- with readers working within the Banking & Credit industries
Introduction
The new government presented its first union budget for 2014-15 in the parliament on 10th July' 2014.
The economic survey highlight that the Indian economy is likely to grow in the range of 5.4 to 5.9 per cent in 2014-15 overcoming the lower than 5 per cent GDP growth in last two consecutive years i.e., 2012-13 and 2013-14. The steps announced in the budget are the beginning towards a sustained growth of 7 to 8 per cent with macro-economic stabilization.
Increase in the basic tax exemption limit in case of individuals is expected to increase disposable incomes and thereby provide some relief against inflation.
The Finance Minister has announced that the sovereign right of the government to undertake retrospective legislation has to be exercised with extreme caution and will not ordinarily bring about any change retrospectively which creates a fresh liability.
The government has proposed that all fresh cases arising from retrospective amendments of 2012 in respect of indirect transfer taxation will be scrutinized by a high level committee.
Unfortunately, the budget does not contain any proposal that would provide relief to taxpayers who are already in litigation on this matter.
The Finance Minister has extended the scope of advance rulings to cover residents, enlarging the scope of Income-tax Settlement Commission and enabling roll back of Advance Price Agreements (APAs).
The budget has announced some significant proposals for the real estate and infrastructure sector such as grant of tax status to Real Estate Investment Trusts (REIT) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvIT), Public – Private Partnerships (PPPs), development of industrial and economic corridors, smart cities linked to transport connectivity, new airports in tier-1 and tier-2 cities, research centres etc.
The Finance Minister has strongly re-affirmed the commitment to introduce Goods & Service Tax (GST), however no date of implementation has been announced.
The increase in FDI limit from 26 to 49 per cent into Insurance & Defence and reducing the mandatory requirements of built up area and capital conditions in the development of smart cities are much awaited steps.
Economic Performance

Key Policy Announcements
Defence
The composite cap on foreign investment in Defence manufacturing to be raised from 26 per cent to 49 per cent with Indian management and control subject to an approval from FIPB.
Real Estate and Infrastructure
FDI policy requirements regarding built up area and minimum capital norms to be reduced from 50,000 square meters to 20,000 square meters and from USD 10 million to USD 5 million respectively. The condition of minimum lock-in period of three year has been retained.
Projects with minimum 30% of its total project cost for low-cost affordable housing to be exempt from built-up area and minimum capital requirement, however, the three year lock-in period shall apply.
15000 km of gas pipelines to be developed using the PPP mode.
Scheme for the development of new Airports in Tier-I & Tier-II cities
Development of sixteen new port projects, policy for encouraging Indian-controlled tonnage and a comprehensive policy to promote the Indian shipbuilding industry are being considered.
Insurance
The composite cap in the Insurance sector is to be increased to 49% from 26% for companies with Indian management and control through FIPB route.
Manufacturing and Industries
The manufacturing unit would be allowed to sell its products through retail including through e-commerce platforms without any additional approval.
The Government is to strengthen research centres in areas such as nanotechnology, materials science and biomedical devices technology through PPPs.
Direct Taxation
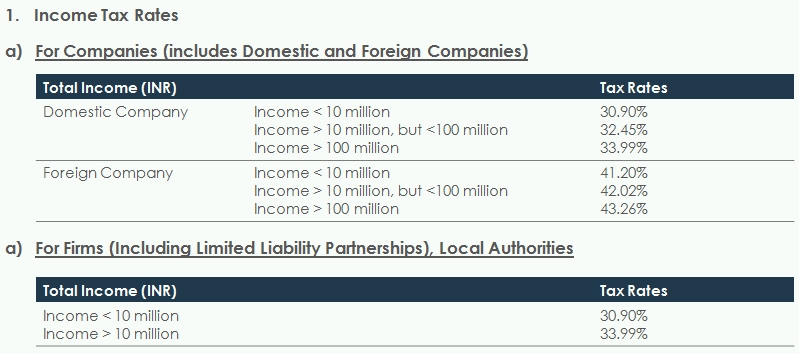
Corporate Tax Rates
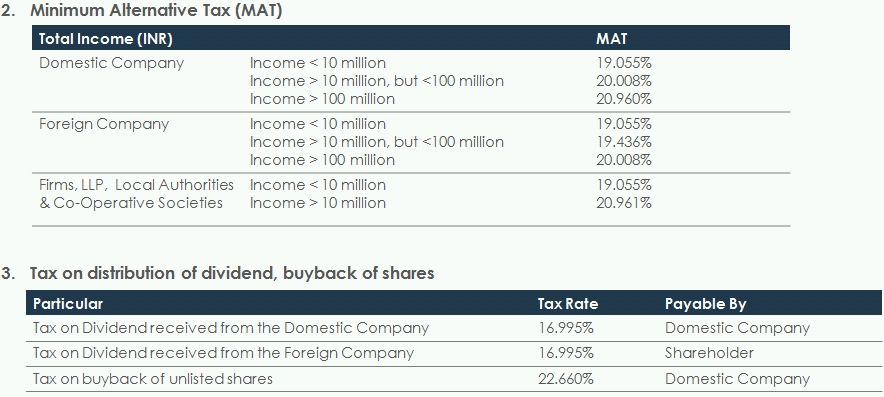
Rates of corporate tax remain unchanged for both domestic and foreign companies.

