In recent years, the amount of patent infringement lawsuits involving pharmaceutical companies has been increasing, creating numerous barriers for said companies when wanting to bring new products into the market. To address this, it is necessary to evaluate the patent infringement risk by conducting freedom to operate (FTO) patent search and analysis, and then generate a strategy based on the evaluation results to reduce the risk of infringement lawsuits.
Text
The objective of FTO patent search and analysis in the pharmaceutical field is to identify patents that could be infringements risks as comprehensively and accurately as possible, so as to effectively prevent legal risks. FTO patent search and analysis is a multi-stage process, usually including patent search, patent screening, patent infringement analysis, conclusions and recommendations, etc., which will be described in detail below.
I、When to conduct the FTO investigation in the pharmaceutical field
1. Before the approval of a research project or during the research and development process
FTO investigation at this stage can help pharmaceutical companies understand the patent landscape of current pharmaceutical drugs and provide guidance and advice on the establishment, research and development of a pharmaceutical project. However, at this stage it fairly common that the design plan for said drug has not been finished, as a result this can result in the FTO investigation being too general and not sufficiently targeted.
2. After the completion of drug development and before marketing
FTO investigation at this stage can help pharmaceutical companies understand when and where to market their new product. As the drug design plan is often completed at this stage, the FTO investigation is far more targeted.
3. Financing, mergers and acquisitions (M&A), licensing and assignment
In the financing or M&A of pharmaceutical companies, FTO investigation is mainly used to help investors or acquirers assess the value of drugs and transaction risk; while during the licensing or assigning pharmaceutical projects, FTO investigation aims to help licensees evaluate the values of these drugs and the associated transaction risk.
II、FTO Patent Search
The FTO patent search is comprehensive, and is essential when trying to identify all the related patents in the FTO investigation. If the patent search is not sufficiently comprehensive, it will increase the infringement risk. Only through implementation of a thorough patent search strategy can an enterprise best protect itself.
For chemical drugs, patents that would affect the freedom-to-operate of certain drugs may include several types, such as compounds, salt forms, crystal forms, preparation methods, uses, combinations, and dosage forms. The claims of patents or patent applications in the chemical field are sometimes written using the broader concept of the compound, which should be reasonably considered when conducting the patent search. For example, assume that the target drug is an EGFR inhibitor, and then EGFR can be used as a key word in the FTO patent search. In addition, since there are certain limitations when searching patents in the chemical field only using keywords, it is necessary to include the structural formula of the drug when carrying out the search.
For bio-pharmaceutical drugs, patents that would affect the freedom-to-operate of certain drugs may also include several types, such as antigens, targets, epitopes, nucleic acids, proteins, expression vectors, expression cells, preparation methods, uses, combinations, and dosage forms. Claims in patents or patent applications in the bio-pharmaceutical field are sometimes written using broader concepts such as family, ligand and receptor, which should therefore be reasonably considered when conducting the patent search. In addition to the use of keywords, FTO patent search should also combine the bio-sequence of the drug in the bio-pharmaceutical field.
1. Search basic information of drug
Before using a specialized search tool for the patent search, it is necessary to first utilize the drug information retrieval tool to search for basic information, including the Chinese and English names of the drug, Chinese and English extension names, Chinese and English trade names, chemical structural formulas, biological sequences, molecular formulas, CAS number, targets and indications. Common information retrieval tools for commonly used drugs include the company's official website, Google, FDA, NMPA, Drugfuture, DrugBank, PubChem, and Adis Insight, etc.
2. Select patent search database
The patent database is determined based on the target country of the search and the drug type. Generally speaking, if a search is based on English keywords and applicants, it is recommended to use foreign commercial patent databases such as Thomson Innovation, Total Patent or PatBase; if it is solely based on Chinese keywords or applicants, it is recommended to use the database provided by SIPO or the CNIPR database introduced by China Intellectual Property Publishing House; if it is a patent search for compound structures, Scifinder search tool is generally used; if searching for a biological sequence, SNT, Genome Quest or BLAST of NCBI are generally used.
3. Patent search element list
The patent search element list generally includes Chinese keywords, English keywords, patent classification numbers, chemical structures, biological sequences, applicants and inventors.
