- within Consumer Protection topic(s)
- in European Union
- with readers working within the Healthcare industries
- within Consumer Protection, Environment and Tax topic(s)
1. Introduction
A customer complaint is "an expression of dissatisfaction on a consumer's behalf to the responsible party."1 It can also be described in a constructive sense as a report from a consumer providing feedback on the quality or a problem with a product or service.
Customers complain when a business does not deliver on its commitment and does not meet customer expectations in terms of the business's product or services. As a practical matter, the most important aspect of every business is the client or the customer and it is therefore vital for a business organisation to accommodate the peculiar needs and reasonable demands of customers.
Customer complaints could alternatively be viewed as:
"The gap between what business promises in terms of the product or services and what customers get. It is a mismatch between how customers perceive the brand and where they fail to get the desired customer service experience.
There could be different types of customer complaints. It could be related to a) improper communication, b) internal processes, or c) poor quality of service. Realizing that a complaint is an opportunity makes it easier to turn conflict into positive change. Customer complaints can tell you how to resolve issues – if you listen to them carefully". 2
The service quality model gap is a framework that professionals use to analyze customer satisfaction and to identify areas for improvement. Most companies, regardless of whether they are sales or service-focused, involve some component of customer service.

(diagram of Customer Gap)3
2. The Customer gap
This is the space or difference between what customers expect from the company's product/service and the actual service they get.
In a simpler form, the customer gap happens when customers do not understand what the product has to offer or misinterpret the service quality. Every company should conduct a gap analysis from time to time, identify gaps, and take steps to close them. Customer gap entails the following:-
- Customer expectations: these are beliefs and thoughts about products or services before accessing and testing them. Generally, expectations are usually set by marketing strategies on the website, media, advertisement agencies, etc.
- Customer perceptions: are the opinions customers form after interacting with the company's product and understanding its core value.
The diagram below captures the service quality gap model describing the relationship between the customer and the company in a bit more detail.4
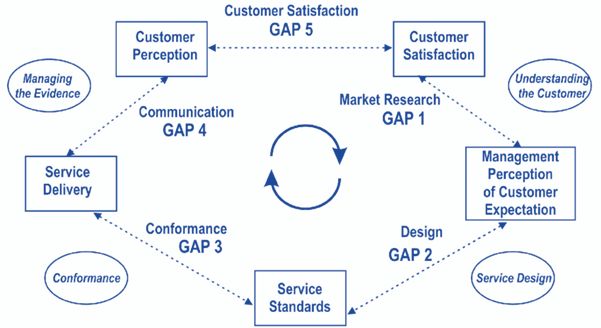
[Service Quality Model Gap]5
The Service Quality Model Gap consists of the following:-
- Gap between management perception and customer
expectation
This gap is the distinction between the customer's expectations and the company's perception of users' needs. It occurs due to the following reasons:
- lack of proper market research;
- Insufficient communication between the company and the clients.
- Gap between management perception and quality service
specification
This gap examines the difference between management's perception of quality service and the steps it takes to provide the required service. However, organizations sometimes understand what their customers expect but lack knowledge of how the relevant products or services will meet up with the standards and expectations the customer desires. - Gap between quality service specification and service
delivery
This gap measures the difference between the quality of service organisations expect from their workers in favour of the customer, how customers are being treated, and how their complaints are being handled. Sometimes customers may receive poor-quality service and complain to the management, and this in turn helps the management to analyse the customer's attitude to products and whether they find them satisfactory or not. This also helps organisations to identify areas for improvement and to provide quality customer services. - Gap between service delivery and external
communication
- The communication gap happens when advertisement of products attracts lots of new customers and make them excited. But the company does not deliver the quality service as advertised and fails to meet customer expectations. The direct result of this is customer dissatisfaction, negative reviews, and customer aversion towards the company's product or services.
- Secondly, the delivery gap represents poor customer service quality or lack of proper guidance on how a product should be used e.g. electronics. This occurs when customer support/success specialists lack adequate knowledge, motivation, or proper niche qualifications to assist customers and resolve their requests.
- Gap between expected service and service received: This gap explains the difference between the quality of service customers expect and their perception of the company's products and services. This occurs when the company's believe that they offered a value or good services to the client but in reality the services do not meet the expectation of the customer.
Although the primary goal and objective of every organisation is to generate profit, the purpose of a business is to offer value in the form of products and/or services to customers, who pay for the value with cash or equivalents.
Customers are bound to complain when they are not satisfied with the services or products they paid for. Some clients get angry and frustrated, and justifiably so, due to the poor quality of products or services received.
