- within Government, Public Sector, Energy and Natural Resources and Real Estate and Construction topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Banking & Credit and Law Firm industries
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitaraman presented her 8th consecutive Union Budget, for the fiscal year 2025-26, in Parliament on February 01, 2025. In this Budget, the proposed development measures span across ten broad areas focusing on Garib, Youth, Annadata and Nari.
- Spurring Agricultural Growth and Productivity;
- Building Rural Prosperity and Resilience;
- Taking Everyone Together on an Inclusive Growth path;
- Boosting Manufacturing and Furthering Make in India;
- Supporting MSMEs;
- Enabling Employment-led Development;
- Investing in people, economy and innovation;
- Securing Energy Supplies;
- Promoting Exports; and
- Nurturing Innovation.
The measures are divided into 4 focus areas namely: Agriculture, MSME, Investment and Exports.
Government Receipts:
- Total receipts (excluding borrowings) estimated at Rs. 34.96 lakh crore.
- Total expenditure pegged at Rs. 50.65 lakh crore.
- Net tax receipts projected at Rs. 28.37 lakh crore.
- Fiscal deficit forecast at 4.4% of GDP.
- Gross market borrowings pegged at Rs. 14.82 lakh crore.
- Capital expenditure allocation at Rs. 11.21 lakh crore (3.1% of GDP).
Schemes And Missions introduced:
- PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana is a programme covering 100 districts with low productivity, moderate crop intensity and below-average credit parameters, aiming to enhance agricultural productivity, irrigation facilities and availability of long & short term credit among others.
- Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses with a special focus on Tur, Urad and Masoor.
- National Mission on High Yielding Seeds aimed at strengthening research, development
- and propagation of high yield seeds.
- Mission for Cotton Productivity is a 5-year mission that will facilitate significant
- improvements in productivity and sustainability of cotton farming and promote extralong
- staple cotton varieties.
- Scheme for First-time entrepreneur launched for 5 lakh women, Scheduled Castes and
- Scheduled Tribes first-time entrepreneurs for providing term loans of up to Rs. 2 crores.
- Social Security Scheme for Welfare of Online Platform Workers to provide identity cards and registration on the e-Shram portal along with healthcare under PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- Urban Challenge Fund to implement the proposals for 'Cities as Growth Hubs', 'Creative
- Redevelopment of Cities' and 'Water and Sanitation' - Allocation – 10000 crores.
- Nuclear Energy Mission for research & development of Small Modular Reactors (SMR) with an outlay of Rs. 20,000 crore will be set up. At least 5 indigenously developed SMRs will be operationalized by 2033.
- Maritime Development Fund with a corpus of Rs. 25,000 crore will be set up. This will be for distributed support and promoting competition.
- Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing Fund 2 will be established as a blended finance facility with contribution from the Government, banks and private investors. This fund of Rs. 15,000 crore will aim for expeditious completion of 1 lakh housing units.
- The government announced establishment of a National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship and Management in Bihar. Alongside, the government also proposed for setting up a Makhana Board in Bihar to improve production, processing, value addition, and marketing and organisation of FPOs.
- Research, Development and Innovation initiative driven by the Private Sector has an outlay of Rs. 20000 crores
- National Geospatial Mission to develop foundational geospatial infrastructure and data. Using PM Gati Shakti, this Mission will facilitate modernization of land records, urban planning, and design of infrastructure projects.
- Gyan Bharatam Mission for survey, documentation and conservation of our manuscript heritage with academic institutions, museums, libraries and private collectors will be undertaken to cover more than 1 crore manuscripts. A National Digital Repository of Indian knowledge systems for knowledge sharing will be set up.
- Export Promotion Mission, with sectoral and ministerial targets, driven jointly by the Ministries of Commerce, MSME, and Finance. It will facilitate easy access to export credit, cross-border factoring support, and support to MSMEs to tackle non-tariff measures in overseas markets.
MSMEs as a Growth Engine:
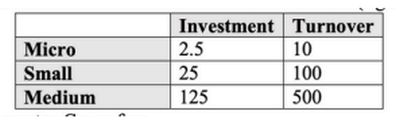
- Revision in classification criterion: Revised limits are as follows (figures in crores):
- Enhanced Credit Guarantee Cover for:
- Micro and Small Enterprises increased from 5 crore to 10 crore, and
- Startups increased from 10 crore to 20 crore, with the guarantee fee being moderated
- to 1 per cent for loans in 27 focus sectors, and
- Well-run exporter MSMEs, increase in term loans of up to Rs. 20 crore
- Focus on an ecosystem for development of cluster, skills and manufacturing abilities in the Toy-sector and enhancement of Product Scheme for Footwear & Leather Sectors.
- Customized credit cards with a Rs. 5 lakh limit for micro enterprises registered on Udyam portal.
Investing in Infrastructure/Economy:
- Each infrastructure-related ministry will come up with a 3-year pipeline of projects that can be implemented in PPP mode.
