- within Food, Drugs, Healthcare and Life Sciences topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Property industries
- within Strategy and Environment topic(s)
Foreword
This report is the result of extensive research into the value being created by artificial intelligence (AI) within the healthcare sector. It is designed to provide actionable insights for leaders at every stage of their AI journey, from those deploying their first pilots to healthcare organizations seeking to scale enterprise-wide AI initiatives.
Artificial intelligence holds tremendous promise for the healthcare sector, offering powerful solutions to some of its most pressing challenges, from rising patient demand and persistent workforce shortages to growing clinical and administrative backlogs.
The research finds that while healthcare organizations are beginning to demonstrate advanced capabilities in their use of AI, many continue to struggle with the challenge of operationalizing use cases and scaling beyond pilots and proofs of concept. A range of barriers continue to impede progress. Fragmented implementations, difficulties in justifying the return on AI investments, and the need for deep cultural transformation — particularly in terms of workforce trust, training and engagement — remain common hurdles. Persistent issues such as data silos, lack of interoperability between systems, and the absence of clear, comprehensive AI regulatory frameworks further complicate adoption.
Where meaningful progress has been achieved, it has been the result of a deliberate strategy. Successful adopters have ensured use cases are closely linked to core value streams such as care delivery, diagnostics, and patient flow. They have embedded AI into everyday workflows rather than treating it as a separate innovation stream, building trust by involving clinicians early and often in the design, testing and refinement of AI tools.
As healthcare organizations embark on transformation, technology and AI should serve as a catalyst. Organizations should:
- Formulate a clear AI strategy, with the aim of improving patient outcomes, workforce experiences, population health, health equity and reducing costs.
- Create sustainable technology and data infrastructure by modernizing legacy systems and investing in secure, interoperable platforms.
- Build trust through transparent AI practices, ethical governance, addressing concerns about bias and invest in robust cybersecurity.
- Foster a culture that integrates AI to uplift the potential of the healthcare workforce and communities they serve.
Without a strategy focused on a clear value proposition, and a structured approach and governance, navigating the challenges and maximizing the impact of AI for healthcare organizations can be difficult. Our aim with this publication is to provide actionable insights on how to develop this strategy, approach and governance to create better outcomes for healthcare.
AI has the potential to fundamentally reshape healthcare — not by replacing the human touch, but by enhancing it. By integrating AI across different clinical and community settings and different operational streams, we can improve outcomes, ease the burden on healthcare workers, and create more resilient, patient-centered health systems. Dr. Anna van Poucke — Global Head of Healthcare KPMG International

Introduction
Healthcare organizations are increasingly experimenting with AI across a range of use cases — from clinical decision support and imaging diagnostics to administrative automation and virtual assistants. However, many are finding it difficult to translate these experiments into meaningful and sustained value.
The Intelligent healthcare publication offers a roadmap for healthcare leaders to responsibly leverage trustworthy AI, helping to ensure it delivers measurable value while supporting sustainable, patient-centric healthcare systems. This report provides C-suite executives and decision-makers with actionable insights to navigate AI adoption complexities. In this report, we:
- Share insights on current AI strategy, investment, and implementation in healthcare, based on KPMG research and interviews with technology leaders globally.
- Explore the traits of intelligent healthcare organizations and strategies for their development.
- Provide a blueprint for intelligent healthcare organizations that outlines key, high-level capabilities for AI-powered, customer-centric healthcare.
The healthcare sector faces distinct adoption challenges
Healthcare presents a uniquely complex environment for AI adoption. Concerns around clinical safety, ethical use, patient data protection, and regulatory compliance create significant friction. Many organizations struggle to modernize legacy infrastructure, overcome data silos, and establish the governance frameworks necessary to scale AI responsibly. The highly fragmented nature of healthcare systems — often characterized by decentralized decision-making, workforce shortages and uneven digital maturity — further complicates progress.
Healthcare is a different territory because you are dealing with people's lives. It's a difficult area where AI adoption will be a little bit slow compared to the other organizations. Chief Technology Officer — Australia
A new generation of AI agents could reshape care delivery
The emergence of intelligent AI agents has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. These agents can act as digital co-pilots, helping clinicians interpret diagnostic results, personalize treatment plans, and manage patient pathways in real time. They can also serve as virtual care navigators, supporting patients with proactive health management, appointment scheduling, and medication adherence. In administrative functions, AI agents are poised to streamline tasks such as claims processing, medical coding, prior authorization, and patient triage — unlocking significant productivity gains and improving staff experience.
A framework for realizing AI's value in healthcare
To move beyond experimentation and deliver impact at scale, healthcare organizations need a clear, structured approach to AI adoption. In this report, we introduce the three phases of AI value — a framework designed to help clinical providers maximize value by aligning AI investments to patient and operational outcomes, prioritize scalable use cases, and prepare for the next generation of AI technologies. Through this lens, we explore how leading healthcare systems are moving from pilots to enterprise-wide transformation — and how others can follow.
Three phases of AI value creation in healthcare
- Enabling workforces and building AI foundations
Establishing the data, governance, technology architecture and skills necessary for responsible AI adoption.
- Embedding AI across the enterprise
Scaling AI solutions across clinical decision support, operational efficiency and patient engagement to deliver greater value.
- Evolving operating models and ecosystems
Shifting toward AI-powered, adaptive healthcare models that foster collaboration across primary care, provider networks, healthcare systems, and broader care ecosystems that include public health, social, mental health care and community-based organizations.
Researchfindings
Healthcare organizations are preparing to further integrate or explore new opportunities with AI, but in an environment where patient safety is critical, they are proceeding with caution, taking an evidence-driven approach to help ensure value-driven AI implementation that safeguards trust with the population and workforces.
