- within Technology topic(s)
- in United States
- with readers working within the Media & Information and Retail & Leisure industries
- within Technology topic(s)
- in United States
- within Real Estate and Construction, Employment and HR and International Law topic(s)
- with readers working within the Retail & Leisure industries
In 2023, the Indonesian government enacted Law No. 4 of 2023 on Development and Strengthening of the Financial Sector (Pengembangan dan Penguatan Sektor Keuangan or "P2SK Law"), which regulates, among others, that the supervision of Crypto Assets would be transferred gradually from the Commodity Futures Trading Supervisory Agency (Badan Pengawas Perdagangan Berjangka Komoditi or "Bappepti") to the Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan or "OJK"), an independent agency that has the authority to supervise the financial services in Indonesia. In P2SK Law, the transfer of authority from Bappebti to OJK shall be conducted within two years after the enactment of P2SK Law on 12 January 2023, thus, starting that day, OJK has the full authority to supervise Crypto Assets.
In December 2024, OJK issued OJK Regulation No. 27 of 2024 on the Implementation of Digital Assets Trading Including Crypto ("OJK Reg. 27/2024") as the implementation of OJK's supervision over Crypto Asset operation. We note that Crypto Assets are regarded as Digital Assets. Under the previous regulating authority (Bappebti), Crypto Assets are classified as commodity. Any actor of businesses related to Digital Financial Assets (including Crypto Assets) shall obtain a business license issued by OJK. The related actors include the Stock Exchange, Clearing Guarantee and Settlement Institutions, Digital Asset Custodies, and Traders.
In this article, we summarize the key highlights of OJK Reg. 27/2024, particularly (i) Classification of the Traded Digital Assets, (ii) Trading Organizers Qualifications and Licenses, (iii) Supporting Activities, (iv) Personal Data and Consumer Protection, and (v) Concluding Remarks.
Classification of the Traded Digital Assets
Through OJK Reg. 27/2024, OJK mandates any Digital Asset to fulfill the following criteria:
(a)It is issued, stored, transferred, and/or traded using a
distributed ledger technology;
(b)It is not a financial asset registered by a financing services
institution;
(c)it is not used in an activity, which violates the laws;
and
(d)It meets other criteria enacted by OJK.
(Article 4 (1) of OJK Reg. 27/2024)
Other than the general criteria above, a digital asset in the form of Crypto Asset must fulfill the following aspects:
(a)It represents an ultimate digital value;
(b)It uses a distributed ledger technology that can be publicly
accessed;
(c)It owns a utility and/or is backed by assets;
(d)It can be traced or does not have features to disguise the
ownership and transaction; and
(e)It has passed the appraisal using the method set by the Stock
Exchange.
(Article 8 (1) of OJK Reg. 27/2024)
We note that, compared to the previous Bappebti Regulation No. 8 of 2021 on Guideline of the Implementation of Physical Market Trading of Crypto Assets on Futures Exchanges, aslastly amended by Bappebti Regulation No. 9/2024 ("Bappebti 8/2021"), there are no significant changes to the criteria for Crypto Assets eligible for trading. As per the Bappebti 8/2021, Crypto Asset trading must be conducted using distributed ledger technology, the traded Crypto Assets must be classified as either Utility Crypto Assets or Crypto-Backed Assets, and they must have undergone an appraisal using the Analytical Hierarchy Process ("AHP") method as determined by Bappebti.
While under the previous regulations, Bappebti was responsible for conducting the appraisal using the AHP method, OJK Reg. 27/2024 authorizes the Stock Exchange to hold the authority to determine the list of Crypto Assets that may be traded (Article 9 of OJK Reg. 27/2024). Consequently, any addition or removal of Crypto Assets from the Crypto Asset List must be submitted to the Stock Exchange for approval (Article 11 of OJK Reg. 27/2024).
