- within Corporate/Commercial Law topic(s)
- in European Union
- with readers working within the Insurance industries
- in European Union
In the second of a series of articles on the industrial automation sector1, we take a deeper dive into the industrial automation market and its sub-segments and provide you with a summary of our industrial automation market database.
Hot on the heels of this article, we will be issuing a review of the industrial automation M&A market and why we believe the sector is going to be a hotbed for M&A activity over the next decade.
MARKET GROWTH EXPECTED TO ACCELERATE THROUGH TO 2030
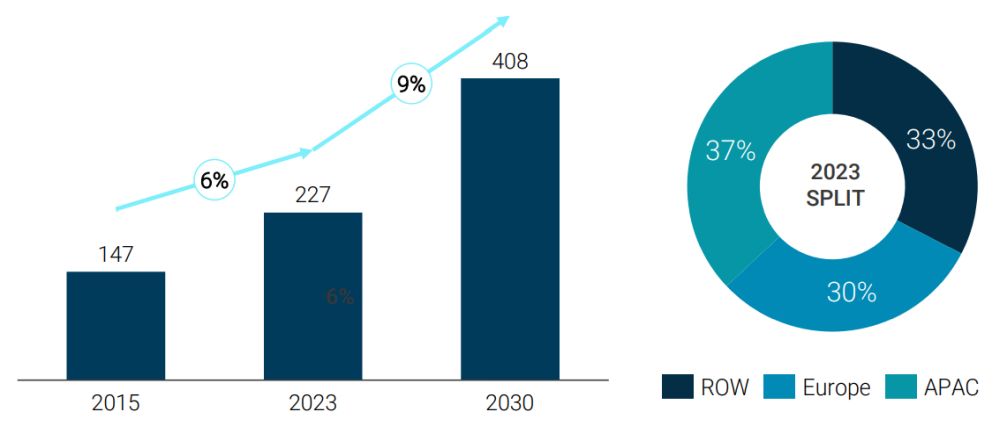
The industrial automation market is on a significant growth trajectory. The outlook through to the end of the decade looks very strong, with all regional markets expected to grow close to 10% CAGR by 2030 and the overall market size to surpass $400 billion (see figure 1). The industry is benefiting from several megatrends and tailwinds, with continued technological innovations driving growth in adoption of digitization and AI, and the continued need for efficient manufacturing processes in a demand-driven, labor-constrained environment. While challenges such as high initial investments and skill shortages exist, the opportunities presented by emerging technologies and increasing demand for automation and personalization across various industries are substantial. The focus on safety, sustainability, and smart manufacturing is expected to shape the future of the sector.
FIGURE 1: MARKET SIZE AND REGIONAL BREAKDOWN (HISTORIC AND FORECAST; $BN)
The overall market growth trend is also evident across the industry's three core subsectors, including Process Automation
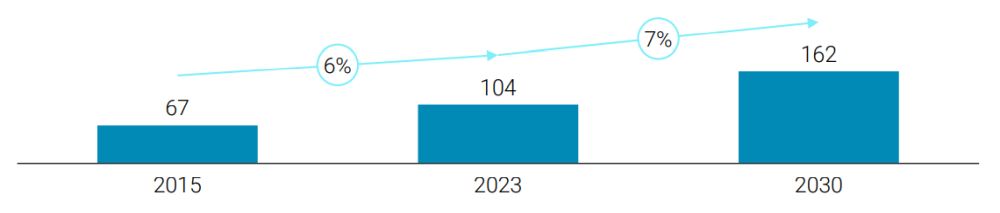
The process automation industry, which uses technology and control systems to automate specific workflows in the overall manufacturing process, is expected to continue on the growth trajectory it has experienced since 2015, growing at 7% CAGR to the end of the decade (see figure 2). This growth continues to be underpinned by (i) greater adoption of machine learning to enhance productivity, optimize processes, improve quality, and drive cost reduction; (ii) predictive maintenance to improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and anticipate and react to maintenance needs; and (iii) embracing cloud computing to improve data collection, monitoring, and processing capabilities to aid real-time decision-making.
A classic example of a company embracing automation and digital transformation is BASF, the global specialty chemicals player. BASF has made a number of strategic investments in digital infrastructure to modernize its operations, including the deployment of IoT sensors, advanced analytical tools and cloud-based platforms to collect and analyze data in real time. In 2023, it expanded its collaboration with Microsoft to leverage the power of cloud computing in its R&D activities and also announced the launch of its Digital Lab, which leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to optimize chemical processes.
FIGURE 2: PROCESS AUTOMATION – MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH (HISTORIC AND FORECAST; $BN)
EXAMPLE END MARKETS
Factory Automation: expected to double CAGR from 5% to 2023 to 10% by 2030
The factory automation industry, which uses control systems and technology to automate machinery and processes in a manufacturing environment, is expected to double its CAGR from 5% (from 2015 to 2023) to 10% from 2023 to 2030, with the market reaching close to $200 billion by the end of the decade (see figure 3). This acceleration in growth stems from a mix of (i) technological advancements, particularly incorporation of robotics and AI in specific manufacturing tasks; (ii) the continued need to drive efficiencies and maintain margins in an economically-pressured environment with rising labor costs and labor shortages in developed economies, particularly as developed countries continue to 'reshore' supply chains; and (iii) evolving market demands as manufacturers seek higher efficiency and productivity (in both an energy-efficient and sustainable manner) whilst maximizing flexibility, quality, and precision to meet the rising demands of consumers.
Together, these factors are fueling innovation and investment as manufacturers seek more efficient and adaptable production methods. An example of an automotive manufacturer at the forefront of embracing innovation and automation in its manufacturing process is Tesla, the global automotive and clean energy company. The business acquired a German automation company in January 2017, which develops automated manufacturing systems for batteries and fuel cells, with the sole purpose of manufacturing automation products to be used by the wider Tesla group to ultimately increase production throughput and volume, and lower costs. Since then, Tesla has set up automationdriven gigafactories across the globe as it looks to scale up vehicle production.
FIGURE 3: FACTORY AUTOMATION – MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH (HISTORIC AND FORECAST; $BN)

