- within Intellectual Property topic(s)
- within Technology topic(s)
- in North America
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit and Technology industries
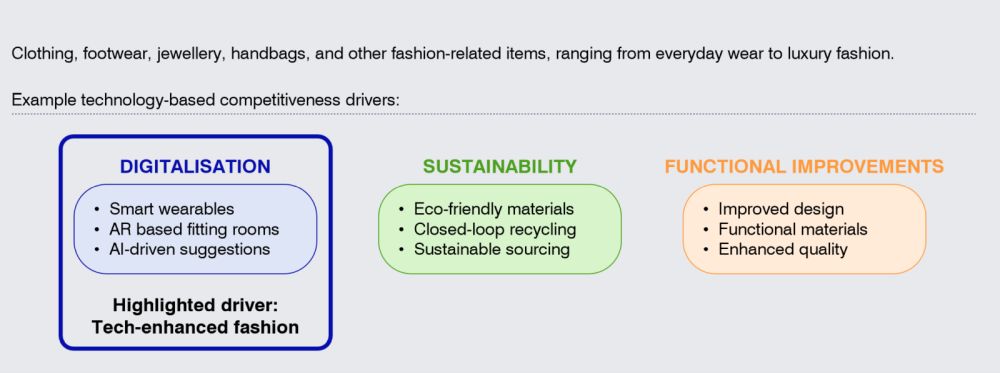
In the Apparel & Accessories (A&A) segment, sustainability is driving the shift toward recycled materials, circular fashion models, and low-waste manufacturing. Brands like Adidas and Patagonia are investing in closed-loop systems that extend product lifespans and reduce environmental impact.
Functional improvement increasingly means scientific and technological innovation in advanced textiles, with moisture-wicking, temperature-regulating, and antimicrobial fabrics enhancing both comfort and durability, as seen in Nike and Lululemon's high-functional apparel.
Digitalisation is perhaps the most transformative trend in the A&A segment. Digital is fundamentally transforming how fashion is designed, produced, and experienced, making technology an integral part of both functionality and style. At the forefront are smart fabrics and wearables, embedding sensors and conductive materials into garments to monitor health, and provide real-time data insights. Artificial Intelligence is transforming personalisation, enabling brands to design and recommend apparel tailored to individual needs, creating hyper-targeted experiences. Meanwhile, Augmented Reality is redefining retail by offering virtual try-ons, reducing the reliance on physical stores while cutting return rates. These technologies not only enhance convenience and functionality but also position fashion as a dynamic, tech-enabled industry, bridging utility with consumer lifestyle aspirations.
In the race to redefine fashion through digital, patents can be a strategic business tool to secure market leadership, drive superior margins, fuel ecosystem innovation, and unlock new opportunities.
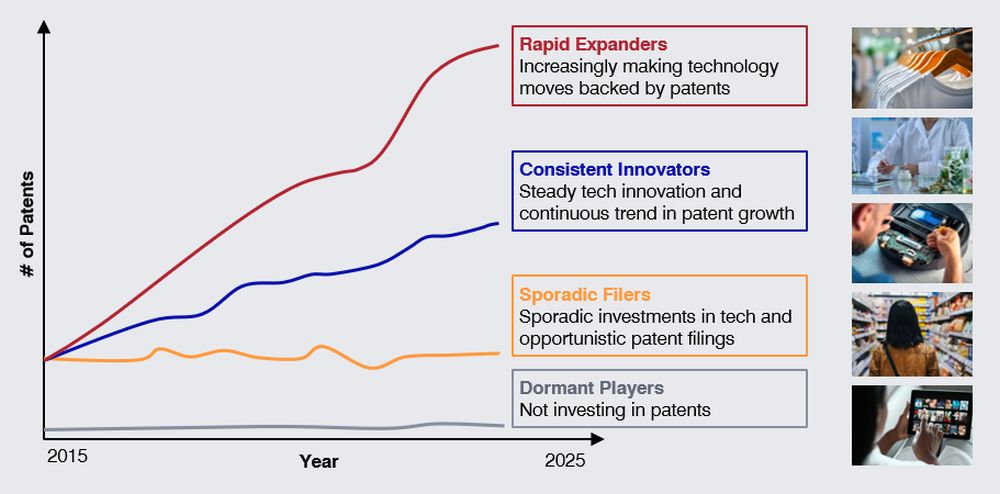
In the A&A patent landscape notable "'Rapid Expanders'" like Nike, Asics and Under Armour are driving innovation in tech-enhanced fashion, with patent filings on smart textiles, biometric-integrated wearables, and AI-driven customisation. At the same time, "Consistent Innovators", including Adidas, Puma and LVMH maintain steady patent growth, using technology to support their go-to-market strategies and competitive positioning. In A&A, there are also many "Dormant Players". Choosing to remain dormant may be a deliberate strategic decision, reflecting priorities focused on other competitive strengths, but may also carry risks as their competitors innovate in tech-enhanced fashion.