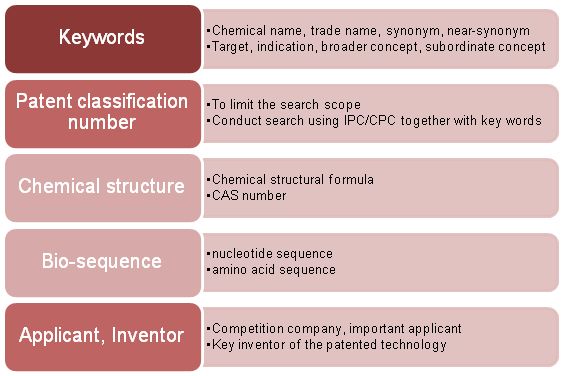
It should be noted that since the description of the patent infringement risk is not necessarily a well-known keyword, the expansion of the keyword is not only obtained in the general information of the drug, but also supplemented in the process of reading the patent document. For the patent classification number, it is generally determined through a comparison based on statistical methods. Meanwhile, attention should also be paid to the classification number of the relevant patent when checking relevant patent documents. It is also necessary to check whether are any missing classification numbers, if that is the case then it is necessary to supplement those that are missing. .
4. Design searching formula
When constructing a search formula, a variety of patent search methods should be used, so as to better ensure the comprehensiveness of results. Firstly, it is necessary to use the drug-related keywords to search. In cases which a large number of unrelated interference patents appear in the patent search results, users can first try adjusting the keywords, before then entering the classification number to narrow the results. You should also ensure you use the correct database for the chemical structure or bio-sequence search. Finally, the applicant's and the inventor's information can be used to perform a supplementary patent search.
III、 FTO Patent Screening
Patent screening can be performed in two stages, preliminary screening and precise screening. In the preliminary screening, the reverse exclusion method is generally adopted, i.e., the patents obviously irrelevant are excluded, and the patents with doubts are all retained, and the protection scope and different versions of the patent may not be considered at this stage. In the precise screening, the technical solutions protected by the independent claims in the preliminary screening list would be compared with the technical facts, before then selecting highly relevant patents by judging the correlation of the technologies as a whole.
It is worth noting that for FTO patent search in China, it can be screened and excluded through the application date and legal status, i.e., patents or patent applications that have been applied for more than 20 years from the application date, ensuring that invalid patents are excluded. For FTO patent search in foreign countries or regions, please keep in mind do that you should not judge whether it is expired based on the application date plus 20 years. Instead, before making a judgment, you should know the calculation method of patent expiration date in each country or region. For example, for US drug patent applications, there are two systems for drug extension protection period (PTA+PTE), and the specific patent expiration date can be obtained from Orange Book or USPTO.
IV、Patent Infringement Analysis
The patent infringement analysis mainly includes the break-up of the technical features of the claims, determination of the protection scope of the claims, break-up of the technical features of target drugs, and comparison analysis of the patent infringement risk.
1. Break down the technical features
Analyze the relationship between the types of independent claims and terms of the claims, split the technical features in the independent claims, and number them to facilitate subsequent comparison analysis of patent infringement risk.
2. Determine the protection scope of claims
Firstly, to understand and grasp the specific meanings of the specific technical features in the claims based on the background technology and the description of the target patent document; secondly, retrieve the examination files of the target patents through the official website of the national patent offices, including Notification of an Office Action, Applicant's Response for the Office Action, Re-examination Dossier, Request for Invalidation, Examination Decision on Request for Invalidation, etc., study the response documents of the target patent in the process of confirming rights or safeguarding rights, determine the interpretation of the technical features by the applicant or patentee and the impact on the protection scope, and determine whether the Prosecution History Estoppel is applicable; finally, determine whether the Dedication Rule is applicable by studying the various embodiments in the patent description and analyzing the relationship between all the embodiments and the claims.
3. Break down technical features of target drug
Determine the technical features of the target drug corresponding to the target patent by combining the information of drug structures, indications, preparation methods, etc., and number the technical features to facilitate subsequent patent infringement comparison analysis.