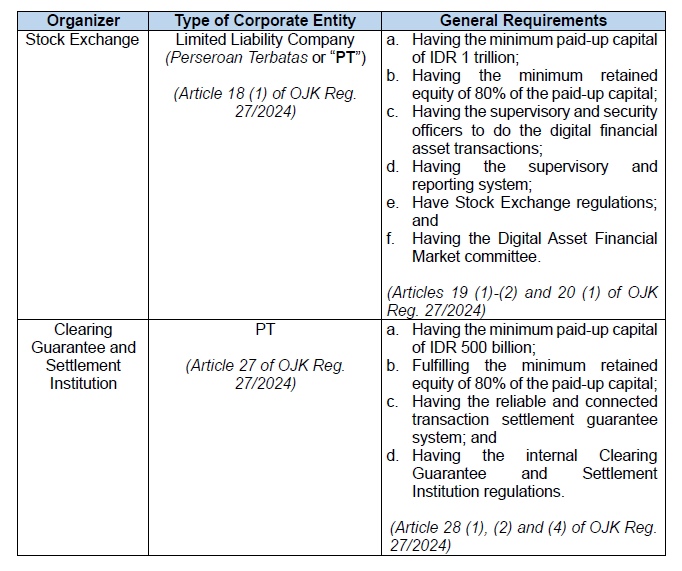
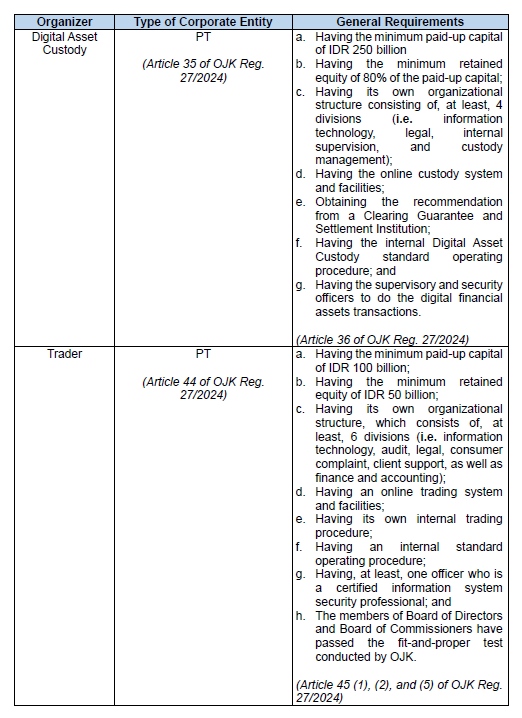
Trading Organizers Qualifications and Licenses
These five trading organizers are authorized to engage in digital
assets and crypto trading. They are the (i) stock exchange, (ii)
clearing guarantee and settlement institutions, (iii) digital asset
custodies, (iv) traders, and (v) other parties enacted by OJK. In
this regulation, OJK introduces requirements for businesses
planning to enter the Crypto Assets market in Indonesia. They
include the types of corporate entities, specific licenses,
etc.
Please refer to the following table where we provide the summary of each organizer's qualifications:
The documents to apply for the business licenses shall be submitted to OJK via the Integrated Licensing and Registration System (Sistem Perizinan dan Registrasi Terintegrasi or SPRINT). Furthermore, OJK will conduct the following actions before approving or rejecting the application:
(a)Examination and analysis of the application documents;
(b)Fit and proper test;
(c)Examination of the operational readiness; and
(d)Other examinations deemed necessary by OJK.
(Article 56 (2) of OJK Reg. 27/2024)
Supporting Activities:
Similarly, OJK also allows the activity of the Crypto Assets businesses to be supported by other activities that directly or indirectly give benefits to the organizers ("Supporting Activity"). The Supporting Activities may include intermediary services related to:
(a)Payment Service Provider;
(b)Digital Financial Asset Transaction Facilitation Service
Provider; and
(c)Other supporting activities.
Each Supporting Activity must obtain OJK's prior approval (Article 102 (2) of OJK Reg. 27/2024).
Personal Data Protection and Consumer Protection:
OJK introduces specific provisions on Personal Data Protection
("PDP") for those, particularly organizers. involved in
the Digital Asset market. Generally, the concept of PDP has already
conformed the existing PDP Law (i.e. Law No. 27 of 2022 on Personal
Data Protection or "PDP Law"), including in terms of
confidentiality and consent of the data subject. However, OJK
requires any organizer to notify OJK after transferring
consumer's data to any third party. The notification must be
made, at least, one day after the data transmission.
With regard to the consumer protection, OJK Reg. 27/2024 requires
the organizers to inform the customers of the mandatory information
on the traded Digital Asset, among others, (i) the name, (ii) the
brief description, (iii) the Issuer, (iv) the risks, (v) the
historic value, (vi) the supply amount, and (vii) the website
(Article 123 (2) of OJK Reg. 27/2024). These provisions are
consistent with Indonesia's consumer protection principles to
ensure transparency for consumers engaging in digital asset
transactions.
Concluding Remarks
With the full transfer of supervisory authority from Bappebti to OJK by January 2025, digital asset businesses must align with the new regulatory framework, by obtaining the necessary licenses and ensuring compliance with consumer protection and data security measures. Although some of the provisions, such as the criteria of digital assets and the types of supporting activities for the organizers remain unchanged, businesses should assess their operational structures, licensing requirements, and risk management to ensure the smooth transition under OJK's supervision.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.