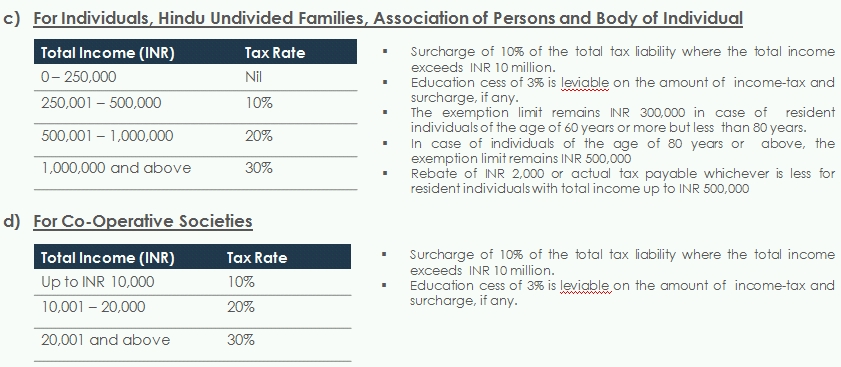
Personal Income Tax
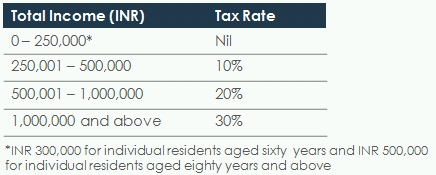
The budget proposes to increase the minimum exemption limit in the case of Individuals, HUF, AOP, BOI, and artificial judicial person from INR 200,000 to INR 250,000.
The applicable surcharge and cess remains unchanged. The tax slab rates applicable are as follows:
Maximum deduction allowable for interest on loan for self-occupied property increased from INR 150,000 to INR 200,000 and towards prescribed tax saving investments increased from INR 100,000 to INR 150,000.
Dividend
Dividends received by an Indian company from any specified foreign company (equity shareholding of 26 per cent or more) is taxable at concessional rate of 15 per cent for all future assessment years without any sunset clause.
The dividend received by the domestic company would require to grossed up for the purpose of computing DDT.

Capital Gain
Unlisted securities and mutual funds (other than equity oriented funds) to be treated as long term capital assets, if held for a period more than 36 months (Earlier 12 months).
Securities held by FIIs in accordance with SEBI regulations to be treated capital asset and taxable under capital gain.
Capital gains from sale of units of mutual funds, including units of equity oriented funds eligible for concessional tax rate of 10% would not be available. It would now be taxable at the rate of 20%.
In relation to capital gains arising from transfer of an asset by way of compulsory acquisition, it has been clarified that the enhanced compensation will be taxed as capital gains in the financial year in which the final order is made.
It is proposed that any transfer of government security carrying periodic payment of interest, through an intermediary from a non-resident to another non resident shall not be taxable as capital gains.
Tax Incentives
Incentive to manufacturing sector
A company is engaged in the manufacturing of any article or things, acquired and installed a new plant & machinery exceeds INR 250 million, would be eligible to claim an Investment allowance of 15% of the cost of such new plant & machinery. This deduction would be available for such investments made till 31 March 2017.
Incentive to power sector
Sunset date for being eligible to claim tax holiday for power generation, distribution or transmission extended to 31 March 2017.
Investment based incentive
The investment based tax incentive (in respect of the eligible capital expenditure) extended 'laying and operating a slurry pipeline for the transportation of iron ore', and 'setting up and operating a semiconductor wafer fabrication manufacturing unit'.
Transfer Pricing
International Transaction
The budget seeks to clarify that even a transaction entered into by an assessee with a resident unrelated third party would be deemed to be an International transaction, if the same is pursuant to a prior arrangement between the third party and Associated Enterprise.
'Roll back' Mechanism for APA
The Budget has proposed to introduce 'Roll back' provision in the present APA scheme. As per the proposal, methodology agreed for determining ALP of an International transaction under an APA could be made applicable to period of up to four years prior to the first year covered under the APA. However, benefit of such 'Roll back' would be available subject to certain conditions/rules which are to be prescribed. The amendment is effective from October 1, 2014.
