- within Corporate/Commercial Law, Government and Public Sector topic(s)
- with readers working within the Insurance and Oil & Gas industries
The rapid rise of AI technology has reshaped how businesses operate across industries and will be a chief catalyst for innovation in the future. Companies that want to stay competitive will need to adapt, and legal counsel charged with facilitating their success should consider how experts can play a vital role.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of transformative innovations, revolutionizing industries from automotive to healthcare and offering opportunities to quickly scale and drive growth. The AI global market is projected to grow at a 36.8% compound annual growth rate over the next several years. And while the U.S. currently leads the market, China is positioning itself to be the world leader in AI technology by 2030. With competition heating up, the race for market dominance intensifies, and businesses across industries are increasing their AI investment. But as the impact of AI technologies becomes increasingly pronounced, driving everlasting change, will it also generate the next big wave of litigation?
Let's take a quick look at the trajectory of AI technology—the opportunities and risks, unfolding areas of litigation concerning AI, and the experts that would be advantageous to retain.
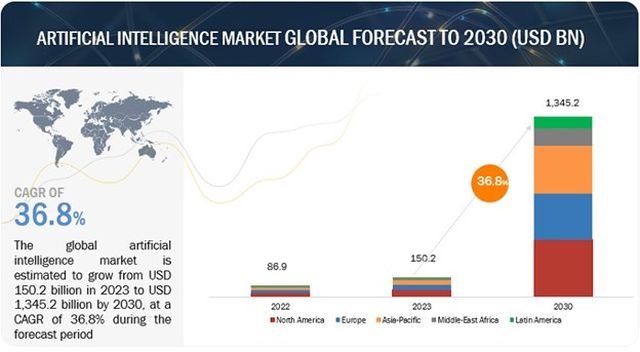
Source: MarketsandMarkets
Wireless and AI Technologies Go Hand-in-Hand and Make a Lasting Impact Across Industries
Like wireless technology, AI technology has significantly impacted a wide range of industries. Both technologies have reshaped businesses, driving efficiency and innovation, and creating new opportunities. But while wireless technology facilitates data transmission, AI technology benefits from access to large datasets brought forth through wireless tech to further improve data-driven capabilities within businesses. For example, advanced wireless technology enables the seamless transfer of vast amounts of data and makes devices interconnected and real-time data exchanges faster and more accessible. At the next level, AI technology analyzes this data to extract meaningful patterns and trends to derive valuable insights and optimize decision-making. With AI, companies can improve operations and resource allocation in fields ranging from logistics to healthcare. They can also use AI-powered analytics to help companies identify customer preferences and predict market trends, enabling them to stay competitive and responsive to changing demands. Like how wireless technology has proven essential to driving new channels of data-related innovation by keeping us connected, AI technology is at the brink of unleashing new avenues for growth but, along with it, a great deal of uncertainty and risk.
Conflicting Views about AI Technology
The impact made by the use of AI technology has been widespread. From manufacturing robots that increase productivity to using ChatGPT to build company websites, various types of businesses stand to reap significant benefits from AI implementations. In fact, according to Forbes Advisor, over 60% of business owners believe that AI will increase productivity and improve customer relationships. A staggering 97% of business owners believe that ChatGPT will help their business.
However, according to the Pew Research Center, Americans are more concerned than excited about the use of AI technology, citing worries over the potential loss of jobs, privacy concerns, and possible misuse of data as some of the reasons.
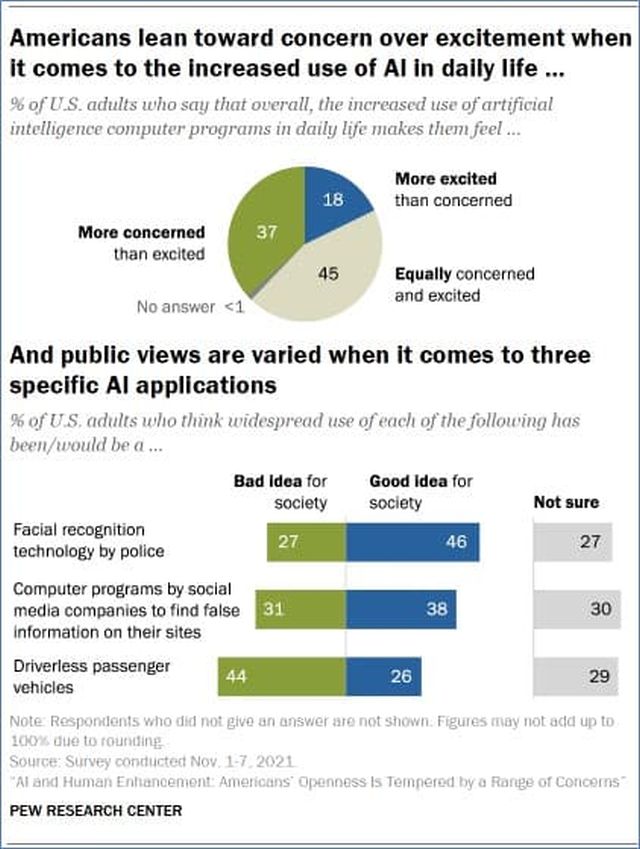
Further, the potential ramifications and legal implications surrounding what results from mass AI adoption garner heightened attention, shaping discussions about where litigation in an AI world will likely arise.
