Edited by Hitender Mehta
All eyes are set on the upcoming monsoon session of the Parliament beginning August 1, 2011, where various bills of great national importance are likely to be debated and passed. The important ones include the likes of Lokpal Bill, Land Acquisition Bill and Companies Bill.
The Government and the team led by Mr. Anna Hazare have released their respective versions of Draft Lokpal Bill. The Bill provides for the establishment of the institution of Lokpal to inquire into allegations of corruption against certain public functionaries and for matters connected therewith. There are however differences between the two drafts on certain key issues.
The Bill relating to the land acquisition is expected to be a fresh initiative, and not an amendment to the Land Acquisition Act of 1894. Amidst much political hype and the ongoing controversy in Uttar Pradesh following recent court orders annulling the land acquisition by the State Government, all affected parties including the State Government, the villagers, the developers, the bankers and the investors are jittery. There appears to be a state of turmoil all across. In this backdrop, the new Bill on land acquisition is stated to encompass the Resettlement and Rehabilitation Bill, too, making it a single piece of legislation.
Another important and long awaited Bill expected to be tabled is the Companies Bill, which seeks to replace the Companies Act, 1956 and introduce a modern company law in line with global best practices.
Much action is there on the cards. Let's keep our fingers crossed!
INCOME TAX
Reimbursement of salary of seconded personnel as liable to tax in India
The Authority for Advance Rulings (AAR), in a recent ruling in case of Verizon Data Services India Private Limited [AAR 865 of 2010], held that reimbursement of salaries of seconded personnel was taxable in India as "fee for included services", under the India-US Treaty.
In the above case, the issue before the AAR was whether the reimbursement of salary of seconded personnel by the applicant to the seconding entity (FCo) outside India resulted in any income liable to tax in India in the hands of FCo.
The AAR held as follows:
- While the seconded personnel rendered services to the applicant, they remained employees of FCo and their employment could only be terminated by Fco. Thus, services rendered by the seconded employees were rendered on behalf of FCo and what accrued to FCo was income from services rendered by its employees to the applicant.
- The services rendered by the seconded personnel were managerial in nature and, therefore, were taxable in India under Section 9(1)(vii) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, which deems payment of fee towards technical, managerial or consultancy services, as income arising in India.
- The condition that services should 'make available' technical knowledge as stipulated in Article 12(4)(b) of the India-US Treaty, applies only to 'technical' services and does not apply to consultancy services unless technical services were embedded therein. Managerial services could be said to be consultancy services and since no technical services were embedded therein, the 'make available' stipulation did not apply and payment for such services constituted 'fee for included services', under Article 12 of the India-US Treaty. Accordingly, the reimbursement of salary of seconded employees was liable to tax in India and the applicant was required to withhold tax in India on the same.
Comments: Supervision and control over activities of employees and liability for acts of the employees are essential ingredients of employer-employee relationship. The AAR, in the aforesaid ruling, has given undue weightage to the fact that the seconded personnel continued to be on the rolls of the FCo, and has not appreciated the distinction between economic employer and legal employer, which was brought out in case of IDS Software Solutions Pvt Ltd [122 TTJ 410] by the Bangalore Bench of the Tribunal. In that case, it was held that the reimbursement of salary of Managing Director of the Indian company, who was on secondment from overseas company, was not liable to tax in India in the hands of such overseas company since the Managing Director's economic employer was the Indian company. The view taken by AAR is also contrary to the view taken in an earlier ruling in case of Cholamadalam MSM General Insurance: [309 ITR 356] and by the Delhi High Court in the case of DIT v. HCL Infosystems Ltd. [274 ITR 261].
Further, the view of the AAR that if consultancy services do not include technical services, the 'make available' condition will not apply, in our view, does not appear to be correct. The Memorandum of Understanding appended to the India-US Treaty, explaining the scope of Article 12(4)(b) of the Treaty, clearly states that consultancy services which are not of technical nature cannot be included services.
Nevertheless, the aforesaid ruling of the AAR has created a lot of uncertainty and multi-national corporations having similar secondment arrangements may need to review the impact of the ruling on the stand taken by them regarding the tax implications. Also, enterprises proposing to enter into similar arrangements shall have to take due care in structuring the transaction to avoid unnecessary tax exposure in India.
Mumbai ITAT ruling on equipment royalty
The Mumbai Bench of the Tribunal (ITAT) in case of Yahoo India P. Ltd. [ITA no. 506/Mum/2008] held that in order to constitute 'royalty' for use of equipment, the relevant test to be applied is whether the payer obtains operational control of the equipment.
