- within Corporate/Commercial Law topic(s)
In brief
- On 2 April 2025, the US announced enhanced tariffs on all countries with whom it trades.
- These US reciprocal tariffs have now been put on a 90-day pause for all countries except China and a few others.
- Impact on India may be in terms of four interlinked effects: (1) export reduction, (2) global slowdown, (3) falling crude prices, and (4) excess capacities.
Key features of US reciprocal tariffs
On 02 April 2025, the US imposed enhanced tariffs across all countries with whom it conducts international trade, leading to significant disturbances in global trade. The announced US reciprocal tariffs, which were to be effective from 09 April 2025, were based on the objective of reducing US imports from a country to achieve trade balance with that country. This strategy can be called as 'Import-substituting reindustrialization'. The formula for calculating reciprocal tariffs is given below.
![]()
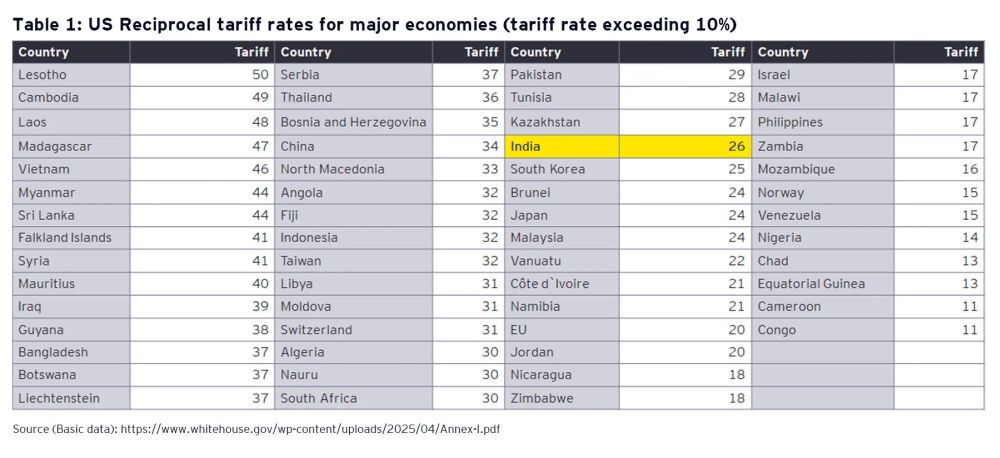
The discounted reciprocal tariff rates were to be added to the commodity specific tariff rates that may be prevailing prior to this announcement. Fifty-seven countries were assigned reciprocal tariffs ranging from 11% to 50%1 (Table 1) while a 10% floor rate was applicable on the remaining countries. These rates were to be levied on all commodities except for those where a tariff rate had already been announced2 or is likely to be announced.
On 9 April 2025, the US temporarily suspended this measure, applying only a 10% rate for a period of 90 days on imports from all countries, except China and a few others. In China's case, the US reciprocal tariff was progressively increased from 34% (2 April 2025) to 245%3 (15 April 2025). On 11 April 2025, a list of 20 commodities such as computers, smartphones and other electronic devices were exempted from reciprocal tariffs, including those from China.
Is a global growth slowdown inevitable?
The IMF (April 2025) has projected a significant slowdown in global growth with global growth falling from 3.3% in 2024 to 2.8% in 2025, a downward revision of 0.5% points vis-à-vis its January 2025 forecast, owing to the effect of the new trade measures.
The US reciprocal tariffs and retaliatory tariffs imposed by countries like China are likely to lead to a decline in global trade volumes as well as global output, which may result in a slowdown in global demand. In the 90-days transitional period also, the volume of imports into the US is expected to fall and import prices are likely to increase due to limitations in accelerating the pace of domestic production.
Another impact would be improvement in US's trade balance and a fall in holdings of US Treasuries by non-US countries. As the price of US bonds go down, their yields would increase, making issue of additional US debt highly costly. Further, even if investment moves back into the US, it may be difficult to get the requisite labor at a competitive rate.
India's growth prospects: Channels of impact
The impact of ongoing tariff wars and related uncertainties on India's GDP growth prospects can be seen in terms of four interlinked effects.
Export reducing effect
India's exports to the US are expected to fall due to the levy of higher tariffs. As the incomes of other countries reduce due to the global slowdown, it would adversely affect India's non-US exports also. India's demand for imports may also fall since many imports are undertaken for processing and re-exporting. However, given the low contribution of net exports to India's GDP growth in recent years, the overall export reducing effect in FY26 may be limited.
As demand for imports from the US goes down, particularly in those countries where retaliatory actions are undertaken, the demand for US dollar as a reserve currency may also fall, leading to an appreciation of the INR, resulting in some negative impact on India's exports.