EXAMPLE END MARKETS

Further acceleration in Warehouse Automation expected
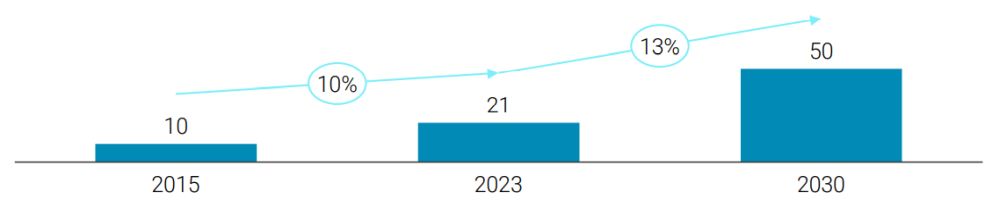
The warehouse automation industry, which implements technology and systems to streamline warehouse workflows, including storage, retrieval, and inventory management processes, is the smallest segment out of the three core segments and is expected to continue to grow at a fast pace, with annual growth of 13% expected to 2030 (see figure 4). This area of the overall industry is set to benefit from (i) technological advancements, particularly the advances in robotics and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) supporting the automation of picking/ sorting/transporting items and ultimately driving cost reduction; (ii) continued growth in e-commerce trade and the desire (and expectation to some extent) for "extra fast" order fulfillment; (iii) greater demand for flexibility and scalability in seasonal industries (e.g. retail); and (iv) growth of analytics and its role in smart warehousing solutions to optimize inventory management, predict demand, and enhance operational efficiency.
These factors are pushing companies to adopt automation technologies that enable them to run leaner, faster, and more efficient warehousing operations. Examples include Walmart (which has been heavily investing in warehouse automation to handle the surge in online shopping, and is working with companies like Symbotic to implement AI-powered robots in its distribution centers), Amazon (with the development of Titan, a robot designed to handle larger, bulkier items in fulfillment centers, which is part of its broader robotics strategy, where over 750,000 robots are deployed across their facilities globally) and IKEA (which, in 2023, started deploying AGVs in its logistics network to improve efficiency and reduce the time it takes to fulfill online orders).
FIGURE 4: WAREHOUSE AUTOMATION – MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH (HISTORIC AND FORECAST; $BN)
EXAMPLE END MARKETS

STRONG TAILWINDS CONTINUE TO SUPPORT PERFORMANCE OF PUBLICLY TRADED AUTOMATION COMPANIES
It is no surprise that these favorable megatrends have supported the strong performance of publicly traded automation companies. As seen in figure 5, on a rebased basis as at Jan-19, our basket of public automation players split by subsector has seen strong share price increases. System integrators and process automation players have seen ~170% improvement in share price whilst discrete factory and warehouse automation players and software companies have seen ~110% improvement, all outperforming the MSCI World Industrials index. Notable outperformers in the process automation segment are Indutrade (a Sweden-based company specialized in high-tech products and solutions that streamline customers' systems and processes) and Ingersoll Rand (a U.S. multinational that manufactures flow control and industrial products). Both have been very acquisitive and benefitted from strong growth across their core end markets. Similarly, large multifaceted automation players like Schneider Electric and ABB have continued to ride the wave of growth across core segments and developed valuable partnerships with software providers as they continue to scale up as large system integrators and look to provide enterprise-wide solutions.
FIGURE 5: REBASED SHARE PRICE PERFORMANCE BY SUB SECTOR FROM JAN-19 TO OCT-24

To view the full article, click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