In the above case, the taxpayer, an Indian company, paid certain amount to Yahoo Holdings (Hong Kong) Ltd., a Hong Kong based company, as consideration for placing banner advertisements on the web portal of Yahoo Hong Kong. The main issue before the ITAT was whether the said payment could be classified as 'royalty' under Section 9(1)(vi) of the Income Tax Act, 1961 for 'use' or 'right to use' any industrial, commercial or scientific equipment. The ITAT held as follows:
- The word "use" in relation to equipment occurring in clause (iva) of Explanation to Section 9(1)(vi) is not to be understood in the broad sense of availing of the benefit of an equipment. The context and collocation of the two expressions "use" and "right to use" followed by the word "equipment" indicate that there must be some positive act of utilization, application or employment of equipment for the desired purpose. What is contemplated by the word "use" in clause (iva) of Explanation 2 to Section 9(1)(vi) is that the customer came face to face with the equipment, operated it or controlled its functions in some manner.
- Uploading and display of banner advertisement on the portal was entirely the responsibility of Yahoo (Hong Kong).
The taxpayer had no right to access the portal of Yahoo (Hong Kong). Therefore, the impugned consideration could not be treated as royalty for use of or right to use any equipment.
Comments: The ITAT decision reinforces the position that an essential ingredient of constituting 'use' or 'right to use' equipment is acquisition of operational control of the equipment by the payer. In arriving at this conclusion, the ITAT relied on recent decision of the Delhi High Court in case Asia Satellite [332 ITR 340] and of AAR in ISRO Satellite [307 ITR 59].
Taxability of transfer of technical know-how and services
The AAR, has, in a recent ruling in the case of Lanka Hydraulic Institute Limited [AAR no. 874 of 2010], held that income from transfer of technical know-how and services would be taxable as royalty.
In the above case, the applicant was a tax resident of Sri Lanka. The Kolkata Port Trust awarded a contract to WAPCOS, a Public Sector Undertaking, which sub-contracted the work to the applicant. The issue before the AAR was whether the payments received by the applicant from WAPCOS were liable to tax in India as per provisions of India-Sri Lanka Treaty.
The AAR held as follows:
- The applicant did not have a Service PE in India since personnel of the sub-contractor appointed by the applicant did not work under the supervision of the applicant.
- The main object of the agreement was to provide technical know-how to WAPCOS and the consideration payable was for the use of scientific work, model, plan and for use of scientific equipment and scientific experience. Therefore, consideration received by the applicant was taxable as "royalty" under Section 9(1)(vi) of the Act as well as Article 12 of the India -Sri Lanka Treaty.
- The consideration was not in the nature of "fees for technical services"; in the absence of a specific Article in India-Sri Lanka Treaty, "fee for technical services" would liable to tax in accordance with Article 22 relating to 'Other Income' and not under Article 7 relating to taxation of 'Business profits'.
Comments: The AAR has interpreted the term 'other personnel' as used in Article 5(2)(i) of the India-Sri Lanka Treaty, relating to Service PE, as not including the personnel of a subcontractor if such personnel are not working under the supervision of the foreign entity. However, the observation of the AAR that in case of a Treaty wherein there is no specific clause for taxation of 'fee for technical services' (FTS), the income would be treated as 'Other income' as not as 'business profits' does not appear to be correct. If the technical services are rendered in pursuance of the business activities of the service provider, payment towards 'fee for technical services', in our opinion, in absence of any specific article in the Treaty dealing with taxation of 'fee for technical services', would fall for consideration under Article 7, relating to taxation of 'business profit'.
Depreciation admissible in case of sale and leaseback transaction
The Delhi High Court, in case of CIT v. Cosmo Films Limited [ITA 1404/2008], has held that the lessor is entitled to depreciation in case of sale and lease back transaction.
In the aforesaid case, the assessee purchased equipment from Haryana State Electricity Board (HSEB), which was already installed at the HSEB's Power Station at Faridabad and immediately leased the said equipment back to HSEB. The assessee claimed depreciation @ 100% (being the applicable rate of depreciation) on the said equipment. The Revenue disallowed depreciation on the ground that the transaction was not one of purchase and lease but was a pure financing transaction.
Against the order of the Tribunal, which upheld the assessee's claim, the Revenue filed an appeal before the High Court. The Revenue referred to the decision of the Supreme Court in the case of Asea Brown Boveri Ltd v. Industrial Finance Corporation of India [AIR 2005 SC 17], and contended that as risks and rewards incidental to the ownership of an asset were transferred to the lessee (HSEB), the transaction was to be considered as one of granting of loan. The assessee's contention was that the transaction was genuine and once ownership of the asset was transferred to the assessee, the assessee was entitled to claim depreciation thereon.