4. Patent infringement comparison analysis
Compare the technical features of the target patent with that of the target drug one by one in the form of a list and deliver the comparison conclusions and brief reasons of each pair of technical features, then analyze and judge the patent infringement risk according to the rule of Literal Infringement and Doctrine of Equivalents, so as to determine whether the target drug falls within the protection scope of the target patent after comprehensively analyzing the judgment results.
Since compound patents are unique compared to other patents, some basic principles for infringement determination of compound patents will be specifically described below.
1) If the target patent protects drug in the form of a chemical name, the chemical name may correspond to a class of compounds or a kind of specific compound. In the case of a class of compounds, as long as the target drug belongs to one of the compounds, it can be considered as falling within the protection scope of the target patent; in the case of a kind of specific compound, it will be recognized as falling into the protection scope of the target patent only if the target drug is the compound itself.
2) If the target patent protects the compound in the form of the structural formula, its various functional groups and molecular stereo configuration should be focused on. If any functional group changes at the atomic level, it can be considered to have no infringement risk, because any change in the functional group will lead to the production of another substance. In addition, as changes in the stereo configuration of the molecule would also result in different protection scopes, in the case that the target patent claim specifically protects a specific molecular configuration, other molecular configurations except the protected configuration does not have the infringement risk.
3) If the target patent protects the molecular formula of a compound, various isomers of the compound should be considered to carry an infringement risk. If the molecular formula of target drug changes at the atomic level compared with that of the target patent, there is no patent infringement risk.
V、Conclusions and Advice
According to the results of patent infringement analysis, if there are high-risk patents, countermeasures should be made to avoid pharmaceutical companies falling into patent infringement litigation or transaction disputes. The general response strategy includes the following methods.
1. Bypass the high-risk patents
The enterprise in question could utilize methods to bypass the protection scope of infringing patents by improving drug designs. Generally speaking, it is not possible to bypass patents protecting compounds or indication patents are, but patents protecting crystalline, preparation patents, and preparation method can be effectively bypassed. For the crystalline type patents, it is suggested that the clients could try to develop new crystal form to bypass the infringing patents, provided that the new crystalline form is bioequivalent to the original crystalline form of the drug. For the patent protecting the drug formulation, it can effectively bypass the target patents by reducing or changing the type or proportion of the auxiliary materials. For the preparation method patent, it can effectively bypass the target patents by changing the synthetic route or reaction conditions.
2. Request for Invalidation of obstacle patent
For patents or patent applications that are difficult to circumvent, but have poor patentability or patentability, it is recommended to submit a request for invalidation or a third party public opinion. Generally speaking, the patents of crystalline forms, dosage forms and treatment methods of drugs are more likely to be invalidated.
3. Waiting for the expiration of obstacle patents
For patents with strong protection that cannot be bypassed, such as compound patents, it is generally recommended to wait for the expiration of the patent. It should be noted that the expiration date of compound patent is generally calculated according to the specific compound patent application date.
4. Licensing or transfer
In cases where patents are difficult to evade and the patentee may be licensed or transferred, for example, if the patentee is a university, or the main business is different from the direction of the patent, it is suggested that negotiations on patent licensing or transfer may be conducted to ensure the free implementation of the patent scheme .
Conclusion
From the above analysis, it can be seen that, whether it is the expression of FTO patent search elements, the selection of patent search databases, the formulation of search formulas and the screening of patent search results, or the analysis of related patent infringements, the patient and careful work of patent analysts are required in order to better evaluate the potential risks for pharmaceutical companies in the process of drug research and development, listing, licensing or financing and mergers and acquisitions of pharmaceutical companies.
Footnotes
1. 韩羽枫. 侵权判定原则在化合物专利案件中的适用[J]. 商法专栏: 知识产权诉讼与执行, 2014, (10): 62-63.
2. 路炜, 肖沪卫. 专利侵权检索与分析报告的规范研究[J].图书情报工作,7714 2008,52(2):73-73.
3. 龙克文. 企业专利信息利用和防侵权检索分析[J]. 中外企业家, 2013 (10): 12.
4. 王吉霞. 专利防侵权调查的检索方法探究[J]. 现代情报, 2014, 34(6): 95-98.
5. What is a freedom to operate (FTO) or infringement search?
6. IP and Business: Launching a New Product: freedom to operate. WIP0.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