Global slowdown effect
To counter the impact of global trade slowdown and fall in growth, countries would need to stimulate their economies. However, many countries with high government debt and fiscal deficit, may not be able to launch any significant fiscal stimulus. In contrast, India may have the scope of launching a monetary stimulus supplemented by a suitable fiscal stimulus.
Excess production capacities impact
Various exporters to the US may face excess production capacities and seek destinations to 'dump' their output. India has to, therefore, design suitable country-specific anti-dumping duties to safeguard itself.
Falling crude prices effect
The impact of falling crude prices on India is likely to be both growth-supportive and inflation-dampening. Global crude prices fell from a level of nearly US$75/bbl beginning April to about US$65/bbl by the middle of April 2025 (Chart 1).
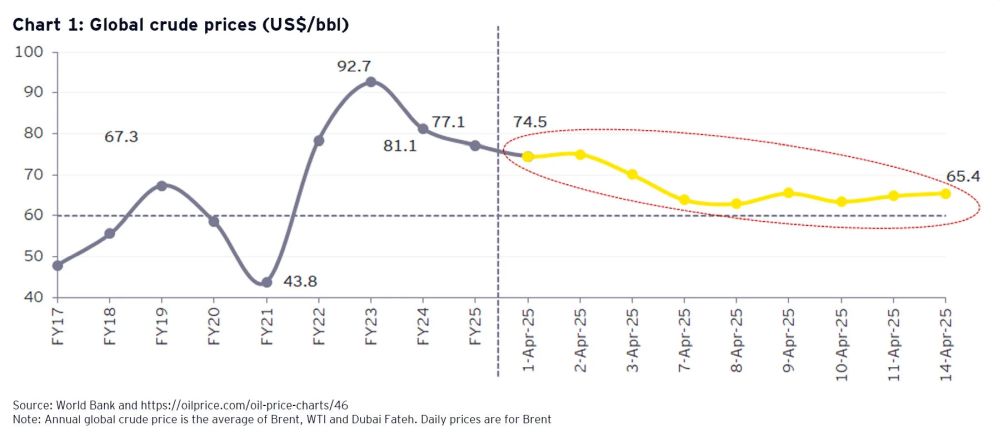
We expect that in FY26, global crude prices may be in the US$60-65/bbl range, compared to US$77/bbl, on average, in FY25.
Role of crude price fluctuations in India's economic growth
As per the RBI4, a fall of US$10/bbl in crude prices, compared to a benchmark of US$75/bbl, leads to an increase in India's GDP growth by about 30 basis points and a decline in CPI inflation by about 40 basis points. Further, being a large importer of crude, as production costs go down, India's exports may become relatively more competitive.
Calibrating India's response
India should calibrate its response considering the levy of US reciprocal tariff rates, the retaliatory tariffs by some countries and other developments including an extended period of uncertainty.
As a short-term measure, India may switch supply sources of crude oil from other countries to the US which would not involve any increase in its current account imbalance. We estimate that an increase of US$25 billion of imports from the US would lead to a fall in India's reciprocal tariff rate to 11.8%, close to the 10% floor. Monthly data indicates that India has already undertaken action in this direction in January and February 2025. It may be best for India to work out a comprehensive trade agreement with the US. As per available information, India has already signed with the US a terms of reference agreement, for the first phase of the proposed bilateral trade agreement, which is likely to be finalized by September-October 2025.
Key highlights of the US tariff impact
On 2 April 2025, which the US administration refers to as the 'Liberation Day,' the US has introduced reciprocal tariffs targeting nearly all trading partners, marking a significant shift in trade policy to prioritize domestic industries and rebalance global trade. We present the key highlights.
The significance of fiscal and monetary policies in India's growth strategy
India's fiscal and monetary policies should be calibrated so as to ensure its GDP growth in FY26 remains close to the potential of 6.5%. These may be supported by lower crude prices. With respect to monetary policy, the rate reduction cycle may be continued until the policy rate comes down to 5%–5.25%. On the fiscal side, while continuing the directional change of reducing the fiscal deficit to GDP ratio towards its sustainable level, its composition may continue to shift in favor of capital expenditure which is associated with higher multipliers.
From a medium- to long-term perspective, to attract higher investments, India could accelerate its land and labour reforms, invest in human resources, skill building and AI and GenAI, select additional sectors for PLI support and minimize regulatory overload. India could also continue to work towards more free trade agreements with the UK, the EU and other select countries in its neighbourhood.
To view the full article click here.
Footnotes
1. Annex I to Executive Order 14257 dated 02 April 2025; https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2025/04/07/2025-06063/regulating-imports-with-a-reciprocal-tariff-to-rectify-trade-practices-that-contribute-to-large-and
2. These include steel and aluminum, and automobile and auto parts etc.
4. For details see In-focus section of September 2022 issue of EY Economy Watch
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