The High Court, dismissing the Revenue's appeal, held as follows:
- The documents brought on record show that there was transfer of title and the ownership of the equipment was that of the assessee. The fact that the transaction was entered into by HSEB in order to raise finance for its day-today needs and that HSEB decided to go in for tapping the system of sale and lease back assets as a mode of raising finance at a lower cost does not bind the assessee. In other words, as per the Court the motive of HSEB in entering into the aforesaid transaction (to raise finance), could not also be said to be the motive of the assessee (to grant loan) and the nature of the transaction was not to be viewed from the prism of the motive of HSEB.
- Merely because an assessee gets a commercial advantage because of the factoring in of a tax benefit, it cannot be said that the transaction is not genuine. There is no finding or evidence to indicate that the transaction was not genuine. The observations of Chinappa Reddy, J in McDowell's case is not good law in view of Union of India v. Azadi Bachao Andolan [263 ITR 706 (SC)] where it was held that "tax planning may be legitimate provided it is within the framework of law";
- The observations in Asea Brown Boveri Ltd (supra) with regard to the nature of a financial lease are not of much use to the Revenue in view of the factual backdrop that the transaction has been found to be genuine. Once it is established that the ownership of the equipment is that of the assessee, it is clear that the assessee is entitled to claim depreciation.
Comments: The aforesaid decision would help substantially clear the air as to the genuineness of the sale cum lease back transactions, which is routinely doubted by the Revenue and impart certainty in relation to the issue of allowability of depreciation to the lessor in such transactions.
We may point out that Explanation 4A to section 43(1) of the Act, inserted, with effect from 01.10.1996, provides the basis for computation of 'actual cost' on which depreciation is to be allowed to the lessor in such cases.
The aforesaid case was argued by Mr. Ajay Vohra and assisted by Ms. Kavita Jha from our Chamber.
Transfer pricing cases
Some of the cases argued by our Chambers are reported below:
- iPolicy Network (P) Ltd. v. ITO
The Delhi Bench of the Tribunal In the c a s e o f i Po l i c y Network (P) Ltd. [ITA No. 5504/Del/10] held that the amendment to the second proviso to section 92C(2) of the Income-tax Act ("the Act"), providing for arm's length range of +/(-) 5%, by the Finance (No.2) Act, 2009, being a substantive amendment, could not have retrospective operation and would be effective prospectively, i.e. from , 01-10-2009. In that case, since adjustment computed by the TPO in the case of iPolicy was within the arm's length range of +/(-) 5% as per the unamended proviso to section 92C(2) of the Act, the same was directed to be deleted. - Destination of the World (Sub-continental) India Pvt. Ltd.
v. ACIT
In the case of Destination of the World (Sub-continental) Pvt. Ltd. [ITA No. 5534/Del/2010], the Delhi Bench of the Tribunal upholding the internal benchmarking undertaken by the taxpayer, engaged in the business of rendering (a) inbound,(b) outbound and (c) domestic travel services, concluded that such internal comparison is valid in all methods and in the first instance, the arm's length price of controlled transactions are to be established by comparing the same with internal controlled transactions undertaken for same or similar economic scenario. - CRM Services India Pvt. Ltd. v. ITO
In the case of CRM Services India (P) Ltd. [ITA No. 4796/Del/2010], the Delhi Bench of the Tribunal held that since the additional capacity was created by the taxpayer, a captive call centre service provider, at the behest of the parent company, the expenditure on rent for the idle premises because of frustration of a prospective contract was on account of the parent company and, therefore, is to be taken into account as operational expenses. The Tribunal at the same time directed that adjustment is to be given for idle capacity to the taxpayer.
SERVICE TAX
Point of Taxation Rules, 2011
Point of Taxation Rules, 2011 were initially optional for 3 months' period from April 1, 2011 to June 30, 2011 w.e.f. July 1, 2011; these rules have become mandatory. According to these rules, the service tax assessees have to pay tax on accrual basis (Payment received or invoice issued whichever is earlier) rather than on realization basis. Subsequently, following clarifications have been issued:
- These rules will not be applicable to professionals like CS/CWA/CA, Architect, etc. provided they are not corporate assessees.
- The service tax w.r.t. invoices issued on or before June 30, 2011, payment of service tax will be on realization basis only, (as earlier).
- The assessees would need to maintain the system to review the payment reconciliation. Whether payment received belong to invoice issued before July 1, 2011 or afterwards in order to avoid duplicate payment of service tax.
