- in South America
- with readers working within the Construction & Engineering industries
- with Senior Company Executives, HR and Finance and Tax Executives
The Canada Border Services Agency ("CBSA") has released an updated list of its verification priorities as of July 2024 (the "July Update"). The July Update identifies the CBSA's current priority industries and products, which are being targeted for trade compliance verifications and other compliance exercises conducted by the CBSA. The July Update includes details on the CBSA's compliance tools and methods that it has been rolling out since 2022 and continues to roll out, particularly in light of the upcoming full implementation of the CBSA's assessment revenue management system ("CARM").
Updated List of Compliance and Verification Priorities
Every six months, the CBSA issues its priorities for its verification exercises as well as its broader compliance programs so importers know what their current focus areas are. These priorities are summarized below.
Compliance Priorities
The CBSA identifies several compliance priorities in the July Update. These include:
- tariff rate quota compliance and appropriate classification of frozen desserts containing 5% of dairy products;
- tariff classification of gloves;
- proper use of GST exemption codes and scrutiny of vaping products that are subject to excise duties and taxes;
- import origin verifications under both the Canada-European Union Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement and the Canada-United Kingdom Trade Continuity Agreement; and
- verification of licensees importing supply managed goods under the Duties Relief Program.
Verification Priorities
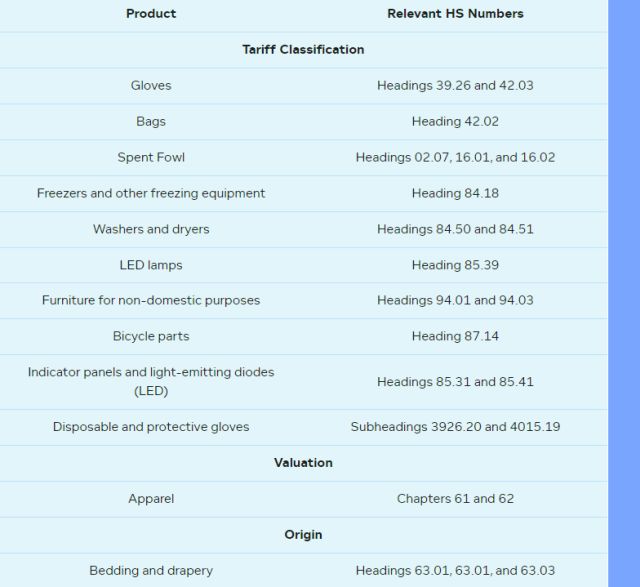
As many importers will know, the CBSA conducts verifications primarily on three declarations made by importers upon the importation of goods into Canada, all of which are key to determining the amount of duties owing: the tariff classification of the goods, their origin for purposes of MFN preferential tariff treatment, and their valuation or "value for duty".
The July Update identifies the CBSA's current priorities for these verifications, which are reproduced in the table below, broken down by the type of verification.
Table 1: CBSA Verification Priorities
Withdrawal of MFN tariff treatment for Russia and Belarus
In its July Update, the CBSA also reiterates that goods originating in Russia or Belarus continue to be excluded from the Most Favored Nation ("MFN") tariff treatment and are therefore subject to a duty of 35%.Goods containing or produced from inputs, such as materials or labour, from Russia or Belarus will attract this high rate of duty unless at least 50% of the cost to produce the goods is incurred in one or more MFN beneficiaries countries or Canada.
This continues to be a compliance priority for the CBSA and they are focusing their monitoring on products of iron or steel, fertilizer, petroleum, non-ferrous metals and tires to ensure compliance with this requirement to benefit from the MFN duty rate.
New Compliance Mechanisms
The July Update discusses in some detail the CBSA's approach to compliance and new compliance tools. It first identifies the fact that the CBSA will begin using its new CARM "to validate duties and taxes and conduct compliance interventions to address areas of suspected non-compliance". The indicates that this will be an important tool for the CBSA as the CARM rollout continues through October of this year.
In addition, the July Update discusses the tools that the CBSA has put in place since January, 2022 to target various circumstances and risks of non-compliance which are intended to complement trade compliance verifications. These notices vary based on the level of confidence the CBSA has that an instance of non-compliance has occurred, and include:
- Trade advisory notices, - alert the importer to potential for non-compliance in their declaration;
- Compliance validation letters - request additional information from the importer in cases where CBSA suspects an instance of non-compliance; and
- Directed compliance letters - issue a monetary assessment to the importer to addresses instances of known non-compliance.
The CBSA notes that these tools are particularly helpful in addressing some of the weaknesses of traditional trade compliance verifications, particularly the fact that these traditional verifications tend to be lengthy, labour intensive and performed well after the importations occur. In contrast, the CBSA argues that the three trade compliance intervention tools target specific import transactions, promote voluntary compliance, provide for early error correction and in turn mitigate the future cost of non-compliance where there are importations that continue to repeat undetected errors. However, the July Update confirms that traditional trade compliance verifications continue to remain "the CBSA's most comprehensive compliance tools".
Even with these new tools, CBSA compliance verifications can be onerous and time consuming exercises and can lead to significant assessments of additional duties interest and penalties for previously imported goods that, in the CBSA's view were not properly declared when imported. The McCarthy Tétrault International Trade and Investments team has significant experience assisting clients with these matters and will continue to monitor developments as the CBSA releases additional information regarding its priorities for 2024 and beyond.
Thanks to Smith Acheampong and Success Ogboe for their assistance in preparing this client alert.
To view the original article click here
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.