Apparel & Accessories
Examples of how Apparel & Accessories companies are leveraging patented digital technologies to win market leadership and secure premium price points.
Nike strategically leverages digital patents to protect market share
Nike has developed a digital-focused patent portfolio, reinforcing its innovation-driven brand identity. To defend its competitive advantage, Nike actively enforces these patents, exemplified by its ongoing patent infringement lawsuit against Lululemon Athletica concerning the Mirror Home Gym and related apps. Nike asserts that Lululemon infringed six patents covering technologies enabling users to target exertion levels, digitally compete, and track performance. Such proactive patent enforcement strengthens Nike's market position and aims to deter imitators.
Perfect Corp. strengthens market position through acquisition of patented AR technologies
Perfect Corp., a leading provider of AI/AR solutions for fashion, offers realistic virtual try-ons and personalised recommendations. To sustain competitiveness, Perfect Corp. has actively secured several fashion-tech patents. In January 2025, the company further strengthened its market position by acquiring Wannaby Inc., known for innovative AR and virtual try-on solutions. Integrating Wannaby's patented technologies expands Perfect Corp.'s portfolio and could enhance its market differentiation. Additionally, Perfect Corp.'s strategic patenting prior to the acquisition may have positioned it favourably in negotiations.
Marks & Spencer boosts revenue potential with AI-driven personalisation patents
Marks & Spencer (M&S) has strategically enhanced its personalisation capabilities by acquiring the IP assets of AI-based fashion marketplace Thread, including proprietary algorithms and source code. Integrating Thread's patented AI enables M&S to offer tailored styling recommendations based on customer preferences and body shapes. Leveraging these recommendation engines could significantly enhance customer experience, potentially creating competitive advantages, expanding market share, and driving revenue growth.
Adidas defends its market position through active patent enforcement
Adidas has built a robust digital patent portfolio covering mobile apps, data tracking, and connected footwear. Actively protecting these innovations, Adidas sued Nike in June 2022, alleging infringement of nine patents related to GPS tracking, personalised training, and smart shoe technology, specifically targeting Nike's mobile apps (Run Club, Training Club, SNKRS) and Adapt self-lacing shoes. The companies settled privately in August 2022. Earlier, Adidas litigated against Under Armour in 2014 over fitness-tracking patents related to MapMyFitness, reaching a licensing agreement in 2016. These cases illustrate Adidas's active approach to protecting its innovations in digital fitness and smart footwear, aiming to block competitors and secure market advantages.
In the digital transformation of Apparel & Accessories, technology is playing an increasingly important role alongside design and branding in shaping competitiveness. Patents play an important role in securing exclusivity for innovation-driven differentiation and enabling companies to commercialise new technologies. Moreover, patents allow brands to expand into new technology-driven digital business models, reinforcing the intersection of fashion, functionality, and digital advancement.
Conclusion
From tech-enhanced fashion to zero-waste food production, technology is reshaping innovation and competition in the consumer goods sector. As technology-based competitiveness becomes increasingly important, companies must make deliberate, business-driven decisions about how they approach patents.
- For “Rapid Expanders”, challenges include to avoid over-filing or filing in areas that don't add value, and to ensure patents are actively used to support business goals – not left as inactive cost items on the P&L.
- “Consistent Innovators” must regularly recalibrate their efforts to stay aligned with evolving strategic priorities and market dynamics. Like the Expanders, they must also ensure that their patent portfolios are actively leveraged, rather than quietly accumulating as overhead cost.
- “Sporadic Filers” may need to reassess whether an opportunistic approach is sufficient in the long term. If investment increases, systematically selecting the right areas is key to making patents count and avoiding unnecessary cost.
- “Dormant Players” must consider whether they can afford the risk of having no patent position in a tech-driven market, and whether they have the innovation capabilities needed to start building meaningful portfolios.
Independent of profile, companies need a business-driven and proactive approach to patents, both to stay ahead and avoid being caught off guard. This means being able to clearly answer:
- Why are we (or aren't we) investing in patents? What is the intended impact on revenue, cost, and risk?
- Are we organised for proactive and impactful IP management? Do we have the right stakeholder interfaces?
- Do we have the capabilities and skillsets needed to execute effectively?
Without clear answers to these questions, patent departments in consumer goods companies may struggle to compellingly articulate the value of patents and their contribution to technology-based competitiveness. This increases the likelihood of being seen primarily as cost centres, making it difficult to secure appropriate investment. Ultimately, companies may face misalignment between their business and technology ambitions, falling short in protecting and capitalising on them.
Patent filing profiles in consumer goods segments
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
[View Source]


