
Per capita healthcare expenditure also increased from CNY 912 in 2013 to CNY 2,460 in 2023. This indicates a growing willingness among Chinese citizens to invest in medical treatment and health care. The increase in disposable income and healthcare spending is an important driver of growth in the medical device industry.
Technology advancements
Several technological advancements have driven the development of the Chinese medical device industry:
Artificial intelligence
AI is being used to enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalise treatment plans and improve patient monitoring. AI-powered tools also help with demand forecasting and inventory management.
5G technology
The integration of 5G technology enables faster and more reliable data transmission, which is crucial for telemedicine and remote monitoring devices. This helps provide real-time healthcare services, especially in rural and underserved areas.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices allow for continuous health monitoring and data collection, which can be used to track patient health metrics in real-time. This technology is particularly useful for managing chronic diseases and elderly care.
Robotics
Advances in medical robotics are improving surgical precision and reducing recovery times. Robotic systems are used for minimally invasive surgeries, rehabilitation and even assisting elderly patients with daily activities.
Big data and analytics
Big data and analytics help make informed decisions by analysing large volumes of health data. This can lead to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery.
Advanced imaging technologies
Innovations in imaging technologies, such as multimodal imaging and magnetic resonance (MR) monitoring, are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic procedures.
3D printing
3D printing is being used to create customised medical devices and implants, which can be tailored to the specific needs of patients. This technology is also speeding up the prototyping and production processes.
Conclusion
China's medical device market is experiencing robust growth, driven by an ageing population, rising disposable incomes and significant technological advancements. The market's rapid expansion, with an average annual growth rate of 15%, highlights its potential to continue outpacing global growth rates. Key regions such as the Bohai Rim, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta and Central China are pivotal in this development, supported by local government incentives and industrial parks like Zhongguancun Medical Device Park in Beijing. As China solidifies its position as the world's second-largest healthcare market, the medical device industry is poised for sustained growth and innovation in the coming years.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

