01 France seeks new African allies in a diplomatic charm offensive
The month of May was an eventful one for France, as it sought to build relationships with a number of African states in a sustained drive to be an active participant in the continent's development, particularly post-COVID-19. The biggest move was the announcement by France of its intent to help stem the continent's growing debt crisis at a post-COVID-19 African debt summit in Paris. Campaign strategies include COVID-19 debt relief and an increase in special drawing rights for African countries. The Macron government similarly led the way in lobbying western nations to write off the debt accumulated by Sudan during the Omar Al-Bashir regime to assist in rebuilding the African state's economy. During the debt relief summit, Rwandan president Paul Kagame noted that diplomatic relations between Rwanda and France were improving following the commitment by the French government to disclose classified information on its role in the 1994 civil war.
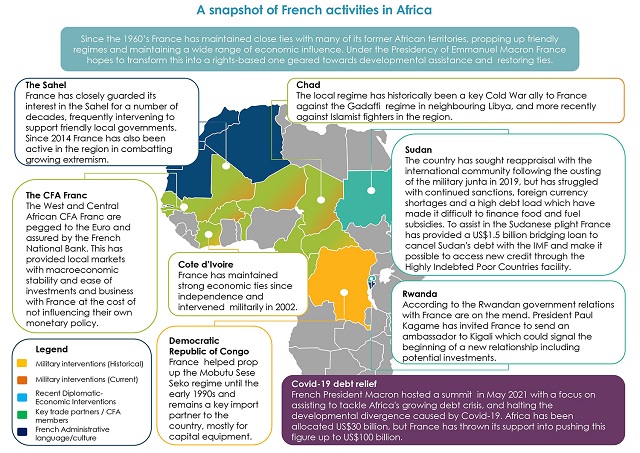
Sources: Brooking Institution, 2019; The Conversation, 2020; Bloomberg, Business Day, Reuters, Times Live
02 Tanzania positions itself as an O&G export and logistics hub with major deal signings
The long-awaited spate of energy developments in East Africa gained further pace in May amid announcements of major deals. This bodes particularly well for Tanzania. The most notable is the revival of the planned US$1.1 billion Dar Es Salaam-Mombasa gas pipeline. The project will see the construction of a 600km connection between the two main port cities of Tanzania and Kenya to carry gas produced by Tanzania's southern offshore fields for Kenyan domestic consumption. At the same time, the construction of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline between Uganda and Tanzania will soon be underway as the final signing of the Host Government Agreement and associated shareholder and tariff agreements to formalise the project's financial and legal structures took place in the latter half of May. The two initiatives will see Tanzania position itself as both an exporter of gas to Kenya as well as a transit hub for oil exports from Uganda to Asian markets.
03 Heineken in talks to buy South African alcohol producer Distell

One of the premium Distell brands; Savanna Dry. As part of the purchase Heineken would acquire the brand alongside other ciders such as Esprit and Hunter's. The Distell portfolio also includes popular wines such as Drostdy Hof and Two Oceans; whiskies like Scottish Leader and Three Ships; and brandies such as Richelieu. Image courtesy: HP Baumeler/WikiCommons
Heineken, the world's second largest brewer, is in talks to acquire South African-based Distell, potentially providing an entry into the wine and spirits market for the European beverage giant. The deal could see a compromise between the two firms who have been competing heavily in the South African alcoholic beverage segment since Heineken launched its Strongbow brand in 2016. Distell has been actively expanding throughout Africa over the past four years, and Heineken's new management team under Dolf van den Brink is potentially eyeing the company as a perfect launchpad to secure market share on the continent. With beer one of the largest consumer beverage expenses in African markets, and states keen to encourage value-added industrialisation, foreign multinationals have been eagerly acquiring stakes in local firms in an effort to grow their margins in the as yet unsaturated African beverage space.
04 Ethiopian telecoms sector moves ahead with market liberalisation
The Ethiopian telecoms sector – one of the last to liberalise in Africa – made the surprise move to signal that its long-awaited telecoms liberalisation strategy is coming into effect. The Ethiopian government announced in mid-May that it would be allowing a Vodafone-led consortium to launch its M-Pesa mobile money service in the country in 2022. This is positive news to potential future market entrants, including current bidders who have collectively offered the government US$500 million to establish local operations. It has long been expected that the 100 million-strong market would be the next state in the region to embrace the mobile fintech revolution, the adoption of which has reached new growth heights following last year's social distancing regulations. Exactly what shape this market was to have remained uncertain as Addis Ababa instituted a directive that only state telecoms provider Ethio telecom would be allowed to operate in the mobile money/fintech space.