- An outlay of Rs. 1.5 lakh crore is proposed for the 50-year interest free loans to states for capital expenditure and incentives for reforms.
- Building on the success of the first Asset Monetization Plan announced in 2021, the second Plan for 2025-30 will be launched to plough back capital of ` 10 lakh crore in new projects.
- For furthering PPPs and assisting the private sector in project planning, access to relevant data and maps from the PM Gati Shakti portal will be provided
- A digital public infrastructure, 'Bharat Trade Net' (BTN) for international trade will be set-up as a unified platform for trade documentation and financing solutions. This will complement the Unified Logistics Interface Platform. The BTN will be aligned with international practices.
Financial Sector Reforms::
- The FDI limit for the insurance sector will be raised from 74 to 100 per cent. This enhanced limit will be available for those companies which invest the entire premium in India.
- The government proposed for 'Grameen Credit Score' framework to serve the credit needs of SHG members and people in rural areas. Moreover, the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development will set up a 'Partial Credit Enhancement Facility' for corporate bonds for infrastructure
- A forum for regulatory coordination and development of pension products will be set up.
- A revamped Central KYC Registry will be rolled out in 2025
- Requirements and procedures for speedy approval of company mergers will be rationalized. The scope for fast-track mergers will also be widened and the process made simpler.
High Level Committee on Regulatory Reforms::
- To conduct the review of all non-financial sector regulations, certifications, licenses, and permissions.
- An Investment Friendliness Index of States will be launched in 2025 to further the spirit of competitive cooperative federalism.
Customs (Special focus on rationalization of tariff structure and addressing duty inversion):
- Fixing of a time-limit of two years, extendable by a year, for finalising the provisional assessment under the Customs Act, 1962.
- Extending the time limit for the end-use of imported inputs in the relevant rules, from six months to one year.
- Removal of 7 tariff rates, leaving behind 8 tariff rates in total.
- Levy of not more than one cess or surcharge: hence, exemption of Social Welfare Surcharge
- on 82 tariff lines that are subject to a cess
- Exemption of 36 lifesaving drugs and medicines from BCD and addition of 6 lifesaving
- medicines to the list attracting concessional customs duty of 5%.
- Full exemption to cobalt powder and waste, the scrap of lithium-ion battery, Lead, Zinc and 12 more critical minerals.
- Addition of two more types of shuttle-less looms to the list of fully exempted textile machinery and Knitted fabrics would now attract BCD of at least Rs. 115 per kg.
- Increment of BCD on Interactive Flat Panel Display (IFPD) from 10% to 20% and reduction of BCD to 5% on Open Cell and other components.
- BCD on parts of Open Cells now exempted.
- 35 additional capital goods for EV battery manufacturing, and 28 additional capital goods
- for mobile phone battery manufacturing now exempted from BCD
- Reduction of BCD from 20% to 10% on Carrier Grade ethernet switches
TDS/TCS (Focus on Rate rationalization):
- The limit for tax deduction on interest for senior citizens is increased from 50,000 to 1 lakh.
- The annual limit of 2.40 lakh for TDS on rent is increased to 6 lakh.
- The threshold to collect tax at source (TCS) on remittances under RBI's Liberalized
- Remittance Scheme (LRS) is to be increased from 7 lakh to 10 lakh. Removal of TCS on remittances for education purposes, where such remittance is out of a loan taken from a specified financial institution.
- In a transaction where both TDS and TCS are applied, TCS shall be omitted.
- delay for payment of TCS up to the due date of filing statement is now decriminalized
Transfer Pricing: A scheme for determining arm's length price of international transaction for a block period of three years. Moreover, with a view to reduce litigation and provide certainty in International Taxation, the scope of Safe Harbor Rules is being expanded.
Other Reforms::
- New Income Tax Bill will be clear with close to half of the present volume, would be simple to understand and reduce litigation.
- Annual value of 2 self-occupied properties can now be claimed as nil without the restrictions placed earlier.
- Extension of the time-limit to file updated returns for any assessment year, from the current limit of two years, to four years.
- The period of registration for small charitable trusts/institutions has now increased from 5 years to 10 years
- The benefits of existing tonnage tax scheme are extended to inland vessels registered under the Indian Vessels Act, 2021
- Benefits to Indian Startups can now be claimed by entities incorporated before 01.04.2030.
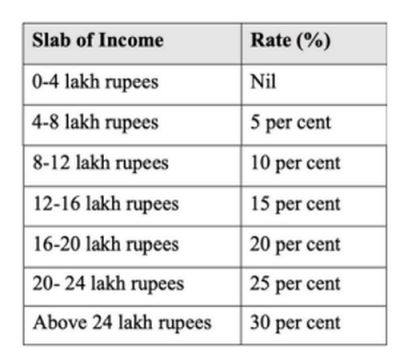
- The new Tax Regime under 115BAC of the Income Tax Act, 1961 is as follows:
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