When a client brings unsatisfactory feedback on products and services that were paid for, it is the responsibility of the seller/service provider to apologise for rendering poor services and for providing poor quality products. Adopting a receptive attitude and taking correctional measures will assist the product/service provider to retain dissatisfied customers, and effecting necessary adjustments would assist in maintaining the good image of the organisation. Some effective expressions that organisations can use in such situations are: "We are sorry for the poor services you received, and we appreciate you bringing this issue to our notice. We promise to make all necessary amendments" or "Thank you for bringing this to our attention. We are sorry you had a bad experience."
Every organisation should have customer service professionals who are responsible for addressing customer needs and ensuring they are satisfied with the organisation's output. Customer service professionals must acquire and exhibit qualities like active listening, empathy, problem-solving, and effective communication skills.
3. Factors that lead to client satisfaction
- Price: Pricing is important because it defines the value that products are worth. It is the tangible price point that makes customers know whether it is worth their time and investment. Price is an important factor influencing consumer buying behavior. Most of the time, consumers place emphasis on the price of the product rather than on any perceived value at the time of purchase. Thus, a change in price influences demand, sales volume, and market share.
- Quality: Product quality refers to how well a product satisfies customer needs, serves its purpose, and meets industry standards. When evaluating product quality, businesses consider several key factors, including whether a product solves a problem, works efficiently, or suits customers' purposes.
- Choice: Varieties of similar products or services from other providers or companies in a fairly competitive market introduces efficiencies in product quality and qualitative services.
- Convenience: Clients prefer getting services in a seamless and cost-effective manner and at their convenience.
4. Procedures for Handling Customer Complaints
There are organisations that have customer care departments. This department deals with client complaints and how complaints can be rectified in order to bring satisfaction to the customer in the long run.
The following are the procedures for handling customers' complaints
- Listening to customer complaints and identifying the problem: A customer complaint highlights a problem, whether the problem is with the organisation's product, services, employees, or internal processes, and by receiving these complaints directly from customers, management can investigate and improve to prevent further complaints in the future.
- Get all the facts and details about the clients'
complaints: It is very important to get all facts and details
why customers are complaining of services or products received from
a company. Once customers are not deriving the necessary
satisfaction from company's branded products or services they
look for alternatives or substitutes. Addressing customer
complaints urgently and deligently will ensure client/customer
retention and continued pratronage.
Customer complaints should be documented for future references as this helps the organisation to avoid repetition of same errors on products and services delivered to clients. It also helps to increase the ability of a regulator or a court of law to establish intention, protect the organisation from charges and claims for defective products and related defamatory action, and gives the organisation a moral advantage. - Follow up on the problem: It is very important to contact customers to find out if they are satisfied with how their complaint was handled. Inform them on what the company is doing to avoid the problem in the future by training staff to follow the proper procedure when handling complaints and how issues can be resolved as quickly as possible.
- Quick Resolution: Aim to resolve the complaint or problem quickly by deliberating options for solving the problem with the staff in charge of the service or product. If there is undue delay, the problem might tend to escalate.
- Reliability: Keep to the promises made to the client for solving the problem and fulfill as promised.
- Customer Feedback: Encourage customers to provide feedback and complaints so as to get the company informed when a problem arises and the privilege to resolve it.
- Appreciation: Appreciate the customer for the opportunity to correct the error in the service rendered or product supplied.
5. Conclusion
Every business has to be customer-centric to sustain itself in any competitive sector. Investing in customer support services will help businesses to understand their complaints and improve their services and experience.
Important attention must always be paid to customer complaints. Intelligent organisations recognize the importance of customer complaints and should always seize this opportunity to improve on their products and services. However, complaints are unavoidable and no matter how qualitative your services or how good your products are, no business can satisfy its customers at all times.
The best way to ensure business growth is to know what customer complaints are and to treat them as highly valuable feedback to instill in the customer service strategy to improve an organisation's brand experience.
Footnotes
1. See, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consumer_complaint accessed on 25th November 2022.
2. See, https://www.revechat.com/blog/importance-customer-complaints-business/ accessed on 4th November 2022.
3. See, https://userpilot.com/blog/customer-service-gap/ accessed on 29th November 2022.
4. See https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figure-2-6-Service-Quality-Gap-Model_fig4_279961983 accessed on 29th November 2022.
5. Available at https://www.slideserve.com/alda/service-quality-powerpoint-ppt-presentation accessed on 29th November 2022.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
[View Source]