Current state
Evolution versus revolution
Due to the inherently human-centric nature of certain healthcare functions, AI's impact thus far has been more evolutionary than revolutionary. Rather than driving radical transformation, its role is primarily focused on streamlining processes and specific use cases. The top five applications are:
- Generative AI (71 percent)
- Speech recognition (70 percent)
- Agentic AI (68 percent)
- Machine learning (66 percent)
- Machine learning (66 percent)
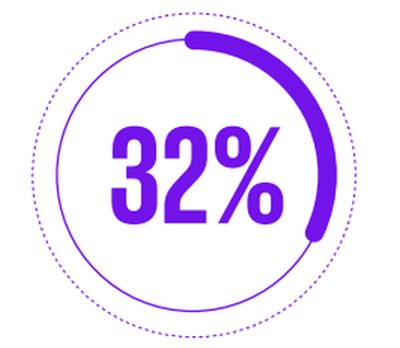
say AI represents greater than 10 percent of their organization's global technology budget
AI investments and impact
Healthcare organizations are starting to allocate larger portions of their IT budgets to AI-related technologies. Our research reveals almost one-third (32 percent) of healthcare leaders say AI represents greater than 10 percent of their organization's global technology budget. But when it comes to making further major investments, there is caution. A little over three-quarters (76 percent) of healthcare respondents agree that it is best to wait to see how the AI tech landscape evolves before making significant investments.
Over the past 15 years, many sectors of the economy have been radically reshaped by digital technologies. Yet the NHS is in the foothills of digital transformation. The last decade was a missed opportunity to prepare the NHS for the future and to embrace the technologies that would enable a shift in the model from 'diagnose and treat' to 'predict and prevent' — a shift I called for...more than 15 years ago. 1 The Rt Hon. Professor the Lord Darzi of Denham, OM KBE FRS FMedSci HonFREng Independent Investigation of the National Health Service in England, September 2024
Growing realization, that organizational change management is required
Fifty-eight percent of healthcare leaders report that AI is either fully embedded in or is a core component of their operations; the remaining respondents are exploring or in the early stages of adopting AI. Many institutions recognize that AI will necessitate shifts in their operational models, requiring a strategic rethinking of workflows and patient care pathways to fully integrate AI.
Success demands a new level of collaboration
Only 44 percent note that their operating model consistently enables cross-functional collaboration. Our interviewees observed that clinical healthcare has traditionally been highly siloed, largely due to the depth of expertise required by specialist clinicians. Each medical specialty — whether cardiology, oncology, radiology or neurology — has developed its own highly specialized knowledge, diagnostic protocols, and treatment methodologies.
This specialization has led to fragmented care pathways, where different specialists manage specific aspects of a patient's condition without seamless coordination.
Additionally, healthcare IT systems have reinforced these silos, with department-specific electronic health record (EHR) systems, imaging databases, and workflow tools often lacking interoperability. AI has the potential to bridge these gaps by enabling more connected, intelligent systems that support integrated care pathways, improving coordination, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
Data quality and management is critical
Data privacy and security have emerged as critical priorities for organizations to proceed in the embedding of AI in their workflows. Organizations have learned that robust governance frameworks are needed to help ensure patient data protection, compliance with evolving regulations, and trust-building in AI-driven processes.
Exploration continues even though long-term ROI is uncertain
Sixty-nine percent of respondents state that they are under pressure from shareholders to demonstrate return on investment (ROI) from their AI investments. Respondents recognize that ROI is not always immediate; while it improves efficiency, its direct financial impact is still being assessed. Despite this, 85 percent are pursuing projects where the ROI is not yet certain.
Next-generation AI is being adopted in healthcare
The healthcare industry already has a high usage of AI agents (68 percent) and is preparing for the next new evolution of AI: autonomous agents (agentic). In fact, 84 percent of respondents feel comfortable with AI making end-to-end autonomous decisions for specific processes in their organization.
Agentic AI holds considerable promise across healthcare operations, from direct patient care to support and back-office processes. It goes beyond simple task automation by proactively identifying clinical and operational issues, recommending solutions and acting in collaboration with human teams.
By integrating seamlessly with electronic health records (EHRs) and hospital management systems, agentic AI can enhance care delivery at the bedside, streamline patient-facing support services, and help optimize administrative workflows behind the scenes. Unlike traditional AI models that rely on predefined inputs and outputs, agentic AI can interpret multimodal patient data, collaborate dynamically with medical teams, and initiate actions based on real-time clinical insights.
For example, AI agents could continuously analyze vital signs, imaging, and lab results to detect early deterioration in high-risk patients, alert clinicians proactively, and even suggest interventions. While reducing cognitive overload for healthcare professionals, agentic AI allows them to focus on complex decision-making and direct patient care, ultimately improving both outcomes and operational efficiency.
However, to implement agentic AI successfully requires modernizing the data infrastructure to support real-time, multimodal inputs; embedding robust governance to help ensure safety, transparency and accountability; and codesigning solutions with clinicians to help ensure AI agents enhance, rather than disrupt, clinical workflows.
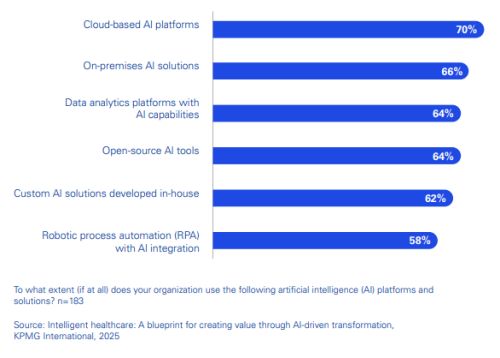
Figure 1: Significant or extensive use of AI in healthcare
To view the full article, click here.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