Transfer Pricing
Computation of arm's length price
The Budget has proposed the concept of price range for determination of ALP. However, the existing concept of arithmetic mean would continue to apply where the number of available comparable are inadequate.
Use of multi year data
As per the transfer pricing regulations, the use of single year data for comparable analysis and multi year data with some exception is available. The budget has proposed to amend regulations to allow the use of multiple year data for comparability analysis.
Taxation of real estate investment trusts and infrastructure investment trust (business trusts) – w.e.f. 1 October' 2014
The SEBI has proposed draft regulations relating to two new categories of investment vehicles, namely:
REIT; and
Infrastructure Investment Trust.
It is proposed to introduce a specific taxation regime for business trusts and investors in such a business trusts in a manner that there is no double taxation.
The key features to the regimes are as follows:
Dividend
SPV (company) distributing dividend to the business trust is subject to DDT.
Dividend is exempt in the hands of the business trust.
Dividend component of the income distributed by the business trust is treated as such in the hands of the unit holder.
Interest
Interest from SPV is not taxable in the hands of the business trust.
SPV is exempted from withholding tax on interest paid to the business trust.
Interest distributed by business trust is taxable in the hands of unit holders.
Interest
Business Trust to withhold tax on distribution attributable to the interest component - from Domestic unit holders @10% and Non-resident unit holders @ 5%.
Capital gains
Capital gains on transfer of units held in trust:
Securities Transaction Tax applicable to transfer of units of Business Trust.
Long term capital gains (LTCG) to be exempt from tax
Short term capital gains taxable at 15% (plus applicable surcharge and cess)
Capital gains on disposal of shares in SPV:
Taxable at normal capital gains (assuming shares in SPV are held as capital asset by Business Trust)
Onward distribution of amount attributable to capital gains is exempt in hands of unit holders
Capital gains arising to Sponsor on exchange of shares in Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) with units of Business Trust:
Exchange of shares of SPV for units of a business trust is not regarded as taxable transfer. Consequently, taxability is deferred till the time of ultimate disposal of the units by the sponsor.
At the time of ultimate disposal of the units of the business trust, the sponsor shall not be entitled to avail the concessional STT-based capital gains tax regime.
The acquisition cost of the units to the sponsor shall be deemed to be the acquisition cost of the shares in the SPV.
The holding period of the shares would also be included in reckoning the holding period of the units.
Withholding Tax
Reduced rate of withholding tax at 5 per cent would apply on interest paid by an Indian company to non-resident taxpayers on monies borrowed by it in foreign currency from a source outside India:
under a loan agreement or by way of issue of long term infrastructure bond up to 30 June 2017 or
by way of issue of any long term bond between 1 October 2014 to 30 June 2017.
In case of non deduction or non payment of tax deducted at source on payment to a residents, the disallowance would restricted to 30% (Earlier 100%).
The payment to a non resident will be allowed as a deduction if the tax deducted at source during the year is deposited on or before the due date of filling of income tax return.
Other Changes
Sum of money received as advance or otherwise in the course of negotiations for transfer of capital asset and such some is forfeited or negotiations do not result in transfer of such asset would be taxable as Income from Other Source.
Benefit of advance ruling extended to resident private limited company.
Indirect Taxation
Custom Duty
General rate of BCD remain unchanged i.e., 10 per cent.
Mineral oils (including petroleum and natural gas) extracted or produced in the continental shelf of India or exclusive economic zone of India and imported prior to the 7th day of February, 2002 have been exempted from the whole of customs duties with retrospective effect. However, no refund of duties already paid in respect of such mineral oils shall be granted.
Benefit of advance ruling extended to resident private limited company.
In case of appeal, mandatory pre-deposit needs to be made to the extent of 7.5 per cent of the amount involved at first appeals level and 10 per cent at second stage level subject to a cap of INR100 million.
Exemption from BCD on specified raw material such as Fatty Acid, Crude Palm stearin, RBD, other Palm Stearin. industrial grade crude oils, Polytetrametylene Ether Glycol.
Exemption from BCD allowed to LCD/ LED panel (below 19 inches), colour television picture tube used in the manufacture of cathode ray televisions, specified parts of LCD/ LED panels.
Exemption from BCD allowed to flat copper wire for use in the manufacture of PV ribbon (tinned copper interconnect) for manufacture of SPV cells or modules.
Exemption from BCD allowed to e-book reader.
Exemption from SAD allowed to Inputs/components used in manufacture of Personal Computers (laptops/desktops) and tablet computers.