- The said rules are not applicable to consulting engineer w.e.f. July 1, 2011 vide Notification No. 41/2011-ST dated June 27, 2011
(Source: Notification No. 18/2011-ST dated March 1, 2011)
CUSTOMS & EXCISE
Refund of 4% CVD (SAD) Extension of time upto September 15, 2011 for using re-credited 4% CVD (SAD) amount in DEPB
The Circular No. 11/2011- Customs dated February 24, 2011; regarding procedure on refund of 4% Countervailing Duty (Special Additional Duty) provides the facility of manual filing of Bill of Entry for utilizing the amount of re-credited 4% CVD refunds (SAD) for payment of duty in case of re-credited DEPB/ Reward Scheme scrips up to June 30, 2011. This period has been extended up to September 15, 2011 for using re-credited 4% CVD (SAD) amount in DEPB with following conditions:
- The extension of utilization of re-credited amount of SAD refund in relevant scrip is granted for two months i.e. upto September 15, 2011. No further extension shall be given.
- The importers shall utilize re-credited amount of SAD refund in scrips for payment of CVD and BCD only and not for payment of SAD subsequently.
- Commissioners of Customs should ensure that issuance of consolidated certificate indicating total amount of 4% SAD refund sanctioned is carried out in time without any delay.
(Source: Customs Circular No.30/2011 dated July 19, 2011)
ER-8 Return notified for manufacturers paying duty at concessional rate of 1%
The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) has notified new return in Form "ER-8" for the manufacturer(s) who are manufacturing "excisable goods" liable to concessional rate of 1% Central Excise Duty (CENVAT) as per Notification No. 1/2011-Central Excise, dated March 31, 2011.
The said Return is to be filed quarterly within 10 days at the end of each quarter viz. April – June, July – September, October – December, January – March. However, the e-filing facility at ACES website has not yet been updated by the CBEC and in order to ensure compliance, the assesses should file "ER-8" return manually with their respective Division / Range office having jurisdiction over their factory, or otherwise.
(Source: Notification No.15/2011-Central Excise (N.T.) dated June 30, 2011)
CORPORATE LAWS/SEBI
Waiver of approval of Central Government for payment of managerial remuneration to professionals by companies having no profits or inadequate profits
In order to promote the development of Indian Corporate sector yet another step towards simplification of procedure under the Companies Act, 1956, MCA has amended Schedule XIII to the Companies Act, 1956 w.e.f. July 14, 2011.
Pursuant to this amendment, no approval of Central Government will be required by the listed companies and their subsidiary companies, which are not having profits or having inadequate profits for payment of remunerations exceeding ` 4 Lacs p.m., if the managerial person:-
- is not having any direct or indirect interest in the capital of the company or its holding company or through any other statutory structures at any time during last two years before or on the date of appointment; and
- is having a graduate level qualification with expert and specialized knowledge in the field of his profession. However, the other general conditions specified in Para (c) of Section II of Part II of Schedule XIII to the Act shall continue to be complied with.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 46/2011 dated July 14, 2011)
Companies Director Identification Number (Third Amendment) Rules, 2011 and Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009 (Amendment) Rules, 2011
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has amended Rule 2(ii) of Companies (Director Identification Number) Rules, 2006 and Rule 2(1)(iv) and Rule 10 of Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009, to include Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN) in Director Identification Number (DIN). To obtain DPIN, application shall be made in Form DIN 1. Further, if a person holds both DIN and DPIN, his DPIN stands cancelled and DIN shall be sufficient for being appointed as a Designated Partner under Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
(Source: MCA G.S.R. 507 (E) dated July 05, 2011)
Guidelines for Fast Track Exit mode for defunct companies under Section 560 of the Companies Act, 1956
To give fast track exit to a defunct company, for getting its name struck off from the Registrar of Companies, the Ministry has modified the existing route and has prescribed the new Guidelines effective from July 3, 2011.
Any defunct company desirous of getting its name struck off from the Registrar of Companies under Section 560 of the Companies Act, 1956 shall now make an application in Form FTE, annexed electronically on the MCA portal accompanied by a filing fee of ` 5,000/-.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 36/2011 dated June 7, 2011)
Filing of Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account in eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) mode
In supersession of MCA Circular no. 9/2011 dated March 31, 2011 and MCA Circular no. 25/2011 dated May 12, 2011, MCA has mandated certain class of companies to file Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account along with Directors' Report and Auditors' Report for the year 2010-11 onwards by using XBRL taxonomy.
The following classes of companies have to file the financial statements in XBRL form only from the year 2010-11.
- All companies listed in India and their Indian subsidiaries
- All companies having a paid up capital of ` 5 crore and above
- All companies having a turnover of ` 100 crore and above.
However, banking companies, insurance companies, power companies and Non-Banking Financial Institutions are exempted from XBRL filing, till further orders.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 37/2011 dated June 7, 2011)
Green Initiatives in the Corporate Governance – Clarification regarding participation by Shareholders or Directors in meetings under the Companies Act, 1956 through electronic mode
The MCA has further clarified that:
- It is not mandatory for companies to provide its directors, the facility to attend meetings through video conferencing.