05 South Africa to prioritise tech manufacturing, including smartphones and EVs
In May, the South African government announced its intention for the country to become a key tech hub on the African continent. The Department of Trade Industry and Competition (DTIC) published a draft Green Paper on the Advancement of New Energy Vehicles in South Africa for public comment. The paper outlines the country's need to secure a position on the electric vehicle value chain as a manufacturer and not only as an importer. The local telecommunications ministry has come forward with a similar strategy for the acquisition of local manufacturing capacity in key technical areas, including smartphones, telecoms infrastructure components, sensors, telematics devices, and satellite and drone parts. This has been devised in conjunction with the DTIC, with plans to collaborate in the launch of an information and communications technology development hub. This wave of localisation is part of a broader move to prioritise value-addition in key manufacturing segments in generating local production ahead of a dependence on foreign imports.
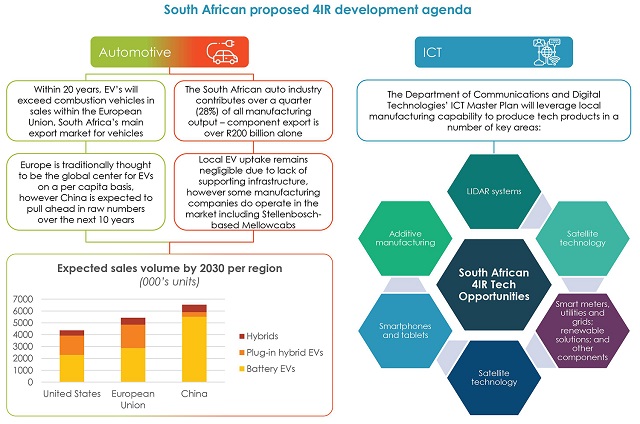
Sources: Statista, 2020; ICT and Digital Economy Master Plan for South Africa, 2020
06 North Africa secures renewable energy boost through new solar initiatives by Algeria, Sudan and French telecoms giant Orange
North Africa is one of the continent's most suited regions for solar power and is currently in the process of furthering the renewable energy agenda as several local stakeholders embarked on solar PV initiatives during May. The most notable saw Algeria announce that it will put out an open call between June and July for independent power producers in procuring 1GW of solar PV. Meanwhile, French telecoms giant Orange SA has promised to fast-track the rollout of solar solutions for its tower installations across North Africa following the success of similar initiatives elsewhere on the continent. South Sudan has similarly begun to adopt solar systems as the subsidy of diesel has pushed up the price of fuel and created shortages, prompting investment into solar solutions as viable alternatives. It is estimated that at the current pace of investment, Sudan will be able to produce 2.4GW of solar power annually within the next 10 years.

The Noor 1 & 2 solar power arrays in Morocco. The Sahara region is one of the world's most ideal locations for solar power, owing to high irradiation and close proximity to potential European export markets in Portugal and Spain. Image courtesy: Richard Allaway/Flickr
07 Guinea launches a new gold mining project as Glencore pilots new tech for mineral tracing
May saw some notable developments in the African mining space. In Guinea, Hummingbird Resources has secured a licence to extract gold at the Kouroussa complex, ending an acquisition process which began in September 2020. This is an important move both for Hummingbird, who will now become a gold producer in multiple African jurisdictions, and for Guinea, whose gold mining industry remains underdeveloped and in need of investment. Meanwhile, Glencore, the world's largest trader of mineral commodities, announced this month that, in conjunction with China Molybdenum Company (CMOC) and the Eurasian Resources Group, it will be launching a blockchain-enabled mineral tracing system for cobalt from mineral consignments from East African mines to their final destinations in electric vehicle (EV) factories. Global stakeholders, such as the European Union, have collaborated in the past few years to initiate mineral tracing systems in eliminating smuggled minerals in the supply chains of EVs, smartphones and other tech products.
08 First ships arrive at Kenya's new deep-water port at Lamu
May marked a milestone for East Africa's economic prospects, as the first ships began to arrive at the new deep-water port of Lamu on Kenya's northern shoreline. The Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia Transport project (LAPSSET) has been in progress for a number of years and is envisioned as a rail, road and pipeline transportation corridor, stretching from the landlocked countries of Ethiopia and South Sudan to the northern port of Lamu. The corridor also allows Kenya to capture a greater share of the Indian Ocean shipping industry, which is growing faster around the Red Sea region. The work is being finalised by the Chinese Communication and Construction Company at a total cost of US$3 billion. LAPSSET developments have faced a number of construction delays, including concerns surrounding the impact of the project on local communities and the environment, alongside the risk of strikes posed by Al-Shabaab rebels from neighbouring Somalia.