Increase in BCD on various type of coal and diamonds to 2.5 per cent.
Increase in export duty on bauxite increased from 10 per cent to 20 per cent.
Excise Duty
General rate of Excise duty remain unchanged i.e., 12.36 per cent.
In case of appeal, mandatory pre-deposit needs to be made to the extent of 7.5 per cent of the amount involved at first appeals level and 10 per cent at second stage level subject to a cap of INR100 million.
Activity of packing, re-packing, labelling etc. for specified products such as vaccines, toothpowder, packaged software, air conditioners, batteries, smart cards etc. to be a considered as 'manufacture'.
In cases where excisable goods are sold at a price below the manufacturing cost and profit and there is no additional consideration flowing from the buyers to the assessee directly or from a third person on behalf of the buyer, value for the assessment of duty shall be deemed to be the transaction value.
Benefit of advance ruling extended to include resident private limited companies.
Exemption from Excise duty is allowed to machine / components required for initial setting up of compressed bio gas plant.
Machines/parts related to manufacture of solar voltaic cells and setting up of solar energy production, projects have been exempted.
Parts consumed within the factory of production for the manufacture of goods to be used for generating solar/wind energy have been exempted.
Increase in excise duty on cigarettes, Pan Masala, Recorded smart cards etc.
Decrease in excise duty on products such as branded petrol, footwear, LED etc.
Service Tax
Rate of service Tax remain unchanged i.e., 12.36 per cent.
Following services to be removed from the negative list of services i.e., now taxable (with effect from enactment of Finance Bill):
Services in relation to Selling of Space or time for Advertisements in broadcast media namely radio and television is now extended to other segments like online and mobile advertisement are now taxable.
Services provided by radio cabs or radio taxis whether or not air conditioned, are now taxable.
The exemption has been withdrawn from the following services:
Passenger transportation by air conditioned contract carriage.
Technical testing or analysis of newly developed drugs including vaccines and herbal remedies on human participants by a clinical research organization approved to conduct clinical trials by the Drug Controller General of India.
Renting of immovable property to educational institutions.
The exemption has been introduced in the following services:
Services provided by Common Bio-medical Waste Treatment Facility operators by way of treatment or disposal of bio-medical waste or processes incidental thereto, to a clinical establishment.
Services provided under all life micro-insurance schemes approved by IRDA, where sum assured does not exceed INR 50,000.
Services provided by way of transport of organic manure by vessel, rail or road.
Services provided by way of loading, unloading, packing, storage or warehousing, transport by vessel, rail or road, of cotton, ginned or bale.
Services provided by Indian tour operators to foreign tourists for a tour outside India.
Services received by RBI from outside India, in relation to management of foreign exchange reserves.
Following are the changes in the existing services exemptions:
Service tax exemption on services received by educational institutes restricted only to specified services as opposed to all auxiliary education services.
The scope of reverse charge mechanism has been extended to cover:
services provided by directors to body corporate; and
services provided by recovery agents to banks, financial institutions and NBFCs
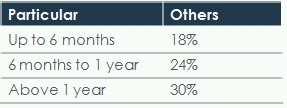
The interest on delay in payment of services tax has been revised to:
In work contract valuation, the service portion of the work relating to movable and immovable is aligned to 70%.
The tax for transport of goods by vessels will be computed on 40 per cent of the service value instead of 50 per cent of the contract value.
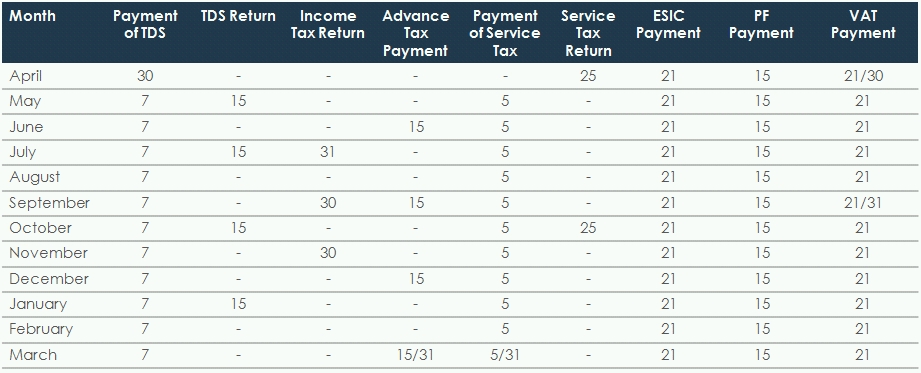
Tax Card
These rates are subject to enactment of the Finance Bill 2014. The Rates are for the Financial Year 2014-15.


ABBREVIATIONS
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