- In respect of shareholders' meetings to be held during financial year 2011-12, video conferencing facility for shareholders is optional. Thereafter, it is mandatory for all listed companies.
- Where the company opts to provide video conferencing facility, they have to comply with the procedures prescribed in the Circular nos. 27/2011 & 28/2011 dated May 20, 2011 in this regard.
- The company is free to select video conferencing facility of any agency but the Chairman of the meeting and Secretary of the company has to ensure that such facility is proper and all persons communicate effectively without any intermediary.
- In the case of e-voting in general meetings, the MCA has presently authorized only National Security Depository Ltd and Central Depository Services (India) Ltd as agencies for providing and supervising electronic platforms for electronic voting subject to the conditions that they obtain a certificate from Standardization Testing and Quality Certification (STQC) Directorate, Department of Information Technology, Ministry of Communications and IT, Government of India, New Delhi.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 35/2011 dated June 6, 2011)
Guidelines for declaring financial institution as Public Financial Institution under Section 4A of the Companies Act, 1956
In order to be declared as Public Financial Institution (PFI) under Section 4A of Companies Act, 1956; a financial institution needs to fulfil the below mentioned criteria:
- A company or corporation should be established under a special Act or the Companies Act being Central Act;
- Main business of the company should be industrial/ infrastructural financing;
- The company must be in existence for at least 3 years and their financial statement should show that their income from industrial/infrastructural financing exceeds 50% of their income;
- The net worth of the company should be Rupees One Thousand Crore.
- Company should be registered as Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC) with RBI or as an Housing Finance Company (HFC) with National Housing Bank;
In the case of CPSUs/ SPSUs, no restriction shall apply with respect to financing specific sector(s) and net worth.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 34/2011 dated June 2, 2011)
ROCs not to accept any request from defaulting companies and directors
In order to ensure corporate governance and proper compliances of provisions of the Companies Act, 1956, MCA has decided that no request, whether oral, in writing or through e-forms, for recording any event based information/ changes shall be accepted by the Registrar of Companies (ROC) from the defaulting companies and their Directors which have not filed Balance Sheet or Annual Return for any of the financial years 2006-07, 2007-08, 2008-09 and 2009-10 with the Registrar of Companies as required u/s 220 and/or u/s 159 of the Companies Act, 1956; unless they file their updated Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Accounts and Annual Return with the ROC.
However, in the interest of other stakeholders' certain event based information/ changes will continue to be accepted by the ROC from such defaulting companies namely Forms 32, 20B, 21A, DIN 3, 21, 23Ac, 23ACA, I INV, 23B, 66.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 33/2011 dated June 1, 2011 and MCA General Circular No. 38/ 2011 dated June 20, 2011)
Allotment of Director Identification Number under Companies Act, 1956
Furnishing of Permanent Account Number (PAN) has been made mandatory in DIN eform-1. Further, all the existing DIN holders who have not furnished their PAN earlier at the time of obtaining the DIN, are required to furnish their PAN by filing DIN-4 e-form by September 30, 2011 failing which their DIN will be disabled and they shall also be liable for penalty. Furthermore, w.e.f. June 12, 2011 all DIN-1 and DIN-4 applications have to be digitally signed by practising Chartered Accountant/ Company Secretary or Cost Accountant.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 32/2011 dated May 31, 2011)
Depreciation for the purpose of declaration of Dividend under Section 205 in case of companies referred to in Section 616 (C) of the Companies Act, 1956
Electricity companies: Depreciation: Special Act v. General Act
The rates of depreciation and methodology notified under Electricity Act, 2003 are inconsistent with the rates given in Schedule XIV of the Companies Act, 1956. The former being a special Act will prevail over the rates notified under Schedule XIV of the Companies Act by virtue of section 616(c) of the Companies Act, 1956.
Accordingly, MCA has clarified that companies referred to in Section 616(c) of the Companies Act can distribute dividend out of profits arrived at after providing for depreciation following the rates as well as methodology notified by CERC and the same shall be sufficient compliance of section 205 of the Companies Act, 1956.
(Source: MCA General Circular No. 31/2011 dated May 31, 2011)
Admission of Limited Liability Partnerships as members of Stock Exchanges
Securities Contract Regulation Rules, 1957 (SCRR) do not explicitly mention LLPs as and eligible entity to be admitted as members of Stock Exchanges as the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 was a subsequent development. As per the LLP Act, LLP is a body corporate. Sub-rule 4A and 5 of Rule 8 of the SCRR provides that Limited Liability Companies (LLC) and partnership firms are eligible to be admitted as members of stock exchanges. In this context, LLPs are akin to LLC and partnership firms.
In view of the above, SEBI has clarified that Stock Exchanges may consider granting membership to LLPs subject to LLP complying with the conditions laid down in Rule 8(4A) of the SCRR, as far as it can apply to LLPs.
