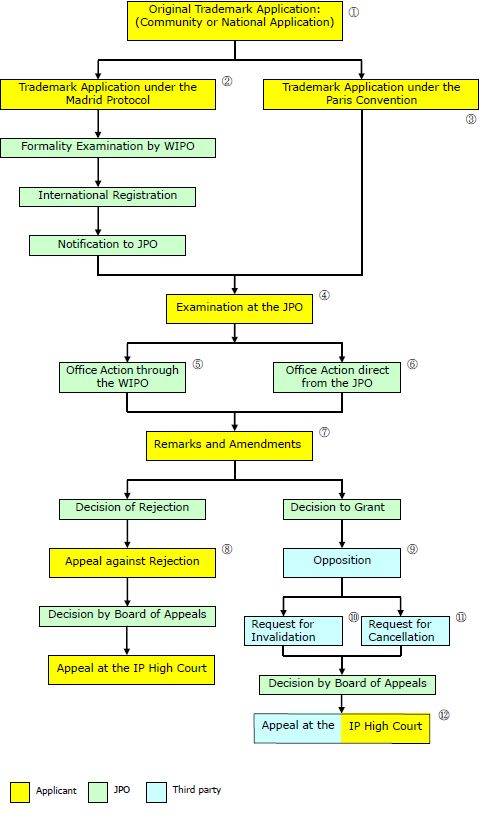
1. The original trademark application must be a trademark application filed in one of the member countries of the Paris Convention or the Madrid Protocol.
2. If the application is rejected or if the registration is cancelled in the home country, a trademark application under the Madrid Protocol loses its basis and is rejected unless converted to a Paris route application.
3. A trademark application may be filed at the Japan Patent Office claiming priority on a trademark application filed in a member country of the Paris convention within 6 months from the priority date. The trademark and designated goods and services must be the same. A three-dimensional mark can be registered, and from 2015 colors, sounds, position and motion trademarks will also be registrable. Trademark applications are published soon after their filing. A published trademark application is protected from copying by a retroactive protection right after the trademark is registered whereby a remuneration equivalent to a royalty may be demanded.
4. Under the present examination practice, the applicant is required to currently be using the trademark or to plan to use the trademark in the near future i.e. within 2 years. When a large number of goods and/or services are designated, the examiner often issues an Office Action requesting evidence of use or plan to use the trademark, or a Declaration showing the intention to use the trademark for all the designated goods and services. A trademark application is rejected when there is a confusingly similar registered trademark of a third party having an earlier filing date designating goods and services similar to those of the application. A trademark is deemed to be confusingly similar if one of appearance, sound, and meaning of the trademark is similar. When determining whether two sounds are similar, the examiner neglects the differences in the sounds of "b" and "p" and "v", "f" and "h", "l" and "r", "m" and "n". Furthermore, the sounds of vowels are aggregated to five vowels "a", "i" "u", "e" and "o" in the examination.
5. When an Office Action is issued against an International Registration of trademark under the Madrid Protocol, an attorney resident in Japan must be assigned to file the response.
6. Although the deadline for filing a response is set by the examiner, the deadline may be extended as necessary if requested by the applicant, unlike the deadlines in patent prosecutions.
7. Goods and services may be submitted by the amendments as long as they are covered by the originally-filed goods and services even if they are not specifically recited. The trademark must be the same as the originally-filed trademark despite the amendments. When a trademark application is rejected due to a registered trademark filed earlier that is confusingly similar, the reason for rejection may be overcome if the earlier trademark is invalidated or cancelled due to non-use.
8. An Appeal may be filed against a Decision to reject a trademark application. The Appeal will be examined by a board of three appeal examiners.
9. Any third party may file an Opposition against the registration of a trademark within 2 months from the publication of the registered trademark. An Opposition may be filed for one or more designated goods and services, and relative and absolute grounds of rejection may be raised.
10. When a trademark is registered in contravention of the Trademark law (registered despite the existence of a confusingly similar trademark, for example), a third party may file an appeal for Invalidation retroactively from the date of the registration.
11. When a trademark has not been used for longer than 3 years including the last 3 years for one or more designated goods and services, a third party may file an appeal for cancellation as far as the designated goods and services for which the trademark has not been used are concerned. If the Appeal is successful, the trademark registration is cancelled as of the decision date.
12. A party receiving an unfavorable decision by the Board of Appeals my file an Appeal to the Intellectual Property High Court requesting cancellation of the decision.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
