- within Media, Telecoms, IT, Entertainment, Law Department Performance, Litigation and Mediation & Arbitration topic(s)
Referendums play a significant role in shaping Australia's Constitution and are a mechanism for the people to directly participate in the democratic process.
What is a referendum in Australia and how does it work?
A referendum is a vote that allows the Australian public to express their opinion on a proposed change to the Constitution. Any proposed changes to the Constitution must get approval from a majority of voters in a referendum before they can be implemented.
The process towards a referendum commences with a proposal for a constitutional amendment, which may arise from various sources such as the federal government, individual citizens, or advocacy groups. However, the proposal must overcome several stages of scrutiny before it can be presented for a referendum.
Since the introduction of the Australian Constitution in 1901, there have been a total of 44 referendums held in Australia. However, only 8 of them were successful.
What is the purpose of referendums?
Referendums exemplify the power of democracy in Australia.
As The Voice to Parliament is proposed for inclusion in the constitution, a referendum is in order. A referendum on the Indigenous Voice to parliament will happen, but the date has not been confirmed yet.
More on The First Nations Voice to Parliament, The Proposed Constitutional Amendment.
Laws governing referendums in Australia
The conduct of referendums in Australia is governed by a framework of laws that ensure the integrity and fairness of the process.
1. The Australian Constitution
The Constitution of Australia is the foundational legal document of the nation.
It outlines:
- The structure of the government,
- The powers and responsibilities of different branches,
- and the rights and responsibilities of its citizens.
For a proposed constitutional amendment to get approval, it must pass a referendum with a double majority. This means that it must get support from a majority of voters in a majority of states and territories. Additionally, it must gain approval by an overall majority of voters nationwide. This ensures that any changes to the Constitution are supported by a significant portion of the Australian population and reflect the collective will of the people.
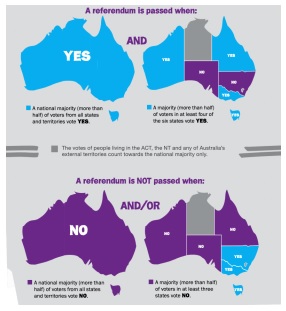
Image By Australian Electoral Commission via
https://www.aec.gov.au/Elections/referendums/files/double-majority-fact-sheet.pdf
2. The Referendum (Machinery Provisions) Act 1984
This legislation sets out the processes for the preparation and conduct of referendums, including:
- Appointment of referendum officers,
- Printing of ballot papers,
- Conduct of the referendum campaign,
- The counting and declaration of referendum results.
This Act ensures that referendums take place in a fair, transparent, and consistent manner and that the rights of voters have protection throughout the process.
3. The Constitution Alteration (Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Voice) 2023 Bill.
This bill is the specific legislation that sets out the proposed changes to the Australian Constitution, which would establish an Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Voice.
Voting in referendums
To vote in a referendum in Australia, eligible citizens aged 18 and over need to be registered on the electoral roll.
Prior to the referendum, the Australian Electoral Commission (AEC) will provide information on the voting process, including the location of polling stations and the option for postal voting.

Image By Australian Electoral Commission