(Source: SEBI Circular No. CIR/MIRSD/12/2011 dated July 11, 2011)
Shareholding of promoters/ promoter group to be in dematerialized mode
To promote dematerialization of securities, encourage orderly development of the securities market and to improve transparency in the dealings of shares by promoters including pledge / usage as collateral, SEBI in consultation with Stock Exchanges, has decided that the securities of companies shall be traded in the normal segment of the exchange if and only if, the company has achieved 100% of promoter's and promoter group's shareholding in dematerialized form latest by the quarter ended September 2011 as reported to the stock exchanges.
In all cases, wherein the companies do not satisfy the above criteria, the trading in securities of such companies shall take place in trade for trade segment.
(Source: SEBI Circular Cir/ISD/ 3/2011 dated June 17, 2011)
Change of name by listed companies
SEBI Circular No. SEBI/MRD/Policy/AT/ Cir-20/2004 dated April 30, 2004 needs to be complied by all listed companies seeking change of name which stated that "At least 50% of its total revenue in the preceding 1 year period should have been accounted for by the new activity suggested by the new name". However, companies, whose gestation period of the business is usually longer and the revenue stream often delayed, found it difficult to comply with the aforesaid provision. Therefore, SEBI has modified para 2.2 of the said circular as under:
2.2. At least 50% of its total revenue in the preceding 1 year period should have been accounted for by the new activity suggested by the new name
Or
The amount invested in the new activity/project (Fixed Assets + Advances + Works In Progress) is atleast 50% of the assets of the company. The 'Advances' shall include only those extended to contractors and suppliers towards execution of project, specific to new activity as reflected in the new name.
To confirm compliance of the aforesaid provision 2.2, the company shall submit auditor's certificate to the exchange.
(Source: SEBI Circular CIR/MRD/DP/ 07 /2011 dated June 16, 2011)
Standardisation of rating symbols and definitions
In order to have easy understanding of the rating symbols and their meanings by the investors, and to achieve high standards of integrity and fairness in ratings, the Corporate Bonds and Securitisation Advisory Committee of SEBI has recommended that the rating symbols and their definitions should be standardised. The New rating symbols and definitions as given in annexures 1-6 of the given circular shall henceforth be used for the new ratings/ reviews by the Credit Rating Agencies.
(Source: SEBI circular CIR/MIRSD/4/2011dated June 15, 2011)
Processing of investor complaints against listed companies in SEBI Complaints Redress System (SCORES)
SEBI has commenced processing of investor complaints in a centralized web based complaints redress system 'SCORES'. The salient features of this system are:
- Centralised database of all complaints,
- Online movement of complaints to the concerned listed companies,
- Online upload of Action Taken Reports (ATRs) by the concerned companies, and
- Online viewing by investors of actions taken on the complaint and its current status.
This Circular supercedes the Circular No.OIAE/Cir-1/2009 dated November 25, 2009 so far as it relates to Annexure-C to the said Circular wherein the companies had to submit physical ATRs on the complaints forwarded by SEBI to them.
(Source: SEBI circular CIR/OIAE/2/2011dated June 3, 2011)
Redemption of Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) into underlying equity shares
SEBI has put in place, the framework for redemption of IDRs in consultation with RBI as under:
- After the completion of one year from the date of issuance of IDRs, redemption of the IDRs shall be permitted only if the IDRs are infrequently traded on the stock exchange(s) in India.
Explanation- For this purpose, IDRs shall be deemed to be "infrequently traded" if the annualized trading turnover in IDRs during the six calendar months immediately preceding the month of redemption is less than five percent of the listed IDRs.
- The issuer company shall test the frequency of trading of IDRs on a half yearly basis ending on June and December of every year.
- When the IDRs are considered "infrequently traded" on the above basis, it shall be the trigger event for redemption.
- The issuer company shall make a public announcement in an English and Hindi language newspaper with wide circulation in the prescribed format (including brief details about the trigger of the redemption event, time period for submission of application and the approach for processing the applications) as well as notify the stock exchanges. Such announcement shall be made within seven days of closure of the half year ending on which the liquidity criteria is tested. A suitable format for this purpose shall be prescribed by the stock exchange(s).
- The IDR holders may submit their application to the domestic depository for redemption of IDRs within a period of thirty days from the date of such public announcement.
- The redemption of IDRs shall be completed within a period of thirty days from the date of receipt of application for redemption.
- Pursuant to such redemption, the domestic depository shall notify the revised shareholding pattern of the issuer company to the concerned stock exchanges within seven days of completion of the process of redemption.