Unfolding Litigation Concerning AI Technology
Like most emerging technologies, fierce competition in the space sparks intellectual property disputes as new proprietary systems, algorithms, tools, and innovation expand. Intense competition can also ignite potential misconduct, creating class action lawsuits, fraud claims, trade secrets disputes, and more.
Additionally, given AI's functional need for vast amounts of data to train generative AI models, concerns over data privacy emerge, giving rise to privacy and data protection lawsuits, cybersecurity claims, and consumer protection cases.
Litigation involving AI technology has begun to increase. In July, a class action lawsuit over allegations of AI scraping was filed against Google. The case was brought by eight individuals representing millions of internet users and copyright holders with estimated damages amounting to $5 billion or more. Likewise, several other lawsuits over alleged misuse of personal data involving AI technology have been filed against Meta, Microsoft, and OpenAI since last year.
Additionally, comedian Sarah Silverman is suing OpenAI for copyright infringement, joining the ranks of several writers who allege that the tech company's AI software unlawfully ingested their works without permission to train its generative-AI product, ChatGPT, to create new content. The outcome of this case could set a precedent for how future matters are handled.
Notably, the use of AI technology to replicate an actor's likeness has recently drawn ire in the entertainment world as well and is a major area of strife in current contract disagreements between actors and production companies. It will likely continue to be central to conflicts going forward.
Beware: The Regulators are Circling
As the AI boom continues to proliferate, government agencies are beginning to take notice.
Considering fair competition, the FTC's Bureau of Competition is looking at Generative AI with an eye toward antitrust and anti-competition concerns. Chief among concerns are tech companies who control sources of data input relied upon by AI tools or adjacent markets, like cloud computing, that would allow companies to offer a range of related products that potentially distort competition or create a monopoly.
In other areas, Massachusetts securities regulators opened an investigation into investment firms' Al use over concerns that firms could put company profits ahead of investors' best interest without proper guardrails. Likewise, the SEC recently proposed new requirements for broker-dealers and investment advisers to eliminate or neutralize conflicts of interest associated with AI predictive tools.
Another inherent issue regarding AI stems from the technology's dependency on multiple sources of data. Pulling from sources with poor data quality, biased information, or insufficient context can perpetuate misinformation, skew predictions, and amplify discrimination. Also, merging sensitive data risks the potential for breaches and questions over privacy and data ownership. Regulators will want to ensure that the proper checks and balances are in place to ensure that the use of data isn't compromised or destructive.
The Role of Experts in an AI World
Undoubtedly, AI technology is here to stay. With it are innovations that reshape our daily lives and propel modern society forward at a quickening pace. In terms of litigation, having a diverse team of experts who can address a myriad of issues across industries will give counsel a competitive edge. These experts would include highly credentialled academics, former regulators, and industry insiders with specialized knowledge in their respective fields.
The best types of experts for counsel to consider are:
- Software engineers who possess a deep understanding of AI algorithms, machine learning models, and their applications. They can analyze the technical aspects of AI systems, assess their functionality, and provide insights into how the technology works.
- Data scientists who can assess the quality, bias, and integrity of the data used to train AI models. They can evaluate data preprocessing, identify potential biases, and analyze how data influences the AI system's outcomes.
- Ethics experts who specialize in the ethical considerations of AI technology, including fairness, transparency, and potential bias. They can evaluate whether AI systems exhibit discriminatory behavior and provide guidance on addressing these concerns.
- Privacy and cybersecurity analysts who can assess whether data handling complies with legal standards and ensure that sensitive information is properly safeguarded.
- Technical experts who can address patent, copyright, and trade secret issues related to AI technology. They can evaluate claims of infringement or misappropriation of AI-related intellectual property.
- Industry insiders with knowledge of industry landscapes, AI adoption in their specific industry, and related industry best practices and operations.
- Former regulators who know industry-specific regulations to assess whether AI systems adhere to relevant legal requirements and standards in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Taking a proactive approach, given the interdisciplinary nature of AI-related litigation, counsel should consider retaining testifying experts with diverse skill sets to comprehensively manage the technical, legal, and ethical dimensions of the issues at hand.
In conclusion, the rapid rise of AI technology has reshaped how businesses operate across industries and will be a chief catalyst for innovation in the future. Companies that want to stay competitive will need to adapt, and legal counsel charged with facilitating their success should consider how experts can play a vital role.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.