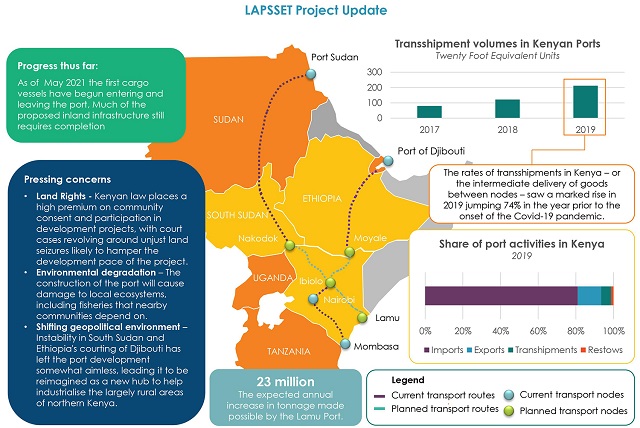
Sources: Human Rights Watch, 2018; Maritime Executive, Hellenic Shipping News, 2020; Times Live 2021
09 MTN expands its services and offerings with World Bank support
South African-based MTN announced in May that it would be partnering with the World Bank in a US$2 billion programme aimed at expanding the reach of its service offerings in South Africa. Within this year, the company aims to employ 10,000 mobile money (MoMo) agents stationed at kiosks around the country who can deposit and withdraw money on a customer's behalf in generating uptake. MTN will also seek to expand its service offerings, including the ability to access microloans and pay for groceries. Meanwhile in Rwanda, MTN is continuing its digitisation strategy in line with the government's agenda to achieve a cashless society by launching a new subsidiary, Mobile Money Rwanda. This will also allow the freedom to develop MTN's local digital strategy in a more independent and agile fashion. Although the company was a late market entrant compared to Vodafone's M-Pesa, superior digitised service and product offerings could ensure the firm's position as a market leader.
10 Southern African states in talks over construction of new border crossing
Regional integration was on the agenda for Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries in May, as Botswana, Zambia and Zimbabwe discussed the construction of a potential new road link across the Zambezi River. The Kazungula Bridge project had until recently not included Zimbabwe, but the other two countries, Botswana and Zambia, have now both agreed to incorporate a Zimbabwean section into the final bridge development. Zimbabwe, as a token of gratitude, has agreed to front a third of the final total cost of the project, which stands close to US$260 million. The country's inclusion in the project represents broader rapprochement in the region since the end of Robert Mugabe's rule in 2017. The former president had disapproved of the project, leading to Zimbabwe's subsequent exclusion. It is believed that Zimbabwe's change in leadership is bringing the country towards improved relations for regional developmental and economic integration agendas.

The Kazungula Bridge crossing over the Zambezi River on the triple border of Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. The construction of such road links across the continent have been essential for the growth of local industries and will be a key factor in the success of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). Image courtesy: JonGT/WikiCommons, 2020
OTHER NOTABLE STORIES
Angola's oil and gas sector to receive further investment and consolidation Continued developments in the Angolan hydrocarbon industry were announced in May as local firms seek to intensify their operations and hedge against the low oil price. Total's offshore Zinia project has come online with production set to continue until 2045. Meanwhile, multinationals BP and Eni are in talks to merge their local operations, including their LNG facilities. If successful, the merger would create Africa's largest energy company.
Somali politicians reach agreement on new elections, avert civil strife The tense standoff which had brought the Somali political system to the point of breakdown in April has come to a fruitful conclusion, with local leaders agreeing to terms that will see elections being held. The Lower House of the Somali Parliament had voted to extend the President's four-year term, a move which was rejected by the Senate and caused the security services to split along clan lines. The new agreement has come at a key time for the country as it seeks to lure in foreign investors to help develop its proven oil and gas reserves.
Egypt and Turkey seek to overhaul tense ties with open talks on Libya In May, Egypt and Turkey held talks to discuss the situation in Libya, where they support competing factions. The meeting forms part of a broader strategy by Turkey to reconcile with other US-aligned North African states in the region. Additional issues discussed included the situation in Syria, as well as cooperation on security issues in the Eastern Mediterranean. The two parties have agreed to hold further tripartite talks along with Libyan representatives to help formulate a long-term solution for the fractured country.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