(Source: SEBI circular CIR/CFD/DIL/3/2011 dated June 3, 2011)
CSR INITIATIVE
My City My Park-Environmental Film Festival
A film festival on the theme –"My City – My Park" was organized by CSR Department PVR Cinemas - PVR Nest on June 10, 2011. The focus of the programme was Park and its importance in our lives. 24 adolescent girls from Reproductive and Child Health Training of Vaish Associates Public Welfare Trust participated in the program. The girls were from Pahadi and Jaunapur slums at Mehrauli.
4 children films based on the theme were screened at PVR Plaza, Saket, Delhi. Children from several Government schools and NGOs were present at the event. Besides, there was quiz on the theme. Enthusiastic children spoke about importance of parks in an area. Some students recited self composed poems too. Young children from an NGO named MAD (Make A Difference) presented a silent play on the theme.
Object of this event was to create awareness among children for environment. How green parks will help clean the environment and keep children fit, open area for children to play. Children should keep the park clean and motivate others to do the same, and saving parks from turning into dump yards.
Scholarship
Vaish Associates Public Welfare Trust Scholarship Program has announced Scholarship Program for underprivileged students from class 6 to college which is to be distributed on July 30 - 31, 2011 at Diwanshree Apartment, Ferozeshah Road, Delhi.
VAISH DEAL TRACKER
Vaish advises Biltech Building Elements Ltd. on acquisition of Mohit Industries Ltd.
Biltech Building Elements Limited (Biltech), an Avantha Group Company engaged in manufacture of lightweight autoclaved aerated concreate ("AAC") a certified green building material, has acquired the AAC business of Mohit Industries Limited (MIL) a listed Indian Company inter-alia engaged in the name & marketing of yarns & grey finished products.
Vaish Associates acted as the legal counsel for Biltech and assisted the Company in conducting legal due diligence, negotiations and drafting of the transaction documents, including the Asset Purchase Agreement and the Escrow Agreement and the closing of the transaction.
The team comprised Mr. Satwinder Singh, Partner; Mr. Amit Bhandari, Head –Real Estate Practice –Mumbai; Mr. Gaurav Jaggi, Ms. Divya Suman and Mr. Hitesh Sablok, Senior Associates.
Vaish advises IFCI VC Fund's ` 30 crore investments in Amber Enterprises
Vaish Associates advised on IFCI Venture Capital Fund's ` 30 crore ($6.75m) private equity investment in Delhi-based consumer durable goods company Amber Enterprises, which is India's largest original equipment manufacturer of home appliance.
The investment was made in the form of compulsory convertible debentures and the money raised would be utilised by the company to fund its capex and working capital requirements of financial year 2011-12.
The team comprised Mr. Satwinder Singh, Partner; Mr. Mohit Chaurasia, Ms. Divya Suman, Senior Associates; and Mr. Pashupati Nath, Associate.
The team advised on the structuring, negotiations and preparation of the term sheet and the investment agreement and other related documents. IFCI Green India Venture Funds was advised by its in-house legal team.
Vaish advises on SPAR Group expansion
The NASDAQ listed SPAR Group has signed a joint venture agreement with Delhi-based Krognos Integrated Marketing Services to expand its operations in India. SPAR will hold a 51 percent ownership interest in the venture and the new venture will operate under the name SPAR Krognos Marketing India Private Limited.
Vaish Associates acted as a legal advisor for SPAR. The team comprised Mr. Vinay Vaish, Partner; Mr. Manish Tully, Principal Associate; and Ms. Juhi Chaudhary, Associate.
Vaish advises Jaypee Group for its water pipeline project
Vaish advised Sangam Power Generation Company Limited; Prayagraj Power Generation Company Limited; and Jaiprakash Associates Limited (hereinafter together referred to as "Companies") for engineering, procurement and construction of the raw water pipeline required for Sangam Thermal Power Project and Prayagraj Thermal Power Project.
Vaish team consisting Mr. Satwinder Singh, Partner; Ms. Rupa Radhakrishnan, Principal Associate; and Mr. Hitesh Sablok, Senior Associate assisted the Companies in negotiating, drafting and finalizing the transaction documents, including the Supply Contracts and the Services Contracts.
Vaish advises De Dietrich's slump purchase of Nile's division for ` 58.5 cr to enter manufacturing in India
Vaish Associates Advocates advised on French company De Dietrich Process Systems' acquisition of Nile Limited's glass-lined equipment and pressure vessels division business for ` 58.5 crore in a slump sale.
De Dietrich is a three hundred year old global provider of mechanical and thermal process engineering for the pharmaceutical and chemical industry and with this buy out has made a foray into the Indian manufacturing industry.
The legal work included legal due diligence, structuring, negotiations and drafting of the transaction documents including the business transfer agreement.
Vaish Associates' Mumbai corporate Partner Martand Singh led the transaction with Senior Associates Amitjivan Joshi, Vivek Talreja and Associate Priyesh Sharma for De Dietrich.
VAISH ACCOLADES
Conferences/ Academic contributions
- Mr. Ajay Vohra and Mr. Rupesh Jain were invited to Seoul, South Korea; to make presentation at the Seminar "Legal and Tax Issues for Companies Investing in India" jointly hosted by KCCI (Korea Chamber of Commerce & Industry) and Yulchon, Attorneys at Law, on June 7, 2011. Mr. Ajay Vohra spoke on the topic, "Legal & Tax Issues for Companies Investing in India" and Mr. Rupesh Jain addressed on "Transfer Pricing Trends and Issues".
- Ms. Divya Suman was invited to address the officers of the Indian Corporate Law Service (ICLS) at The Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA) on June 15, 2011. She spoke on the topics "Statement of Affairs, Taking possession and Inventory of Assets, Valuation and sale of Assets;" and "Recovery of dues from Contributories, Preferential payments & Distribution including Settlement of Claims, Data Collection & Reporting."
- Mr. Gaurav Jain contributed an article titled "Taxation of Foreign Companies in Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010 - A Summation" on www.taxindiaonline.com. His article was published on July 19, 2011 and can be accessed at the URL: http://www.taxindiaonline.com/RC2/inside2.php3?filename=bnews_detail.php3&newsid=12790
- Mr. Hitender Mehta was invited to address the Gurgaon CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI on the topic "Limited Liability Partnerships –Practical Aspects" in its meeting held on July 15, 2011.
- Mr. Hitesh Sablok was invited to address the study circle meeting on "Foreign Direct Investment - Recent Updates" organized by East Delhi Study Group of NIRC of ICSI on July 16, 2011.
- Ms. Puneeta Kundra was invited to address the Study Circle Meeting on "Limited Liability Partnership – Legal & Tax Implications" organised by NIRC of ICSI on July 15, 2011.
- Mr. Rupesh Jain was invited to address Seminar on "Private Equity-Catalyst to Economic Growth" organized by NIRC of ICSI on June 25, 2011 at New Delhi. His topic of presentation was "Tax Considerations in International Financing Transactions".
- Mr. Sachit Jolly co-authored the India Branch Report on "Key practical issues to eliminate double taxation of business income" published in "Cahiers de Droit Fiscal International", for the 2011 IFA Congress in Paris, France.
- Mr. Satwinder Singh was invited to following forums:
-
- "Workshop on FEMA –from Concepts to Practice" organised by All India chartered Accounts' Society on July 23, 2011 at New Delhi.
- Seminar on "Private Equity-Catalyst to Economic Growth" organised by NIRC of ICSI on June 25, 2011. His topic of presentation was "Regulatory and Drafting Considerations and Role of Company Secretary".
- Mr. Satwinder Singh and Mr. Pashupati Nath contributed a chapter on the Indian Q&A for "PLC Cross-border Restructuring and Insolvency Handbook 2011/12", published by the Practical Law Company Limited.
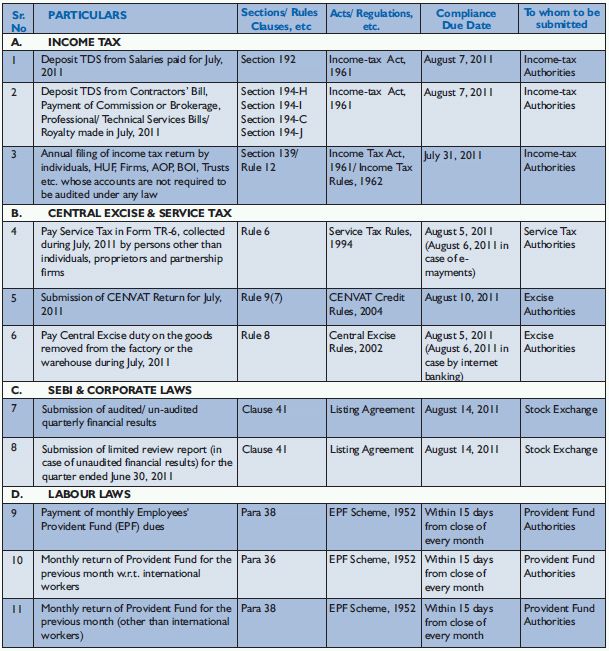
IMPORTANT DATES WITH REGULATOR(S) COMPLIANCE CHECKLIST
July-August, 2011
© 2011. All rights reserved with Vaish Associates
Advocates, IPR & IT Laws Practice Division
Flat # 903, Indra Prakash Building, 21, Barakhambha Road, New Delhi
110001 (India)
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist professional advice should be sought about your specific circumstances. The views expressed in this article are solely of the authors of this article.
